Mean Deviation of a series can be defined as the arithmetic average of the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (mean, median, or mode). Mean Deviation is also known as the First Moment of Dispersion or Average Deviation. Mean Deviation is based on all the items of the series. Theoretically, the mean deviation can be calculated by taking deviations from any of the three averages. But in actual practice, the mean deviation is calculated either from mean or median. While calculating deviations from the selected average, the signs (+ or -) of deviations are ignored and are taken as positive.
Coefficient of Mean Deviation
Mean Deviation is an absolute measure of dispersion. In order to transform it into a relative measure, it is divided by the average, from which it has been calculated. It is known as the Coefficient of Mean Deviation.
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean ( ) =
) = 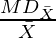
Mean Deviation from Mean in Case of Individual Series
In the case of individual series, the mean deviation is calculated by totalling the deviations from the mean or median and dividing the total by the number of items. Steps to calculate mean deviation from the mean in the case of individual series-
Step 1: Calculate the specific average (Mean) from which the mean deviation is to be found.
Step 2: Obtain absolute (positive) deviations of each observation from the mean.
Step 3: Absolute deviations are totalled up to find out ∑|D|.
Step 4: Apply the formula
Mean Deviation from Mean 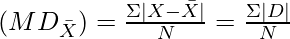
Example 1:
Calculate mean deviation from the mean for the given data: 10, 16, 22, 24, 28.
Solution:
Mean  =
= 
Mean  =
= 
Mean  = 20
= 20
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 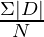
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  = 5.6
= 5.6
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 0.28
Example 2:
Calculate mean deviation from mean for the given data: 20, 24, 32, 40, 50, 54, 60.
Solution:
Mean ( ) =
) = 
Mean  =
= 
Mean  = 40
= 40
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  = 12.57
= 12.57
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 0.31
Mean Deviation from Mean in Case of Discrete Series
Step 1: Calculate specific average from which the mean deviation is to be found.
Step 2: Obtain the absolute deviations |D| of each observation from the specific average.
Step 3: Multiple absolute deviations |D| with respective frequencies (f) and obtain the sum of products to get ∑f |D|.
Step 4: Divide ∑f |D| by number of items to get mean deviation.
Mean Deviation from Mean 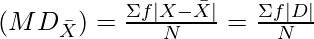
Example 1:
Calculate mean deviation from mean and coefficient of mean deviation.

Solution:
Mean  =
= 
Mean  =
= 
Mean  = 11.125
= 11.125
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  = 0.6875
= 0.6875
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 0.0617
Example 2:
Calculate mean deviation from mean and coefficient of mean deviation.
Solution:
Mean  =
= 
Mean (\bar{X}) = \frac{1070}{40}
Mean  = 26.75
= 26.75
Mean Deviation from Mean =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  = 12.58
= 12.58
Coefficient of Mean Deviation = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation = 0.47
Mean Deviation from Mean in Case of Continuous Series
In the case of continuous series, the formula for mean deviation is the same as that of the discrete series. For the given frequency distribution, the mid-points of class intervals have to be found out and they are taken as ‘m’. In this way, a continuous series assumes the shape of a discrete series. After that, all the steps of discrete series are applied. Symbolically,
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
=  =
= 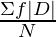
Example 1:
Calculate mean deviation from mean and coefficient of mean deviation.

Solution:
Mean  =
= 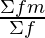
Mean  =
= 
Mean  = 5.2
= 5.2
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  = 1.48
= 1.48
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 0.28
Example 2: Calculate mean deviation from mean and coefficient of mean deviation.
Solution:
Mean  =
= 
Mean  =
= 
Mean  = 94.8
= 94.8
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  =
= 
Mean Deviation from Mean  = 19.968
= 19.968
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 
Coefficient of Mean Deviation from Mean = 0.210
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...