Window to Viewport Transformation in Computer Graphics with Implementation
Last Updated :
08 Aug, 2022
Window to Viewport Transformation is the process of transforming 2D world-coordinate objects to device coordinates. Objects inside the world or clipping window are mapped to the viewport which is the area on the screen where world coordinates are mapped to be displayed.

General Terms:
- World coordinate – It is the Cartesian coordinate w.r.t which we define the diagram, like Xwmin, Xwmax, Ywmin, Ywmax
- Device Coordinate –It is the screen coordinate where the objects are to be displayed, like Xvmin, Xvmax, Yvmin, Yvmax
- Window –It is the area on the world coordinate selected for display.
- ViewPort –It is the area on the device coordinate where graphics is to be displayed.
Mathematical Calculation of Window to Viewport:
It may be possible that the size of the Viewport is much smaller or greater than the Window. In these cases, we have to increase or decrease the size of the Window according to the Viewport and for this, we need some mathematical calculations.
(xw, yw): A point on Window
(xv, yv): Corresponding point on Viewport
We have to calculate the point (xv, yv)

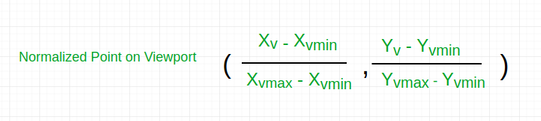
Now the relative position of the object in Window and Viewport are same.
For x coordinate,

For y coordinate,

So, after calculating for x and y coordinate, we get


Where sx is the scaling factor of x coordinate and sy is the scaling factor of y coordinate


Example: Let us assume,
- for window, Xwmin = 20, Xwmax = 80, Ywmin = 40, Ywmax = 80.
- for viewport, Xvmin = 30, Xvmax = 60, Yvmin = 40, Yvmax = 60.
- Now a point ( Xw, Yw ) be ( 30, 80 ) on the window. We have to calculate that point on the viewport
i.e ( Xv, Yv ).
- First of all, calculate the scaling factor of x coordinate Sx and the scaling factor of y coordinate Sy using the above-mentioned formula.
Sx = ( 60 - 30 ) / ( 80 - 20 ) = 30 / 60
Sy = ( 60 - 40 ) / ( 80 - 40 ) = 20 / 40
- So, now calculate the point on the viewport ( Xv, Yv ).
Xv = 30 + ( 30 - 20 ) * ( 30 / 60 ) = 35
Yv = 40 + ( 80 - 40 ) * ( 20 / 40 ) = 60
- So, the point on window ( Xw, Yw ) = ( 30, 80 ) will be ( Xv, Yv ) = ( 35, 60 ) on viewport.
Here is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w, int x_wmax,
int y_wmax, int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax, int x_vmin,
int y_vmin)
{
int x_v, y_v;
float sx, sy;
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
x_v = x_vmin + (float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx);
y_v = y_vmin + (float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy);
cout<< "The point on viewport: ("<<x_v <<","<< y_v<<")" ;
}
int main()
{
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w, int x_wmax,
int y_wmax, int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax, int x_vmin,
int y_vmin)
{
int x_v, y_v;
float sx, sy;
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
x_v = x_vmin + (float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx);
y_v = y_vmin + (float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy);
printf("The point on viewport: (%d, %d )\n ", x_v, y_v);
}
void main()
{
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w, int x_wmax,
int y_wmax, int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax, int x_vmin,
int y_vmin)
{
int x_v, y_v;
float sx, sy;
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
x_v = (int) (x_vmin + (float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx));
y_v = (int) (y_vmin + (float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy));
System.out.printf("The point on viewport: (%d, %d )\n ", x_v, y_v);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
}
|
Python3
def WindowtoViewport(x_w, y_w, x_wmax, y_wmax,
x_wmin, y_wmin, x_vmax,
y_vmax, x_vmin, y_vmin):
sx = (x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin)
sy = (y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin)
x_v = x_vmin + ((x_w - x_wmin) * sx)
y_v = y_vmin + ((y_w - y_wmin) * sy)
print("The point on viewport:(", int(x_v),
",", int(y_v), ")")
if __name__ == '__main__':
x_wmax = 80
y_wmax = 80
x_wmin = 20
y_wmin = 40
x_vmax = 60
y_vmax = 60
x_vmin = 30
y_vmin = 40
x_w = 30
y_w = 80
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20,
40, 60, 60, 30, 40)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w,
int x_wmax, int y_wmax,
int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax,
int x_vmin, int y_vmin)
{
int x_v, y_v;
float sx, sy;
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) /
(x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) /
(y_wmax - y_wmin);
x_v = (int) (x_vmin +
(float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx));
y_v = (int) (y_vmin +
(float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy));
Console.Write("The point on viewport: " +
"({0}, {1} )\n ", x_v, y_v);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80,
x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60,
x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20,
40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function WindowtoViewport(x_w, y_w, x_wmax,y_wmax, x_wmin,
y_wmin,x_vmax, y_vmax, x_vmin,y_vmin)
{
let x_v, y_v;
let sx, sy;
sx = (x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
x_v = x_vmin + ((x_w - x_wmin) * sx);
y_v = y_vmin + ((y_w - y_wmin) * sy);
document.write("The point on viewport: (" + x_v + ", "
+ y_v + " )<br>");
}
let x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
let x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
let x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
</script>
|
Output:
The point on viewport: (35, 60 )
Time Complexity: O(1), as we are not using any looping statements.
Space Complexity: O(1) , as we are not using any extra space.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...