Spring Data JPA – @Column Annotation
Last Updated :
29 Dec, 2021
Spring Boot is built on the top of the spring and contains all the features of spring. And is becoming a favorite of developers these days because of its rapid production-ready environment which enables the developers to directly focus on the logic instead of struggling with the configuration and setup. Spring Boot is a microservice-based framework and making a production-ready application in it takes very little time. In this article, we will discuss how to change the column name in the Spring project using JPA. @Column annotation is used for Adding the column the name in the table of a particular MySQL database.
Syntax:
@Column(name=”DESC”, nullable=false, length=512)
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
Attribute:
Name: The name of the column.
length: The column length.
nullable: Whether the database column is nullable.
Example
Step 1: Go to this link. Fill in the details as per the requirements. For this application:
Project: Maven
Language: Java
Spring Boot: 2.5.6
Packaging: JAR
Java: 11
Dependencies: Spring Web,Spring Data JPA, MySql Driver
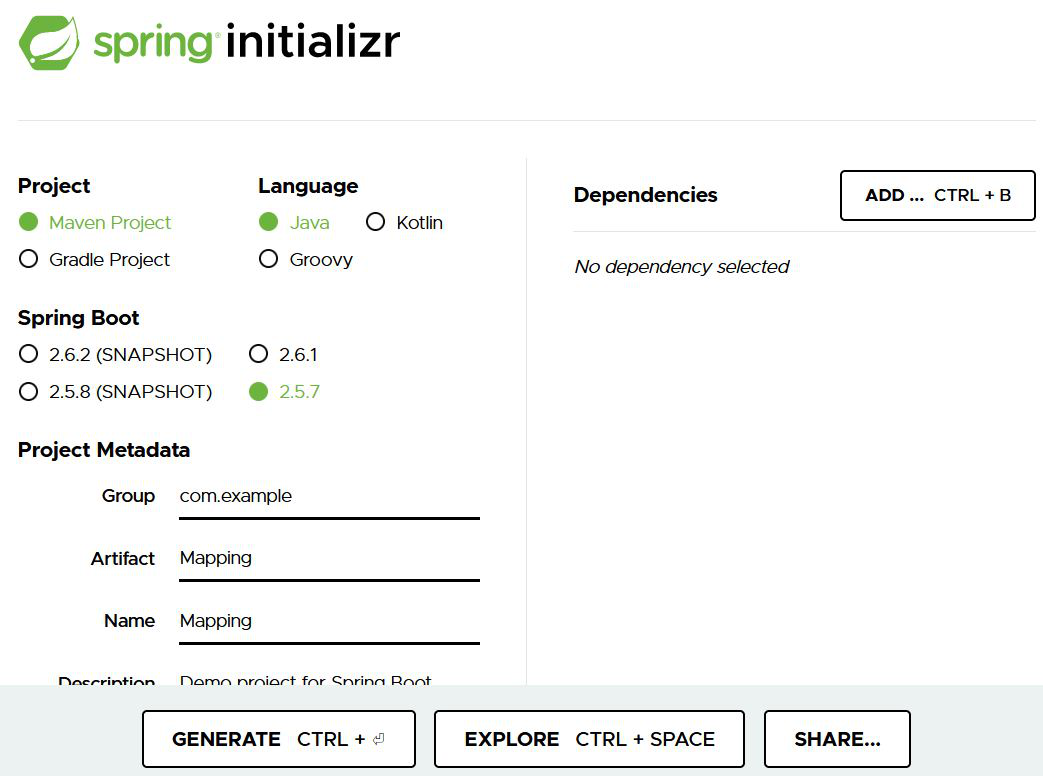
Click on Generate which will download the starter project.
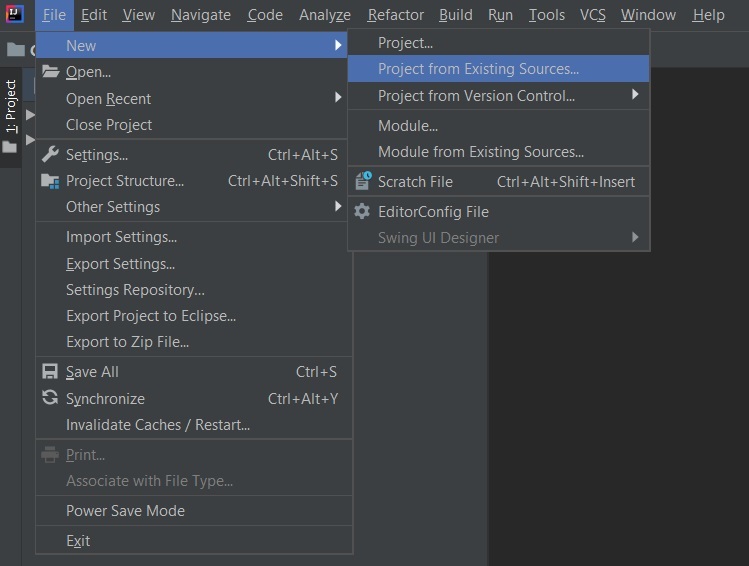
Step 2: Extract the zip file. Now open a suitable IDE and then go to File > New > Project from existing sources > Mapping and select pom.xml. Click on import changes on prompt and wait for the project to sync as pictorially depicted below as follows:
Step 3: Adding the necessary properties in the application.properties file. (mapping is the database name)
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Aayush
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mapping
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
Step 4: Create a model folder in the project folder and make a StudentInformation class.
ProjectStructrure:

StudentInformation.java
Java
@Entity
@Table(name = "Student")
public class StudentInformation {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int rollno;
@Column(name = "Student_name")
private String name;
public int getRollno() { return rollno; }
public StudentInformation() {}
public StudentInformation(int rollno, String name)
{
this.rollno = rollno;
this.name = name;
}
public void setRollno(int rollno)
{
this.rollno = rollno;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
}
|
Run the main application:
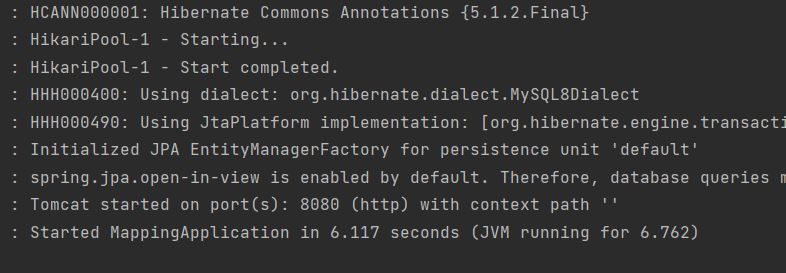
Database output:

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...