ACCOUNTANCY
Class 12
Time allowed : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 80
Paper Code: 67/1/1(CBSE 2020)
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them :
(i) This question paper comprises two Parts – A and B. There are 32 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Part A is compulsory for all candidates.
(iii) Part B has two options i.e. (1) Analysis of Financial Statements and (2) Computerized Accounting. You have to attempt only one of the given options.
(iv) Heading of the option opted must be written on the Answer-Book before attempting the questions of that particular OPTION.
(v) Question nos. 1 to 13 and 23 to 29 are very short answer-type questions carrying 1 mark each.
(vi) Question nos. 14 and 30 are short answer type–I questions carrying 3 marks each.
(vii) Question nos. 15 to 18 and 31 are short answer type–II questions carrying 4 marks each.
(viii) Question nos. 19, 20 and 32 are long answer type–I questions carrying 6 marks each.
(ix) Question nos. 21 and 22 are long answer type–II questions carrying 8 marks each.
(x) Answers should be brief and to the point. The answer of each part should be written at one place.
(xi) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions of three marks, 2 questions of four marks, 1 question of six marks and 2 questions of eight marks. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
(xii) However, separate instructions are given with each part and question, wherever necessary.
PART A
( Accounting for Not-for-Profit Organizations, Partnership Firms and Companies)
1. In case the partners’ capitals are fixed, in which account will withdrawal of capital be recorded ?
Answer: Capital Account
2. Meera, Myra and Neera were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. They decided to share future profits in the ratio of 7 : 5 : 3 with effect from 1 st April, 2019. Their Balance Sheet as on that date showed a balance of 45,000 in Advertisement Suspense Account. The amount to be debited respectively to the capital accounts of Meera, Myra and Neera for writing off the amount in Advertisement Suspense Account will be :
(A) ₹ 18,000, ₹ 18,000 and ₹ 9,000
(B ₹ 15,000, ₹ 15,000 and ₹ 15,000
(C) ₹ 21,000, ₹ 15,000 and ₹ 9,000
(D) ₹ 22,500, ₹ 22,500 and Nil
Answer: (A) ₹ 18,000, ₹ 18,000 and ₹ 9,000
3. Mona and Tina were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. Naina was admitted with 1/6th share in the profits of the firm. At the time of admission, Workmen’s Compensation Reserve appeared in the Balance Sheet of the firm at ₹ 32,000. The claim on account of workmen’s compensation was determined at ₹ 40,000. Excess of claim over the reserve will be:
(A) Credited to Revaluation Account.
(B) Debited to Revaluation Account.
(C) Credited to old partner’s Capital Account.
(D) Debited to old partner’s Capital Account.
Answer: (B) Debited to Revaluation Account.
4. Diya, Riya and Tiya were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 3 : 5. Tiya died on 28th November, 2019. Her share of profit was taken equally by Diya and Riya. Diya’s share of profit in the new firm will be _________ .
Answer: Diya’s share of profit in the new firm = 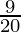
Explanation:
Tiya’s share in the profit = 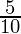
Diya will gain  of
of  =
= 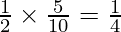
Diya’s share of profit in the new firm = 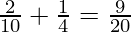
5. X and Y were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 7 : 3. Z was admitted for 1/5th share in the profits which he took 75% from X and remaining from Y. Calculate the sacrificing ratio of X and Y.
Answer: Sacrificing ratio of X and Y = 3:1
Explanation:
Sacrificing ratio of X =  (75% or
(75% or  from X)
from X)
Sacrificing ratio of Y =  (25% or
(25% or  from Y)
from Y)
6. Name an item that is never shown on the payment side of Receipts and Payments Account, but is shown on the debit side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer: Depreciation on Fixed Assets
7. A, B and C were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 5 : 3 : 2. C retired and his capital balance after adjustments regarding reserves, accumulated profits/losses and his share of gain on revaluation was ₹ 2,50,000. C was paid ₹ 3,22,000 including his share of goodwill. The amount credited to C’s capital account, on his retirement, for goodwill will be :
(A) ₹ 72,000
(B) ₹ 7,200
(C) ₹ 24,000
(D) ₹ 36,000
Answer: (A) ₹ 72,000
8. Rahul, Sahil and Jatin were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 3 : 2. Rahul died on 15th October 2017. At that time, the capitals of Sahil and Jatin after all the adjustments were ₹ 3,56,000 and ₹ 2,44,000 respectively. Sahil and Jatin decided to adjust their capital according to their new profit-sharing ratio by opening current accounts. Calculate the new capitals of Sahil and Jatin.
Answer: New capital of Sahil and Jatin will be ₹3,60,000 and ₹2,40,000 respectively.
Explanation:
The new profit-sharing ratio of Sahil and Jatin will be 3 : 2.
Total capital of the new firm = Old capital of Sahil + Old capital of Jatin
Total capital of the new firm = ₹3,56,000 + ₹2,44,000 = ₹6,00,000
Sahil’s capital in the new firm = 
Jatin’s capital in the new firm = 
9. Sun and Star were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 1. Moon was admitted as a new partner in the firm. New profit-sharing ratio was 3 : 3 : 2. Moon brought the following assets towards his share of goodwill and his capital :
If his capital is considered as ₹ 3,80,000, the goodwill of the firm will be :
(A) ₹ 70,000
(B) ₹ 2,80,000
(C) ₹ 4,50,000
(D) ₹ 1,40,000
Answer: (B) ₹ 2,80,000
Explanation:
Share of Goodwill of Moon = Total amount brought in by Moon – Share of Capital of Moon
Share of Goodwill of Moon = ₹4,50,000 – ₹3,80,000 = ₹70,000
Goodwill of the firm = Share of Goodwill of Moon X Reciprocal of the profit-sharing ratio of Moon
Goodwill of the firm = 
10. Rohan, Mohan, and Sohan were partners sharing profits equally. At the time of dissolution of the partnership firm, Rohan’s loan to the firm will be:
(A) Credited to Rohan’s Capital Account.
(B) Debited to Realisation Account.
(C) Credited to Realisation Account.
(D) Credited to Bank Account.
Answer: (D) Credited to Bank Account.
11. Excess of issue price of a debenture over its face value is called ________ .
Answer: Debenture Premium
12. Which of the following statements does not relate to ‘Reserve Capital’ :
(A) It is part of uncalled capital of a company.
(B) It cannot be used during the lifetime of a company.
(C) It can be used for writing off capital losses.
(D) It is part of subscribed capital.
Answer: (C) It can be used for writing off capital losses.
13. Name an item which is transferred to credit side of Realisation Account at the time of dissolution of partnership firm, but does not involve cash payment.
Answer: Partner’s Capital A/c (When any asset is taken over by a partner)
14. How would the following items be treated while preparing the financial statements of a sports club?
Answer:
OR
From the following information of a charitable dispensary, calculate the amount of medicines consumed during the year that would appear in the Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st March, 2019 :
Answer:
15. Ram, Mohan and Sohan were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 1 : 1. Ram withdrew ₹ 3,000 every month and Mohan withdrew ₹ 4,000 every month. Interest on drawings @ 6% p.a. was charged, whereas the partnership deed was silent about interest on drawings. Showing your working clearly, pass the necessary adjustment entry to rectify the error.
Answer:
Workings:
(i)
(ii)
Interest on Drawings of Ram = 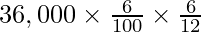
Interest on Drawings of Mohan = 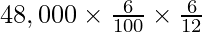
OR
Yadu, Vidu and Radhu were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 4 : 3 : 3. Their fixed capitals on 1st April, 2018 were ₹ 9,00,000, ₹ 5,00,000 and ₹4,00,000 respectively. On 1st November, 2018, Yadu gave a loan of ₹ 80,000 to the firm. As per the partnership agreement :
(i) The partners were entitled to an interest on capital @ 6% p.a.
(ii) Interest on partners’ drawings was to be charged @ 8% p.a.
The firm earned profits of ₹ 2,53,000 (after interest on Yadu’s loan) during the year 2018-19. Partners’ drawings for the year amounted to Yadu : ₹ 80,000, Vidu : ₹ 70,000 and Radhu : ₹ 50,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ending 31st March 2019.
Answer:
16. Furkan, Tanmay and Barkat were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. The firm closes its books on 31st March every year. Tanmay died on 31st July, 2019. His executor was entitled to :
(i) His capital ₹ 8,00,000 and his share of goodwill which was valued for the firm at ₹ 96,000
(ii) His share of profit as per partnership agreement, which was to be calculated on the basis of average profit of last 3 years. Average profits of the last 3 years were ₹ 78,000.
(iii) Tanmay’s executors were paid ₹ 95,000 by cheque at the time of his death and the balance was transferred to his executor’s loan account.
Pass the necessary journal entries in the books of the firm, on Tanmay’s death, for the above transactions.
Answer:
Workings:
(i) Average Profit = ₹78,000
Profit upto the date of death = 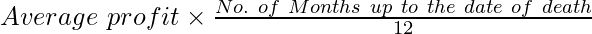
Profit up to the date of death = 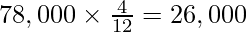
Share of Profit of Tanmay = 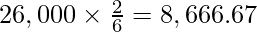
(ii) Firm’s Goodwill = ₹96,000
Tanmay’s Share of Goodwill = 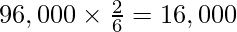
It will be distributed in the gaining ratio of 3:1 between Furkan and Barkat.
17. Raunit Styles Ltd. was registered with a capital of ₹ 85,00,000 divided into equity shares of ₹ 100 each. The company invited applications for issuing 45,000 shares. The amount was payable as ₹ 25 on application, ₹ 35 on allotment, ₹ 25 on first call and balance on final call. Applications were received for 42,000 shares and allotment was made to all the applicants. Kavi, to whom 3,300 shares were allotted, failed to pay both the calls. His shares were forfeited.
Present the Share Capital in the Balance Sheet of the company as per Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013.
Answer:
Notes to Accounts:
18. Pass the necessary journal entries for the following transactions on the dissolution of the partnership firm of Tony and Rony after the various assets (other than cash) and external liabilities have been transferred to Realization Account :
(i) An unrecorded asset of ₹ 2,000 and cash ₹ 3,000 was paid for liability of ₹ 6,000 in full settlement.
(ii) 100 shares of ₹ 10 each have been taken over by partners at market value of ₹ 20 per share in their profit sharing ratio, which is 3 : 2.
(iii) Stock of ₹ 30,000 was taken over by a creditor of ₹ 40,000 at a discount of 30% in full settlement.
(iv) Expenses of realisation ₹ 4,000 were to be borne by Rony. Rony used the firm’s cash for paying these expenses.
Answer:
19. From the following Receipts and Payments Account of Dee Club for the year ending 31 st March, 2019 and additional information, prepare an Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st March, 2019 :
(i) The club has 400 members, each paying an annual subscription of ₹ 150.
(ii) Salaries paid included ₹ 3,150 for the year 2017-18 and outstanding salaries for the year 2018-19 were ₹ 4,250.
(iii) 9% investments were made on 30th November, 2018. The club had a similar investment of ₹ 8,000 at the beginning of the year.
(iv) Depreciate furniture @ 10% p.a. No depreciation is charged on the furniture sold.
Answer:
Workings:
(i) Total interest on investment = 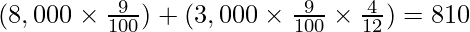
20. (i) Vayee Ltd. purchased the following assets of E.X. Ltd. :
Land and Building of ₹ 60,00,000 at ₹ 84,00,000; Plant and Machinery of ₹ 40,00,000 at ₹ 36,00,000
The purchase consideration was ₹ 1,10,00,000. Payment was made by accepting a Bill of Exchange in favour of E.X. Ltd. of ₹ 20,00,000 and remaining by issue of 8% debentures of ₹ 100 each at a premium of 20%.
Record the necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of Vayee Ltd.
Answer:
(ii) Zed Ltd. issued 2,00,000, 8% debentures of ₹ 100 each at a discount of 6% redeemable at a premium of 10% after 5 years. The amount was payable as follows :
On application – ₹ 50 per debenture and On allotment – balance.
Record the necessary journal entries for the issue of debentures in the books of Zed Ltd.
Answer:
OR
Mahesh Ltd. had issued 20,000, 10% debentures of ₹100 each. 8,000, 10% debentures were due for redemption on 31st March, 2019. The company had a balance of ₹ 4,40,000 in the Debenture Redemption Reserve Account on 31st March, 2018. The company invested the required amount in the Debenture Redemption Investment on 1st April, 2018. Pass the necessary journal entries for redemption of debentures. Ignore the entries for interest on debentures.
Answer:
Note: Since DRR already exists with more than 25% of the nominal value of debentures in the question, it has been assumed that redemption is done ‘out of profits’ and 100% of the nominal value of debentures is transferred to DRR.
21. Badal and Bijli were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2019 was as follows :
Raina was admitted on the above date as a new partner for 1/6th share in the profits of the firm. The terms of agreement were as follows :
(i) Raina will bring ₹ 40,000 as her capital and capitals of Badal and Bijli will be adjusted on the basis of Raina’s capital by opening current accounts.
(ii) Raina will bring her share of goodwill premium for ₹ 12,000 in cash.
(iii) The building was overvalued by ₹ 15,000 and stock by ₹ 3,000.
(iv) A provision of 10% was to be created on debtors for bad debts.
Prepare the Revaluation Account and Current and Capital Accounts of Badal, Bijli and Raina.
Answer:
Workings:
(i) New profit sharing ratio = 3 : 2 : 1
Capital of the firm (According to Raina’s Capital) = 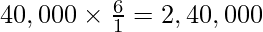
Capital according to the new profit sharing ratio:
Badal’s Capital = 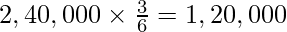
Bijli’s Capital = 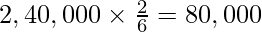
OR
Prem, Kumar, and Aarti were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 3 : 2. Their Balance Sheet as at 31 st March, 2019 was as under :
On the above date, Kumar retired. The terms of retirement were :
(i) Kumar sold his share of goodwill to Prem for ₹ 8,000 and to Aarti for ₹ 4,000.
(ii) Stock was found to be undervalued by ₹ 1,000 and building by ₹ 7,000.
(iii) Investments were sold for ₹ 11,000.
(iv) There was an unrecorded creditor of ₹ 7,000.
(v) An amount of ₹ 30,000 was paid to Kumar in cash which was contributed by Prem and Aarti in the ratio of 2 : 1. The balance amount of Kumar was settled by accepting a Bill of Exchange in favour of Kumar.
Prepare the Revaluation Account, Capital Accounts of partners and the Balance Sheet of the reconstituted firm.
Answer:
22. (i) R.P. Ltd. forfeited 1,500 shares of Rahim of ₹ 10 each issued at a premium of ₹ 3 per share for non-payment of allotment and first call money. Rahim had applied for 3,000 shares. On these shares, amount was payable as follows :
On application – ₹3 per share
On allotment (including premium) – ₹5 per share
On first call – ₹3 per share
On final call – Balance
Final call has not been called up. 1,000 of the forfeited shares were reissued for ₹ 8,500 as fully paid-up.
Record the necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of R.P. Ltd.
Answer:
Workings:
(i) Calculation of the amount forfeited:
(ii) Max Ltd. forfeited 500 shares of ₹ 100 each for non-payment of first call of ₹ 20 per share and final call of ₹ 25 per share. 250 of these shares were re-issued at ₹ 50 per share fully paid-up.
Pass the necessary journal entries in the books of Max Ltd. for forfeiture and re-issue of shares. Also prepare the Share Forfeiture Account.
Answer:
OR
Karur Ltd. invited applications for issuing 2,40,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each at a premium of ₹ 4 per share. The amount was payable as under :
On application – ₹ 4 per share (including premium ₹ 2)
On allotment – ₹ 4 per share
On first and final call – ₹ 6 per share (including premium ₹ 2)
Applications for 3,00,000 shares were received and pro-rata allotment was made to all the applicants. Excess application money received on application was adjusted towards sums due on allotment. All calls were made and were duly received except from Rohini, who failed to pay allotment and first and final call on 7,500 shares applied by her. These shares were forfeited. Afterwards, 40% of the forfeited shares were re-issued at ₹ 11 per share as fully paid-up.
Pass the necessary journal entries in the books of Karur Ltd. Open call-in-arrears and call-in-advance accounts wherever necessary.
Answer:
PART B
OPTION 1
(Analysis of Financial Statements)
23. State any one limitation of Financial Statement Analysis.
Answer: It ignores qualitative aspects as the quality of management, quality of staff etc. are ignored while carrying out the analysis of financial statements.
24. State the impact of ‘Bills Receivable discounted dishonoured on the due date’ on the liquid ratio of 0·75: 1. Also give reason in support of your answer.
Answer: No Change, because it results in an increase in assets (debtors) and decreases in another asset (bank) with the same amount.
25. State whether the following statement is true or false.
‘Inventory Turnover Ratio measures the level of financial leverage.’
Answer: False
26. The total debtors of X Ltd. were ₹ 9,00,000. It had created a provision of 10% for bad and doubtful debts. What amount of debtors will be used for calculating the ‘Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio’?
Answer: ₹9,00,000
27. Give an example of an activity which is always financing with regards to the Cash Flow Statement.
Answer: Payment of dividend
28. On 1.10.2018, Micro Ltd. issued 20,000, 8% debentures of ₹ 100 each and paid interest of ₹ 80,000 on these debentures on 31 st March, 2019. Calculate the cash flow from financing activities for the period ending 31 st March, 2019.
Answer:
29. An investment normally qualifies as cash-equivalent only when from the date of acquisition it has a short maturity period of :
(A) One month or less
(B) Three months or less
(C) Three months or more
(D) One year or less
Answer: (B) Three months or less
30. Calculate the ‘Total Assets to Debt Ratio’ from the following information :
Answer:
Total Assets to Debt ratio = 
Total Assets = Shareholders’ Funds + Total Debt
= 7,50,000 + 19,50,000
= ₹27,00,000
Debt = Total Debt – Current Liability
= 19,50,000 – 4,50,000
= ₹15,00,000
Total Assets to Debt ratio = 
Total Assets to Debt ratio = 1.8 : 1
OR
Under which major head/sub-head will the following items be presented in the Balance Sheet of a company as per Schedule III, Part I of the Companies Act, 2013?
(i) Computer software
(ii) Calls-in-advance
(iii) Outstanding salary
(iv) Securities Premium Reserve
(v) Patents
(vi) Interest accrued on Investment
Answer:
31. From the following information, prepare Comparative Statement of Profit and Loss :
Answer:
OR
Prepare a common size Balance Sheet of L.X. Ltd. from the following information :
Answer:
32. (i) From the following information of Nova Ltd., calculate the cash flow from investing activities :
Additional Information :
During the year, a machine costing ₹ 50,000 on which the accumulate depreciation was ₹ 35,000, was sold for ₹ 12,000.
Answer:
Working Notes:
(ii) The profit of Jova Ltd. for the year ended 31 st March, 2019 after appropriation was ₹ 2,50,000.
Additional Information :
The following was the position of its Current Assets and Current Liabilities as at 31 st March, 2018 and 2019.
Calculate the Cash flow from operating activities.
Answer:
Working Notes:
(i) Net Profit = 2,50,000 + Transfer to general reserve
= 2,50,000 + 22,500
Net Profit = ₹2,72,500
PART B
OPTION 2
(Computerised Accounting)
23. When the accumulated data from various sources is processed in one shot it is called :
(A) Real Time Processing
(B) Data Validation
(C) Processing and Revalidation
(D) Batch Processing
Answer: (D) Batch Processing
24. Height of a person is a ___________ attribute whereas academic qualification can be ___________ attribute.
Answer: Height of a person is a Single Value attribute whereas academic qualification can be Multi Value attribute.
25. Name the accounting subsystem which deals with recording of different items purchased and issued specifying the price, quantity and data.
(A) Purchase and Accounts Payable subsystem
(B) Expense Accounting subsystem
(C) Inventory subsystem
(D) Costing subsystem
Answer: (C) Inventory subsystem
26. Match the movement of mouse with the keystrokes :
(A) (i) (c) and (ii) (a)
(B) (i) (b) and (ii) (d)
(C) (i) (a) and (ii) (d)
(D) (i) (b) and (ii) (c)
Answer: (B) (i) (b) and (ii) (d)
27. A ___________ query is used to extract aggregate of data items for a group of records rather than a detailed set of records.
Answer: A Summary query is used to extract aggregate of data items for a group of records rather than a detailed set of records.
28. A ##### error appears when :
(A) A negative data is used.
(B) Column is not wide enough.
(C) Negative time is used.
(D) All of the above
Answer: (D) All of the above
29. The existence of data in a primary key field is :
(A) Not necessarily required.
(B) Required but need not be unique.
(C) Required and must be unique.
(D) All of the above
Answer: (C) Required and must be unique.
30. Write and explain the formula to calculate ‘Dearness Allowance’ and ‘Gross Salary’.
Answer:
Dearness Allowance = BPE X (Applicable rate of DA for the month)
Where,
BPE = 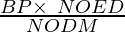
BP = Basic Pay
NOED = Number of Effective Days Present
NODM = Number of Days in a Month
Gross Salary = BPE + DA + HRA +TRA
Where,
HRA = House Rent Allowance
TRA = Transport Allowance
OR
Explain ‘Contra voucher’ and ‘Receipt voucher’.
Answer: (i) Contra Voucher: It is used when cash is deposited in the bank from the office and when cash is withdrawn from the bank for office use. It is used only in the case of fund transfer between Cash and Bank only.
(ii) Receipt Voucher: Receipt Voucher is used to record all the receipts or inflow of money in the business. All the receipts such as Debtors, Loan, Advances, Refund of Loan, etc. are recorded under the receipt voucher.
31. State any four limitations of a computerised accounting system.
Answer: Limitations of Computerised Accounting System:
1. Huge Cost: Incurring huge costs in training the specialised personnel to make them understand the use of accounting software is one of the major disadvantages of the computerised accounting system. There are significant costs associated with setting up a computerised accounting system and periodically updating different hardware and software.
2. Requires Proper Control: A computerised accounting system stores a significant amount of critical data. As a result, proper control must be maintained to prevent data loss.
3. Resistance: Introduction of a computerised accounting system may lead to protest or resistance from its current employees. It might be because of their lack of confidence or worry that the implementation of such a system might decrease their importance in the organisation.
4. Interruption: Converting from a manual accounting system to a computerised accounting system takes a lot of time. The workforce may need more time to become used to the new working environment, which could result in low productivity.
OR
What is meant by ‘data validation’? Give two examples when the cell will give error if the values are not meeting the conditions.
Answer: Data Validation is used to define restrictions on the type of data entered into a cell. It gives user the control to receive particular inputs.
You can go through ‘What is Data Validation in Excel?’ for more details.
32. Name the error which appears on the screen of your computer while using Excel, when the formula refers to a deleted cell. Also explain how to correct that error.
Answer: The error that appears on the screen of your computer while using Excel is a #REF! error.
This error occurs when a cell reference is not valid. To correct this error following steps should be followed:
(i) Click the cell which displays the error and see if it displays calculation steps.
(ii) Review the possible causes.
To correct the error delete the cell referred to in the formula.
Other Sets:
CBSE Class 12 Accountancy Solved Question (Paper-67/2/1-2020)
CBSE Class 12 Accountancy Solved Question Paper (Paper Code: 67/1/3, 2020)
CBSE Class 12 Accountancy Solved Question Paper (Paper Code: 67/1/2, 2020)
Other Question Papers:
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Solved Question Paper-2019 Set 1
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Solved Question Paper- 2020 Set 1
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Solved Question Paper- 2020 Set 2
CBSE Class 12 Economics Solved Question Paper 2020 – Set 1
CBSE Class 12 Economics Solved Question Paper 2020 – Set 2
CBSE Class 12 Economics Solved Question Paper 2020 – Set 4 (58/4/2)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...