Spring Data JPA – Delete Records From MySQL
Last Updated :
21 Feb, 2022
Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and setup. Spring Boot is a microservice-based framework and making a production-ready application in it takes very little time. Java persistence API is like an interface that contains most of the methods that are used for data manipulation in the MySQL table and hibernate is the implementation of these methods, So we don’t have to create any method for inserting the data in the MySQL, deletion the records from the table. Let’s understand how to delete the records from the Mysql using Springboot and JPA. The most efficient way to delete the records is with the help of the primary key. Because the primary key uniquely identifies each record of the table. We can use the JPA method deleteById() for deleting the record of the particular primary key. Let’s see the example below.
Step By Step Implementation
Go to Spring Initializr. Fill in the details as per the requirements. Click on Generate which will download the starter project. Extract the zip file
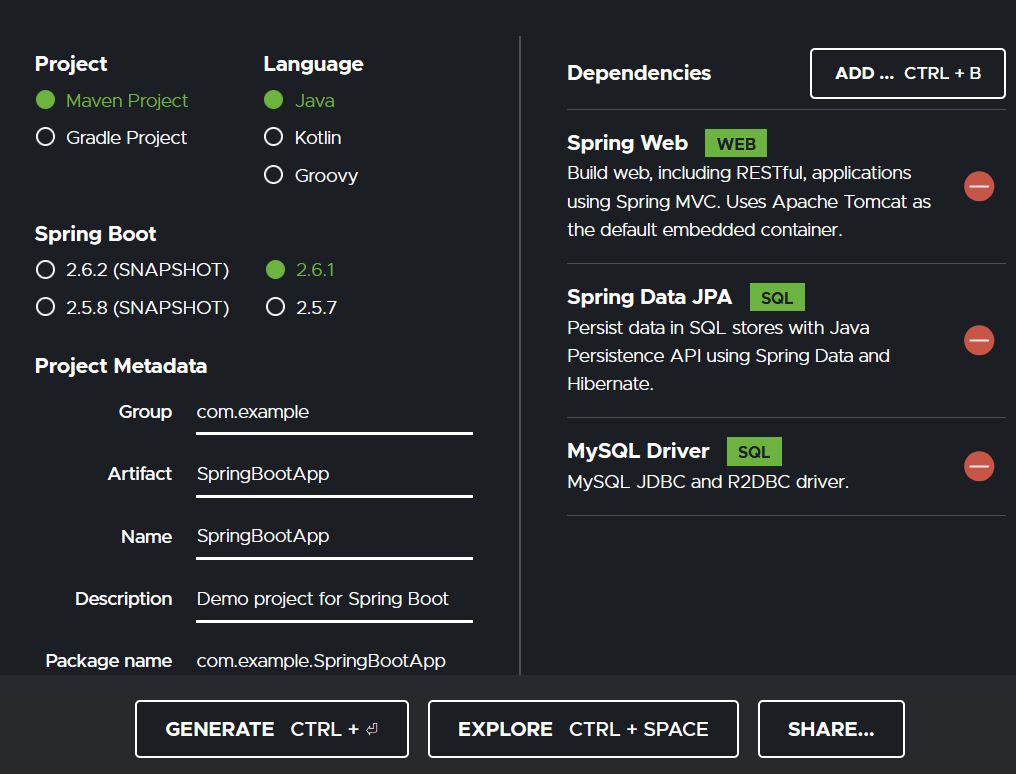
Pom.xml:
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootApp</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringBootApp</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
Extract the zip file. Now open a suitable IDE and then go to File->New->Project from existing sources->Springbootapp and select pom.xml. Click on import changes on prompt and wait for the project to sync.
Note: In the Import Project for Maven window, make sure you choose the same version of JDK which you selected while creating the project.
For database operation we have to configure the Spring application with the database also it is required to add configuration of the database before executing the Spring project. All the configuration is added in the file application.properties of the Spring project.
application.properties file:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Aayush
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
Project Structure:

User.java file:
Java
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
int id;
String name;
User() {}
User(int id, String name)
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
|
UserRepo:(This file is used for extending the JPA methods with hibernate implementation)
Java
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
interface UserRepo extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> {
}
|
SpringBootAppApplication.java file:
Java
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootAppApplication
implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired UserRepo ob;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootAppApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception
{
User first = new User(1, "Aayush");
ob.deleteById(1)
}
|
Previous table output:

Run the main application:

Database Output:

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...