What is Arithmetic Line-Graph or Time-Series Graph?
Last Updated :
11 Sep, 2023
A time series is an arrangement in which the values of variables are recorded in relation to the time of occurrence. In the case of a long series of data, time series helps identify the trend, periodicity, etc. The time period can be defined as a year, quarter, month, week, days, hours, and so on. A time series graph is also called a Line Graph or a Histogram. The absolute histograms are the histograms used to graph actual time series data. On the other hand, an index histogram is used to graph the index number of the provided data.
Steps for Making Time Series Graph
Step 1: Since “time” is an independent variable, show it along the X-axis in the graph. The other variable is measured along the Y-axis because it is a dependent variable.
Step 2: Place a point on the graph for each pair of values that represents the independent variable’s value on the X-axis and the dependent variable’s value on the Y-axis.
Step 3: To create the time series graph, straight lines (not freehand lines) are used to connect all the data points that so obtained.
Important points to consider while constructing Time Series Graph
1. The equal distance on the X-axis is the equal time duration, and the equal distance on the Y-axis is the equal absolute amount.
2. A suitable and self-explanatory title should be provided to the graph.
3. If more than one variable is shown on a graph, then for each curve, different types of lines should be used. Also, an index should be provided to show the scale of graph and meaning of different types of lines used.
4. Units, years, etc., should be indicated horizontally instead of vertically to prevent the reader from turning the graph in another direction.
There are two types of time series graphs: (I) Graphs with One Variable, and (II) Graphs with Two Variables or More than Two Variables.
(I) One Variable Graph
The X-axis is used to measure time, and the Y-axis is used to measure the value of the variable if there is just one variable to be presented. In this graph, plotting the various time points against the respective values and linking them with straight lines is done. The fluctuation of the mentioned line represents variations in the variable, and the distance of the points from the graph’s base line denotes the magnitude.
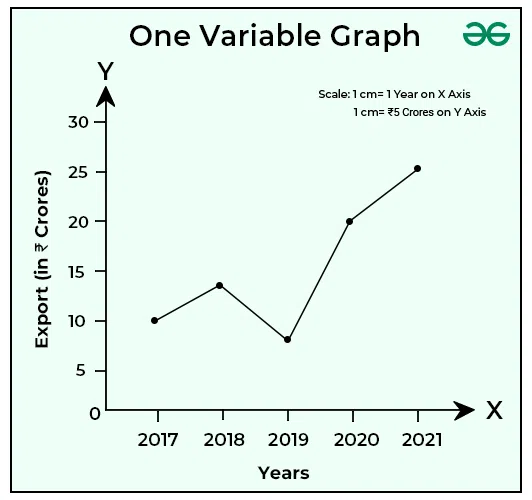
Example 1: Create a time series graph with the annual export data given below.
|
Years
|
Exports (in crores)
|
|
2017
|
10
|
|
2018
|
14
|
|
2019
|
8
|
|
2020
|
20
|
|
2021
|
25
|
Solution:
False Base Line
We already know that the scale of the Y-axis should start at zero. But if this rule is carefully followed and there is a significant distance between zero and the variable’s smallest value, the curve will be strongly pulled up and away from the origin. For instance, if the variable starts at 1,000 and its following values only change by very small amounts, a large amount of space would be needed to display the variable. The false base is used to solve this problem.
- The interval between zero and the variable’s smallest value is omitted when a false base is used.
- The graph should clearly show any instances of false base.
- In this case, a vertical line usually divides into two parts with some blank space between them. A zigzag or connected line is used to represent this blank area.
Objectives of using a False Base line
1. To present the variations in the data.
2. To save the space in the graph. This means by using a false base line, a significant part of the graph is not wasted.
3. To enhance communication through better visuals.
Example 2:
The following data shows the annual salary of the employees in different years. Use this information to draw a time series graph.
|
Years
|
Salary (in thousands)
|
|
2000
|
25
|
|
2005
|
30
|
|
2010
|
38
|
|
2015
|
45
|
|
2020
|
55
|
Solution:
In this graph, a false base line is used to present the time series data. This is so because the lowest value is 25 and after that, the value increases. Moreover, it also facilitates meaningful presentations and saves a lot of space.
(II) Two or more than two Variables Graph
If two or more values are plotted on the same graph, it is best to use different types of lines, such as dotted, broken, or thick lines. This type of graph is generally used to display data on exports and imports, maximum and minimum temperatures, mortality and birth rates, revenues and expenses, etc. The variables can either be specified in “same units” or “different units” when two or more variables are to be shown on the same graph.
1. Two-variable graphs measured in the “Same Units”
Two or more variables can be plotted on the same graph if the units of measurement are the same. The process for creating this graph is similar to that for one variable, except there will be two or more curves rather than just one.
Example 3:
The following data shows the exports and imports in different years. Use this information to draw a time series graph.
|
Year
|
Exports (in crores)
|
Imports (in crores)
|
|
2017
|
5
|
9
|
|
2018
|
7
|
12
|
|
2019
|
10
|
15
|
|
2020
|
6
|
9
|
|
2021
|
13
|
16
|
Solution:
The graph shows two curves, one for the imports and one for the exports. In this, Time is shown along the X-axis, and Exports/Imports are shown along the Y-axis.
2. Two-variable graphs measured in “Different Units”
In case two variables are measured in two different units then two scales should be presented, one on the left and one on the right. For instance, the same graph can show imports of the same time period in terms of ₹ crores and million tons. But to compare different curves, the average values of all the variables are obtained on a single line that is frequently put in the center of the graph. This line is referred to as the Common Average Line.
How to draw the Common Average Line?
- The first step is to determine the average of both variables and mark this average point on each scale.
- Next, draw a straight line connecting these two average points. This is referred to as the Common Average Line.
Example 4:
The following data shows the imports in different years. Use this information to draw a time series graph.
|
Years
|
Imports (in Million tons)
|
Imports (in ₹crores)
|
|
2018
|
100
|
10
|
|
2019
|
125
|
12
|
|
2020
|
90
|
9
|
|
2021
|
110
|
13
|
|
2022
|
130
|
17
|
Solution:
In the above question, the value of imports is provided in different units, thus the graph is created using two scales. In this, Time is shown along the X-axis, and Imports are shown along the Y-axis.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...