Mathematics | Renewal processes in probability
Last Updated :
05 Oct, 2018
A
Renewal process is a general case of Poisson Process in which the inter-arrival time of the process or the time between failures does not necessarily follow the exponential distribution. A counting process N(t) that represents the total number of occurrences of an event in the time interval (0, t] is called a renewal process, if the time between failures are independent and identically distributed random variables.
The probability that there are exactly n failures occurring by time t can be written as,

and,
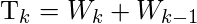
Note that the times between the failures are T1, T2, …, Tn so the failures occurring at time
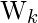
are,
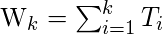
Thus,
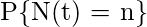
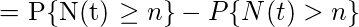
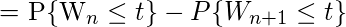
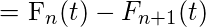 Properties –
Properties –
- The mean value function of the renewal process, denoted by m(t), is equal to the sum of the distribution function of all renewal times, that is,
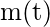
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com $= E[N(t)] $](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b399315e6a347da09d4ac9e9fd1c4ea2_l3.png)
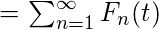
- The renewal function, m(t), satisfies the following equation:
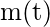
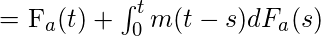 where
where 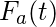 is the distribution function of the inter-arrival time or the renewal period.
is the distribution function of the inter-arrival time or the renewal period.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...