NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Science
Last Updated :
17 Nov, 2023
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World- This article includes free NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World, according to the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, and guidelines.
These detailed solutions have been developed by the subject matter experts at GFG, to help the students of Class 10 create a solid conceptual base for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World and do well in exams.

The solutions to all the exercises in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World have been collectively covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 10.
To learn about the topics discussed in Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World of Science NCERT Class 10 from scratch, head over to Human Eye.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World : In Text Questions (Page No. 190)
Q1. What is meant by Power of Accommodation of the Eye?
Answer:
Accommodation of the eye is the ability of the eye to increase or decrease its focal length in order to form the image of the object on the retina.
Q2. A Person with a Myopic Eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of Corrective Lens used to restore Proper Vision?
Answer:
As the person has myopia, it can be corrected using a concave lens of focal length equal to 1.2 m.
Q3. What is the Far Point and Near Point of the Human Eye with Normal Vision?
Answer:
Near point of an eye is the distance at which the human eye can see the objects without strain. It is 25 cm for a human eye. Far point of an eye is the maximum distance at which a human eye can see clearly. It is infinity for human eye.
Q4. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the Defect the Child is suffering from? How can it be Corrected?
Answer:
As the child cannot see far away object, the child is probably suffering from myopia. It can be corrected using a concave lens of an appropriate power.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World: Exercise
Q1. The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) Presbyopia (b) Accommodation (c) Near-Sightedness (d) Far-Sightedness
Answer:
The ability of the human eye to focus on near and distant objects by adjusting its focal length is termed as accommodation. Hence, option (b) accommodation is the correct answer.
Q2. The Human Eye forms the Image of an Object at its
(a) Cornea (b) Iris (c) Pupil (d) Retina
Answer:
Human eye has a layer at its end which is connected to the brain through nerve cells. Retina acts as a screen and forms the image of the object by receiving the light coming from the object. The nerve cells behind the retina convert the light to electrical signals and thus we are able to see. Hence, option (d) retina is the correct answer.
Q3. The Least Distance of distinct vision for a young adult with Normal Vision is about
(a) 25 m (b) 2.5 cm (c) 25 cm (d) 2.5 m
Answer:
The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about 25 cm. Hence, option (c) 25 cm is the correct answer.
Q4. The Change in Focal Length of an Eye Lens is caused by the Action of the
(a) Pupil (b) Retina (c) Ciliary muscles (d) Iris
Answer:
Human eye has the ability to change its focal length by adjusting the size of pupil. The adjustment of the size of the pupil is done with the help of ciliary muscles. Thus, option (c) ciliary muscles is the correct answer.
Q5. A Person needs a Lens of Power –5.5 Dioptres for correcting his Distant Vision. For correcting his Near Vision he needs a Lens of Power +1.5 dioptre. What is the Focal Length of the Lens required for correcting (i) Distant Vision, and (ii) Near Vision?
Answer:
We know that power of lens (P) = 1/focal length of lens (f)
(i) Given P = -5.5 D
Using P = 1/f
-5.5 = 1/f
f = -0.181 m
Thus, a lens of focal length -0.181m is required for correcting distant vision.
(i) Given P = 1.5 D
Using P = 1/f
1.5 = 1/f
f = 0.66 m
Thus, a lens of focal length 0.66 m is required for correcting near vision.
Q6. The Far Point of a Myopic Person is 80 cm in front of the Eye. What is the Nature and Power of the Lens required to Correct the problem?
Answer:
Myopia is a condition in which a person cannot see far away objects as the image of object is formed in front of the retina. Myopia can be corrected by using a concave lens of appropriate power. Power of lens is calculated as follows:
Given f = -80 cm = -0.8 m( we use negative sign as image is formed in front of the retina)
We know that P = 1/f
P = 1/(-0.8) = -1.25 D
Q7. Make a diagram to show how Hypermetropia is Corrected. The near point of a Hypermetropic Eye is 1 m. What is the Power of the Lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the Near Point of the Normal Eye is 25 cm.
Answer:
Hypermetropia is a condition in which a person is not able to see near objects clearly as the image of the object is formed behind the retina. It can be corrected using convex lens. The image for correction of hypermetropia using convex lens is shown below:
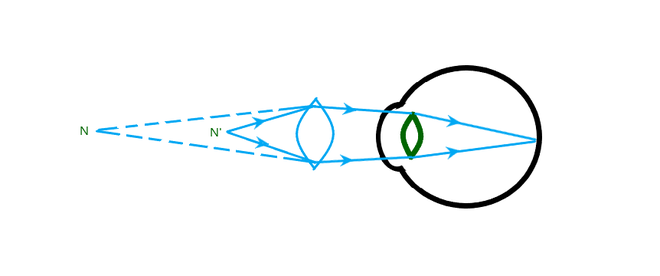
The convex lens used in the above diagram forms a virtual image at the point N (new near point of the eye) of the object which is placed at the point N’. Thus the image of the virtual image so formed by the convex lens is now formed on the retina.
Given u = -25 cm (negative sign is used as we move towards left from retina)
v = -100
We know that 1/v – 1/u = 1/f
⇒ -1/100 – (-1/25) = 1/f
⇒ 1/f = -1/100 + 1/25 = 3/100
⇒ f = 100/3 cm = 1/3 m
Also P = 1/f
⇒ P = 1/(1/3) = 3D
Thus a lens of power 3D is required to correct this defect.
Q8. Why is a Normal Eye not able to see clearly the Objects placed closer than 25 cm?
Answer:
Ability of eye to alter its focal length is upto a certain limit only and it cannot be decreased or increased below or above that limit. Thus the human eye cannot see the objects placed closer than 25 cm as 25 cm is the near point of the eye and focal length of eye cannot be decreases beyond 25 cm.
Q9. What happens to the Image Distance in the Eye when we Increase the Distance of an Object from the Eye?
Answer:
The image distance does not change in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye and the image is still formed on the retina. This is due to accommodation of eye through which it can change the focal length of lens in eye. Thus increasing the distance of object from eye does not affect the image distance in eye but the eye lens increases its focal length by becoming thinner.
Q10. Why do Stars Twinkle?
Answer:
The twinkling of stars is due to the refraction of light coming from the stars. Stars are very far away from us and are equivalent to point sources of light. As the light from the stars pass through the Earth’s atmosphere which has different refractive index at different points, multiple refractions occur and the light coming from the stars flickers due to refraction which make the stars twinkle.
Q11. Explain why the Planets do not Twinkle.
Answer:
Planets are closer to the Earth than the stars and thus appear bigger in size due to which they act as a collection of a large amount of point sources of light. Though the light coming from planets also undergo refraction but the net effect of the refraction gets neutralized due to presence of multiple point sources and the flickering is not visible to the human eye due to which planets do not twinkle.
Q12. Why does the Sun appear Reddish Early in the Morning?
Answer:
Visible Light is composed of seven colors. Each color has a different wavelength. In morning the sun rays have to travel a greater distance to reach the Earth due to which the colors of the spectrum with shorter wavelengths are scattered and not able to reach us. As blue light has the least wavelength, it gets scattered the most and the red light has highest wavelength and gets scattered the least and is able to reach us. This leads to sun appearing reddish in the early morning.
Q13. Why does the Sky appear Dark instead of Blue to an Astronaut?
Answer:
When the light enters Earth’ s atmosphere, it is scattered by the various particles present in our atmosphere. Blue color is scattered the most and hence sky appears blue to us but in case of an astronaut, he is above the atmosphere of the Earth and no scattering of light takes place due to which the sky appears dark to an astronaut.
Important Topics Discussed in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World
In NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World, we have to study the following topics:
Also, Check:
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World- FAQs
Q1. Name the Important Parts of Human Eye?
Some important parts of human eye are:
- Cornea
- Iris
- Pupil
- Retina
- Ciliary Muscles
- Aqueous humour
Q2. Which part of Eye acts as a Screen for the Image Formation?
Retina at the back of eye acts as a screen for the image formation.
Q3. What is Scattering of Light?
Scattering of light is the spreading of light in different directions by the suspended particles in the atmosphere.
Q4. What is the SI unit of Power of lens?
SI unit of power of lens is Dioptre (D).
Q5. State Mirror Formula.
Mirror formula is as follows:
1/f = 1/u + 1/v
where,
- f is focal length of mirror
- u is the distance of object from the mirror
- v is the distance of image from the mirror
Q6. Why should I use NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World?
It is recommended to use NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Physics Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World so that the student can know how to write an effective and correct answer.
Q7. Where can I find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World online?
You can find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Physics Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World online on www.geeksforgeeks.org.
Q8. Are NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World enough for exam preparation?
It is advised to first read NCERT and NCERT solutions to get an idea about the answer writing. From the exam point of view, main focus should be on the concepts.
Q9. What Topics are Covered in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World?
Some topics covered in Chapter 10 of Class 10 Physics are The human eye, scattering of light, refraction of light, dispersion of light and defects of vision.
Q10. What are the Mistakes that Students Makes in Chapter 11 The Human Eye And The Colourful World of NCERT Class 10 Science?
Some common mistakes that students make in this chapter are:
- Confusing mirror formula with lens formula
- Not drawing the direction of ray of light in lens diagram
- Assuming the u, v and f in mirror or lens formula as positive or negative.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...