The MERN stack is one of the most well-known stacks used in web development. Each of these technologies is essential to the development of web applications, and together they form an end-to-end framework that developers can work within. MERN Stack comprises 4 technologies namely: MongoDB, Express, React, and Node.js. It is designed to make the development process smoother and easier.

Let’s discuss some common MERN Interview questions that you should prepare for the interviews. These questions will be helpful in clearing the interviews specially for the full stack development role.
A MERN Stack Developer is a skilled programmer who specializes in building web applications using four key technologies: MongoDB, Express, React, and Node.js. These technologies work together to create both the front-end (what the user sees and interacts with) and back-end (the server-side logic that powers the application) of a website.
MERN in abbreviated form is:
- ExpressJS
- MongoDB
- ReactJS
- NodeJS
ReactJS is a popular JavaScript library for creating user interfaces (UIs) of web applications. It helps developers build reusable components, which are like building blocks for creating complex UIs. ReactJS is known for its efficiency and uses a virtual DOM (Document Object Model) to render components quickly. It operates on the client side, meaning it runs in the web browser, and uses JSX, an extension of JavaScript, to define UI components.
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) framework is a way of organizing code for web applications. It separates the application into three parts: the Model, the View, and the Controller. Each part has a specific job to do. The Model is responsible for storing and managing data. It represents the data in a way that is easy for the application to understand.
5. Explain the building blocks of React?
The five main building blocks of React are:
- Components: These are reusable blocks of code that return HTML.
- JSX: It stands for JavaScript and XML and allows to write HTML in React.
- Props and State: props are like function parameters and State is similar to variables.
- Context: This allows data to be passed through components as props in a hierarchy.
- Virtual DOM: It is a lightweight copy of actual DOM which makes DOM manipulation easier.
Replication can occasionally, enhancing read capacity can be achieved through replication, enabling clients to distribute read operations across multiple servers. Improvements in data localization and availability for distributed applications can be attained by storing data copies across various data centers. Additionally, maintaining surplus copies serves specific purposes such as backup, reporting, and disaster recovery.
A higher-order component (HOC) is a function that takes a component as input and generates another component. Essentially, it stems from the compositional structure of React. These components are termed “pure” because they can adopt any dynamically provided child component without replicating or altering the behavior of the input components.
HOC may be utilised in the following usage cases:
- Reuse of code, reasoning, and bootstrap abstraction
- Represent Highjacking
- State manipulation and abstraction
- Props manipulation
React assesses the necessity for a real DOM update when there’s a change in a component’s props or state. This evaluation involves comparing the newly returned element with the one previously displayed. If they are not equal, React proceeds to update the DOM. This process is referred to as reconciliation.
Sharding is a method for distributing data across multiple machines to facilitate data sharing. MongoDB utilizes sharding to support installations with extensive data sets and demanding performance requirements. This enables MongoDB to achieve horizontal scalability. At the collection level, MongoDB distributes data across the shards in the cluster.
|
ES6 class syntax is used in class-based components. It may employ lifecycle methodologies.
|
Comparing functional components to class-based functions, they are easier.
|
|
Components of a class extend React components.
|
Functional Components primarily concentrate on the application’s user interface (UI), not on its behaviour.
|
|
To access the properties and methods that you specify inside the class components in this section, you must use the keyword.
|
These are really render functions in the class component, to be more accurate.
|
MongoDB serves as a document-oriented database manager specifically crafted for the storage of substantial data volumes. It stores data in a binary JSON format and incorporates the concepts of collections and documents. Being a cross-platform, NoSQL database, MongoDB is distinguished by its high performance, scalability, and flexibility, enabling smooth querying and indexing operations.
12. What is the purpose of ExpressJS?
ExpressJS is a web application framework meticulously crafted to facilitate the development and hosting of Node.js projects. Under the MIT license, it stands as an open-source framework. ExpressJS adeptly orchestrates the interaction between the front-end and the database, ensuring a secure and seamless data transfer.
MongoDB accommodates an extensive array of data types as values within its documents. In MongoDB, documents bear a resemblance to JavaScript objects, and they adhere to the key/value-pair structure inherent in JSON. Beyond the fundamental key/value concept of JSON, MongoDB introduces support for various additional data types. The prevalent data types in MongoDB include:
- Null
- Boolean
- Number
- String
- Date
- Regular expression
- Array
- Embedded document
- Object ID
- Binary Data
REPL, short for “Read Eval Print Loop,” is a straightforward program designed to receive commands, assess them, and display the outcomes. Its purpose is to establish an environment akin to a Unix/Linux shell or a Windows console, allowing users to input commands and queries while receiving corresponding outputs. The functions performed by REPL include:
- READ – This reads the input provided by the user, parses it into JavaScript data structure, and stores it in the memory.
- EVAL – This executes the data structure.
- PRINT – This prints the outcome generated after evaluating the command.
- LOOP – This loops the above command until the user presses Ctrl+C twice.
A callback serves as the asynchronous counterpart to a function. Node.js extensively utilizes callbacks, invoking them upon the conclusion or completion of a specific task. For example, consider a function tailored for file reading; it initiates the file reading process and promptly relinquishes control to the execution environment, enabling the execution of subsequent instructions.
16. What are pure components in MERN Stack?
In the MERN stack, pure components can be viewed as standard components, differing primarily in their engagement with the shouldComponentUpdate method. Pure components are primarily tasked with conducting a comparison of props and state whenever there is a change in either props or state.
Node.js, in its most basic state, operates as a single-threaded process. Developers lack access to child threads or thread management techniques. Although certain operations, like asynchronous I/O, prompt the creation of child threads, these activities occur in the background without disrupting the main event loop or executing any JavaScript code for the application.
18. What are some features of MongoDB?
- Indexing: It offers support for generic secondary indexes and delivers distinctive capabilities for unique, compound, geospatial, and full-text indexing.
- Aggregation: It furnishes an aggregation framework founded on the concept of data processing pipelines.
- Special collection and index types: It includes support for time-to-live (TTL) collections, allowing data that should expire at a specific time to be managed effectively.
- File storage: It offers a user-friendly protocol for storing extensive files and their corresponding metadata.
- Sharding: Sharding involves the segmentation of data across multiple machines.
When developing a React application, a deeply nested component often needs to consume data provided by another component much higher in the hierarchy. The simplest approach is to pass a prop from one component to the next, traversing the hierarchy from the source component to the deeply nested one. This process is referred to as prop drilling.
20. How do you manage packages in your node.js project?
The management of dependencies can be handled by various package installers along with their corresponding configuration files. Among them, npm and yarn are commonly utilized. Both these tools offer comprehensive JavaScript libraries, incorporating advanced features for controlling environment-specific configurations. To ensure consistency in library versions across a project, package.json and package-lock.json are employed. This practice helps avoid compatibility issues when transitioning the application to different environments.
A syntactic extension to JavaScript, provides access to the full capability of JavaScript. React components are constructed using JSX, where any JavaScript expression can be incorporated by enclosing it in curly braces. After compilation, JSX expressions are transformed into standard JavaScript objects. Consequently, JSX can be assigned to variables, used as arguments, returned from functions, and employed within if statements and for loops.
Express.js manages routing through the use of the `express.Router()` method. This method yields an instance of a router, enabling the definition of routes for the application. Below is an illustration of how to define a basic route using this router:
Javascript
const express = require('express')
const router = express.Router()
router.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!')
})
module.exports = router
|
The virtual DOM serves as a JavaScript representation of the real DOM (Document Object Model) employed by React to enhance rendering performance. When a modification occurs in the virtual DOM, React conducts a comparison between the new and old virtual DOMs. Subsequently, only the altered parts are updated, contributing to a faster and more efficient rendering process.
Javascript
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times.</p>
<button onClick={handleClick}>Click me!</button>
</div>
);
}
|
24: What is middleware in Node.js and how is it used?
In Node.js, middleware is a function that takes in the request and response objects, as well as the next middleware function in the application’s request-response cycle. It can be employed to alter the request or response objects, as well as to execute various tasks such as logging, authentication, and error handling.
Javascript
function logMiddleware(req, res, next) {
console.log(`[${req.method}] ${req.url}`);
next();
}
app.use(logMiddleware);
|
A RESTful API is an architectural style for constructing web APIs. It utilizes HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to execute CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations on resources, identifying these resources through URLs. A key characteristic of a RESTful API is its statelessness, signifying that each request carries all the essential information for its completion.
The event loop in JavaScript facilitates asynchronous programming. In JS, all operations occur on a single thread, yet by employing clever data structures, we can simulate the effect of multithreading. The Event Loop manages asynchronous tasks by queuing and listening to events.
Streams in Node.js are instances of EventEmitter designed for handling streaming data. They prove particularly useful in managing and manipulating large files, such as videos or mp3s, over the network. Streams employ buffers as temporary storage. There are primarily four main types of streams:
- Writable: Streams to which data can be written, exemplified by `fs.createWriteStream()`.
- Readable: Streams from which data can be read, as illustrated by `fs.createReadStream()`.
- Duplex: Streams that are both Readable and Writable, exemplified by `net.Socket`.
- Transform: Duplex streams, capable of modifying or transforming data as it is both written and read, such as `zlib.createDeflate()`.
Buffers, in a general sense, are temporary memory utilized by streams to retain data until it is consumed. Unlike JavaScript’s Uint8Array, buffers introduce additional use cases and are primarily employed to represent a fixed-length sequence of bytes. Buffers support legacy encodings such as ASCII, utf-8, etc. They are allocated as fixed (non-resizable) memory outside the V8 engine.
29. Why use Express.js over Node.js?
In backend development, Node.js is commonly paired with Express.js for improved ease and scalability. While Vanilla JavaScript suffices for front-end coding, larger web apps benefit from React or Angular. A full app with just Node.js can lead to complex code, so combining Node.js with Express.js leverages speed and simplicity, creating scalable web APIs. This synergy is seen in popular stacks like MEAN and MERN.
- MongoDB is an open-source NoSQL database written in C++ language. It uses JSON-like documents with optional schemas.
- It provides easy scalability and is a cross-platform, document-oriented database.
- MongoDB works on the concept of Collection and Document.
- It combines the ability to scale out with features such as secondary indexes, range queries, sorting, aggregations, and geospatial indexes.
- MongoDB is developed by MongoDB Inc. and licensed under the Server Side Public License (SSPL).
31. What is a Collection in MongoDB?
In MongoDB, a collection is a set of documents. If a document is akin to a row in a relational database, then a collection can be likened to a table. Documents within a collection can possess varying “shapes,” meaning collections have dynamic schemas.
In MongoDB, indexes play a crucial role in optimizing query resolution. Essentially, an index stores a compact portion of the dataset in a format conducive to efficient traversal. It retains the values of a specific field or set of fields, organized based on the specified field values within the index.
React employs forms to enable users to interact with web applications.
- Using forms, users can interact with the application and enter the required information whenever needed. The form contains certain elements, such as text fields, buttons, checkboxes, radio buttons, etc
- Forms are used for many different tasks such as user authentication, searching, filtering, indexing, etc
- getInitialState(): This is executed before the creation of the component.
- componentDidMount(): This is executed when the component gets rendered and placed on the DOM.
- shouldComponentUpdate(): This is invoked when a component determines changes to the DOM and returns a “true” or “false” value based on certain conditions.
- componentDidUpdate(): Is invoked immediately after rendering takes place.
- componentWillUnmount(): Is invoked immediately before a component is destroyed and unmounted permanently.
Redux is an open-source, JavaScript library used to manage the application state. React uses Redux to build the user interface. It is a predictable state container for JavaScript applications and is used for the entire application’s state management.
36. What are the components of Redux?
- Store: Holds the state of the application.
- Action: The source information for the store.
- Reducer: Specifies how the application’s state changes in response to actions sent to the store.
React Router is a routing library built on top of React, which is used to create routes in a React application. This is one of the most frequently asked to react interview questions.
38. Why do we need to React Router?
- It maintains consistent structure and behavior and is used to develop single-page web applications.
- Enables multiple views in a single application by defining multiple routes in the React application.
ShadowDOM is a web standard that provides a way to encapsulate HTML and CSS code, making it isolated from the rest of the page. It allows developers to create custom HTML elements with their own styles and behavior. On the other hand, VirtualDOM is a lightweight representation of the actual DOM in memory. It is used in React to optimize rendering performance by reducing the number of DOM manipulations.
No, Node.js is not entirely single-threaded. It uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that allows multiple operations to be processed simultaneously. However, the execution of JavaScript code is single-threaded.
fore they are initialized with a value will result in an error. This restriction is known as the Temporal DBefore the introduction of ES6, variable declarations were limited to the use of `var`. ES6 brought two new ways to declare variables: `let` and `const`. Both `let` and `const` declarations are confined to block scope, meaning they can only be accessed within the curly braces `{}` that surround them. In contrast, `var` does not have such limitations. Unlike `var`, which can be accessed before its declaration, attempting to access `let` or `const` variables beead Zone, which is the period from the beginning of the execution of a block where `let` or `const` variables are declared until they are initialized. If there is an attempt to access these variables during this zone, JavaScript will throw a reference error.
Example: Below both `let` and `const` variables are within the Temporal Dead Zone (TDZ) from the commencement of their enclosing scope to the point at which they are officially declared.
console.log(varNumber); // undefined
console.log(letNumber); // Throws the reference error letNumber is not defined
var varNumber = 9;
let letNumber = 1;
MongoDB is a NoSQL database used to store large amounts of data without any traditional relational database table. Instead of rows & columns, MongoDB used collections & documents to store data. A collections consist of a set of documents & a document consists of key-value pairs which are the basic unit of data in MongoDB.
Let’s see how we can connect nodejs with MongoDB:
Javascript
const express = require("express");
const ejs = require("ejs");
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
});
const contactSchema = {
email: String,
query: String,
};
const Contact = mongoose.model("Contact", contactSchema);
const app = express();
app.set("view engine", "ejs");
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: true
}));
app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/public'));
app.get("/contact", function(req, res){
res.render("contact");
});
app.post("/contact", function (req, res) {
console.log(req.body.email);
const contact = new Contact({
email: req.body.email,
query: req.body.query,
});
contact.save(function (err) {
if (err) {
throw err;
} else {
res.render("contact");
}
});
});
app.listen(3000, function(){
console.log("App is running on Port 3000");
});
|
Connecting Node JS and React JS is an important part of developing full-stack web application, where React is used for frontend and Node for backend
Example: This example shows basic program for backend server.
Javascript
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.post("/post", (req, res) => {
console.log("Connected to React");
res.redirect("/");
});
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 8080;
app.listen(PORT, console.log(`Server started on port ${PORT}`));
|
Example: This example shows basic program for frontend.
Javascript
import logo from "./logo.svg";
import "./App.css";
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img
src={logo}
className="App-logo"
alt="logo"/>
<p>A simple React app.....</p>
<a className="App-link"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer">
Learn React
</a>
<form action="../../post"
method="post"
className="form">
<button type="submit">
Connected?
</button>
</form>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
|
Output:
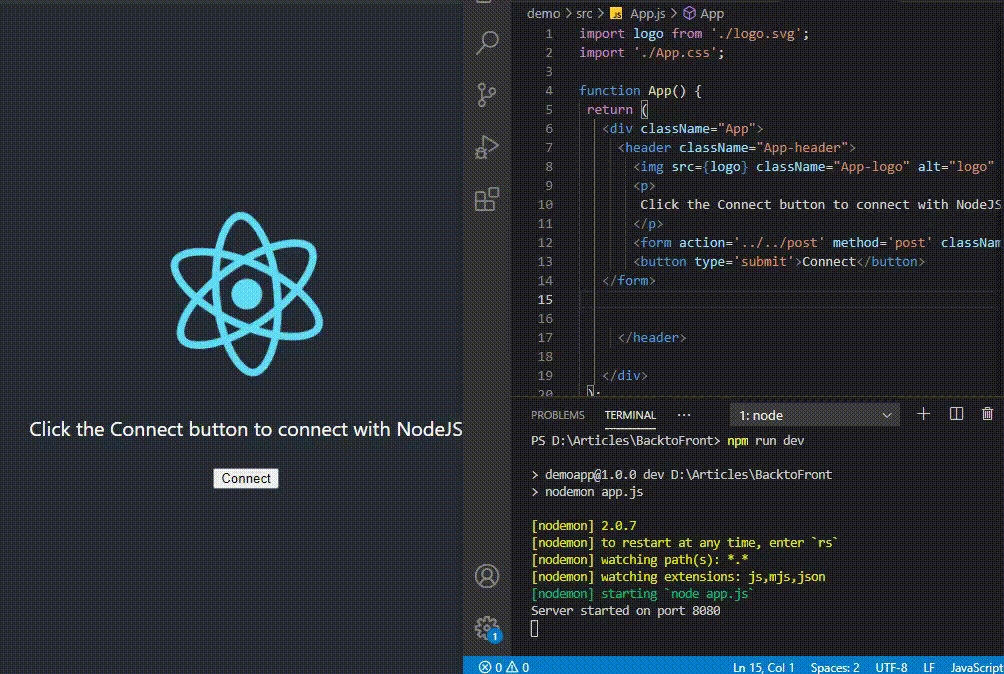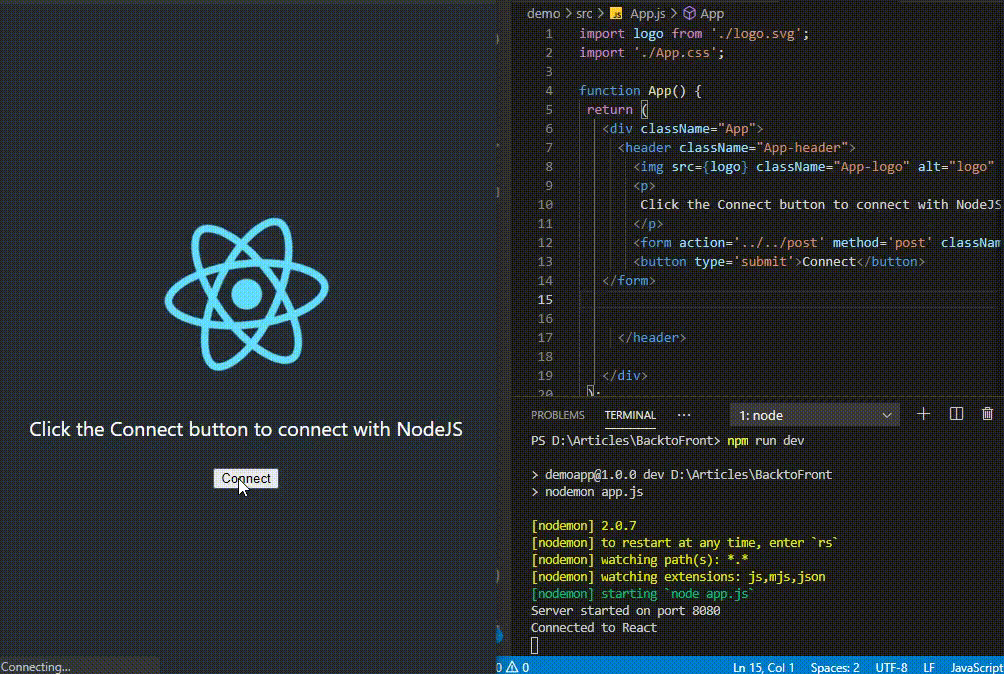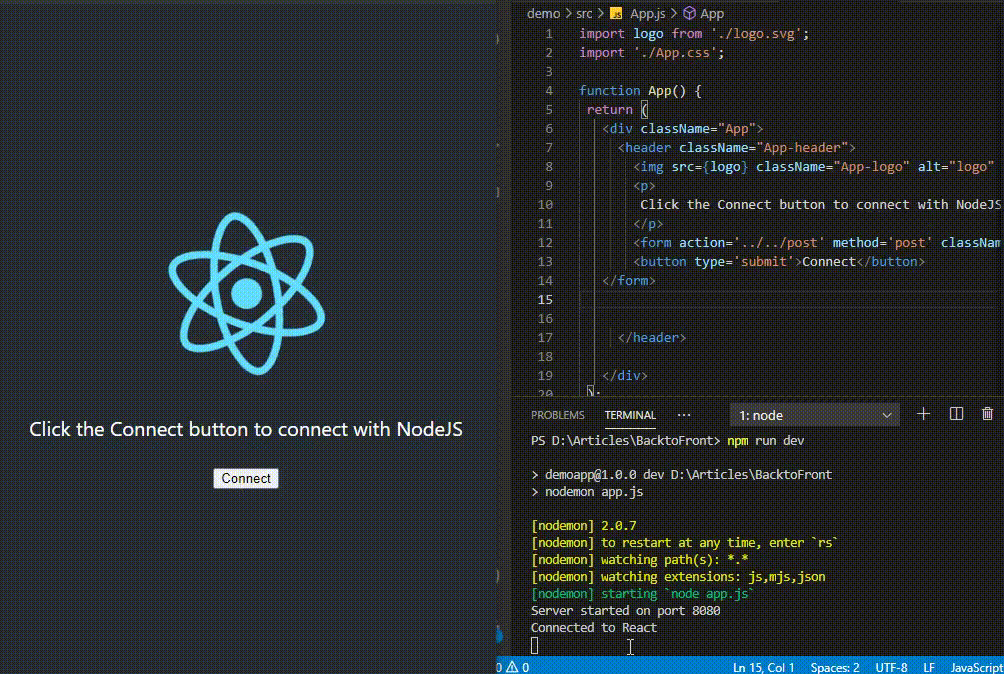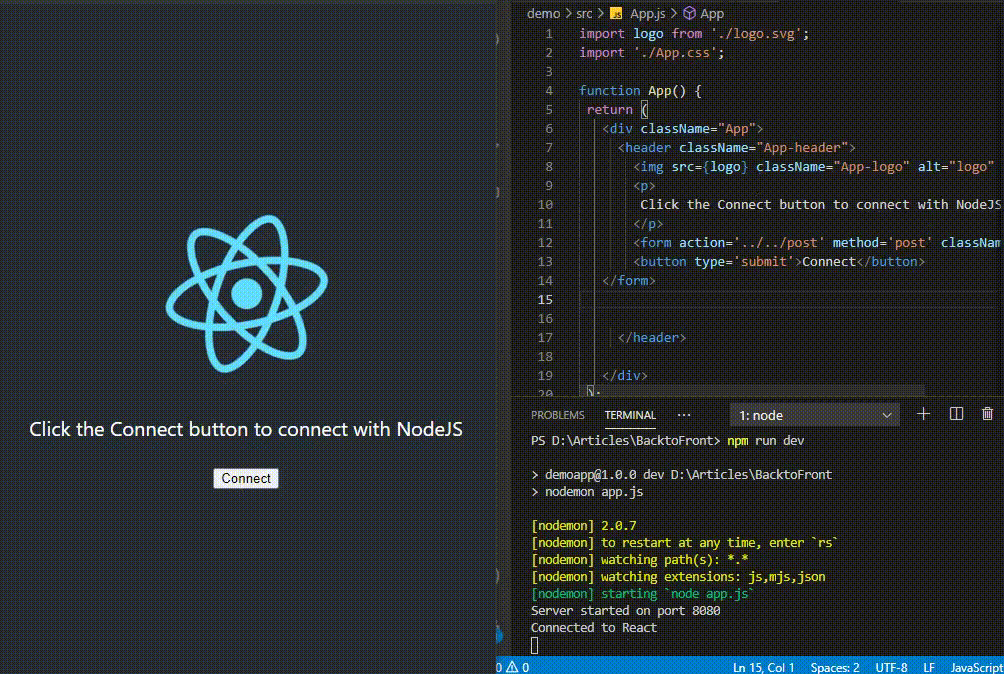
Output
The MongoDB Aggregation Pipeline serves as a framework for data processing and transformation within MongoDB. It involves a series of sequential stages, facilitating operations like filtering, projection, grouping, and sorting on documents. Each stage in the pipeline processes the data and forwards the results to the subsequent stage, culminating in the generation of the final output.
45. How can you use the like operator to query MongoDB?
In MongoDB, you can implement a functionality similar to the “like” operator by employing regular expressions with the `$regex` operator in the `$match` pipeline stage of an aggregation query. For instance, the subsequent query identifies documents in which the “name” field commences with “Nick”:
db.myCollection.aggregate([
{ $match: { name: { $regex: /^Nick/ } } }
])
46. Name a few techniques to optimize React app performance.
Some techniques to optimize React app performance include:
- Memorization: Enhance performance by memoizing functions and components, preventing unnecessary re-renders.
- Virtualization: Leverage libraries such as `react-virtualized` for optimized rendering of extensive lists or grids.
- Code Splitting: Divide your code into smaller segments and load them selectively based on necessity.
- Lazy Loading: Employ React’s `lazy()` and `Suspense` to load components lazily.
- Optimize Renders: Use shouldComponentUpdate, PureComponent, or React.memo to prevent unnecessary renders.
- Minimize Re-renders: Utilize `shouldComponentUpdate`, `PureComponent`, or `React.memo` to minimize unnecessary renders.
- Avoid Unnecessary State Updates: Exercise caution with `setState` to minimize unnecessary re-renders.
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Optimize initial load times by rendering components on the server side.
In Node.js, a module consolidates cohesive code into a singular unit that can be parsed by consolidating relevant functions within a single file. Exporting a module involves defining and exporting functions, allowing them to be imported into other files using the required keyword.
CORS, which stands for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, is a mechanism based on HTTP headers. It facilitates the ability of a web application hosted at one origin (domain) to request access to resources from a server located at a different origin. In essence, CORS is a browser-based system that permits controlled access for scripts running on a client’s browser to interact with and retrieve resources from origins or domains beyond their own.
When elements are rendered twice, the Virtual DOM initiates a comparison process to identify the components that have undergone changes. It identifies and focuses on the altered components on the page, excluding those that remain unchanged. This approach minimizes DOM modifications resulting from user interactions and enhances browser performance by optimizing DOM manipulation. The primary objective is to execute functions swiftly and efficiently.
JSX offers several benefits:
- It ensures speed by optimizing the compilation process into vanilla JavaScript.
- JSX is inherently type-safe, promoting well-structured code and enabling early error detection during compilation.
- It consistently simplifies and accelerates template writing, especially for those familiar with HTML syntax.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...