Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree
Last Updated :
07 Aug, 2023
Consider lines with a slope of -1 that cross through nodes. Print all diagonal elements in a binary tree that belong to the same line, given a binary tree.
Input : Root of below tree
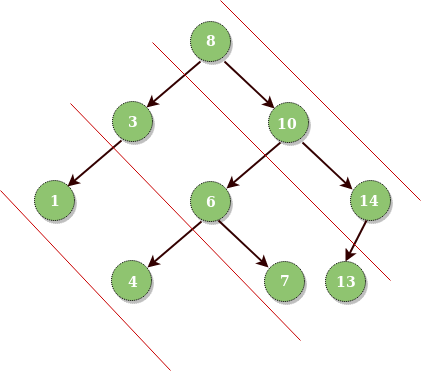
Output :
Diagonal Traversal of binary tree:
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4
Observation : root and root->right values will be prioritized over all root->left values.
The plan is to make use of a map. Different slope distances are used in the map as a key. The map’s value is a node vector (or dynamic array). To save values in the map, we traverse the tree. We print the contents of the map after it has been constructed.
Below is the implementation of the above idea.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
void diagonalPrintUtil(Node* root, int d,
map<int, vector<int>> &diagonalPrint)
{
if (!root)
return;
diagonalPrint[d].push_back(root->data);
diagonalPrintUtil(root->left,
d + 1, diagonalPrint);
diagonalPrintUtil(root->right,
d, diagonalPrint);
}
void diagonalPrint(Node* root)
{
map<int, vector<int> > diagonalPrint;
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrint);
cout << "Diagonal Traversal of binary tree : \n";
for (auto it :diagonalPrint)
{
vector<int> v=it.second;
for(auto it:v)
cout<<it<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Vector;
public class DiagonalTraversalBTree
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int data)
{
this.data=data;
left = null;
right =null;
}
}
static void diagonalPrintUtil(Node root,int d,
TreeMap<Integer,Vector<Integer>> diagonalPrint)
{
if (root == null)
return;
Vector<Integer> k = diagonalPrint.get(d);
if (k == null)
{
k = new Vector<>();
k.add(root.data);
}
else
{
k.add(root.data);
}
diagonalPrint.put(d,k);
diagonalPrintUtil(root.left,
d + 1, diagonalPrint);
diagonalPrintUtil(root.right,
d, diagonalPrint);
}
static void diagonalPrint(Node root)
{
TreeMap<Integer,Vector<Integer>>
diagonalPrint = new TreeMap<>();
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrint);
System.out.println("Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree");
for (Entry<Integer, Vector<Integer>> entry :
diagonalPrint.entrySet())
{
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def diagonalPrintUtil(root, d, diagonalPrintMap):
if root is None:
return
try :
diagonalPrintMap[d].append(root.data)
except KeyError:
diagonalPrintMap[d] = [root.data]
diagonalPrintUtil(root.left,
d+1, diagonalPrintMap)
diagonalPrintUtil(root.right,
d, diagonalPrintMap)
def diagonalPrint(root):
diagonalPrintMap = dict()
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrintMap)
print ("Diagonal Traversal of binary tree : ")
for i in diagonalPrintMap:
for j in diagonalPrintMap[i]:
print (j,end=" ")
print()
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.left.right.left = Node(4)
root.left.right.right = Node(7)
diagonalPrint(root)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
public static void diagonalPrintUtil(Node root, int d, Dictionary<int, List<int>> diagonalPrint)
{
if (root == null) return;
if (!diagonalPrint.ContainsKey(d))
{
diagonalPrint[d] = new List<int>();
}
diagonalPrint[d].Add(root.data);
diagonalPrintUtil(root.left, d + 1, diagonalPrint);
diagonalPrintUtil(root.right, d, diagonalPrint);
}
public static void diagonalPrint(Node root)
{
Dictionary<int, List<int>> diagonalPrint = new Dictionary<int, List<int>>();
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrint);
Console.WriteLine("Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree");
foreach (KeyValuePair<int, List<int>> entry in diagonalPrint)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", entry.Value));
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function diagonalPrintUtil(root, d, diagonalPrint = new Map()) {
if (!root) return;
let k = diagonalPrint.get(d) || [];
k.push(root.data);
diagonalPrint.set(d, k);
diagonalPrintUtil(root.left, d + 1, diagonalPrint);
diagonalPrintUtil(root.right, d, diagonalPrint);
}
function diagonalPrint(root) {
const diagonalPrint = new Map();
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrint);
console.log("Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree");
for (const [key, value] of diagonalPrint) {
console.log(value);
}
}
const root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
|
Output
Diagonal Traversal of binary tree :
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4
Time complexity: O( N logN )
Auxiliary Space: O( N )
The identical problem may be solved with a queue and an iterative method.
C++14
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
vector<int> diagonal(Node* root)
{
vector<int> diagonalVals;
if (!root)
return diagonalVals;
queue<Node*> leftQueue;
Node* node = root;
while (node) {
diagonalVals.push_back(node->data);
if (node->left)
leftQueue.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
node = node->right;
else {
if (!leftQueue.empty()) {
node = leftQueue.front();
leftQueue.pop();
}
else {
node = NULL;
}
}
}
return diagonalVals;
}
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
vector<int> diagonalValues = diagonal(root);
for (int i = 0; i < diagonalValues.size(); i++) {
cout << diagonalValues[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
};
class BinaryTree {
public static List<Integer> diagonal(Node root)
{
List<Integer> diagonalVals = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return diagonalVals;
Queue<Node> leftQueue = new LinkedList<>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null) {
diagonalVals.add(node.data);
if (node.left != null)
leftQueue.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
node = node.right;
else {
if (!leftQueue.isEmpty()) {
node = leftQueue.peek();
leftQueue.remove();
}
else {
node = null;
}
}
}
return diagonalVals;
}
public static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return node;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(8);
root.left = newNode(3);
root.right = newNode(10);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(14);
root.right.right.left = newNode(13);
root.left.right.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right.right = newNode(7);
List<Integer> diagonalValues = diagonal(root);
for (int i = 0; i < diagonalValues.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(diagonalValues.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import deque
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def diagonal(root):
out = []
node = root
left_q = deque()
while node:
out.append(node.data)
if node.left:
left_q.appendleft(node.left)
if node.right:
node = node.right
else:
if len(left_q) >= 1:
node = left_q.pop()
else:
node = None
return out
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.left.right.left = Node(4)
root.left.right.right = Node(7)
print(diagonal(root))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
}
class GFG {
public static List<int> Diagonal(Node root)
{
var diagonalVals = new List<int>();
if (root == null)
return diagonalVals;
var leftQueue = new Queue<Node>();
Node node = root;
while (node != null) {
diagonalVals.Add(node.data);
if (node.left != null)
leftQueue.Enqueue(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
node = node.right;
else {
if (leftQueue.Count > 0) {
node = leftQueue.Peek();
leftQueue.Dequeue();
}
else {
node = null;
}
}
}
return diagonalVals;
}
public static Node NewNode(int data)
{
var node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = node.right = null;
return node;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = NewNode(8);
root.left = NewNode(3);
root.right = NewNode(10);
root.left.left = NewNode(1);
root.left.right = NewNode(6);
root.right.right = NewNode(14);
root.right.right.left = NewNode(13);
root.left.right.left = NewNode(4);
root.left.right.right = NewNode(7);
var diagonalValues = Diagonal(root);
for (int i = 0; i < diagonalValues.Count; i++) {
Console.Write(diagonalValues[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function diagonal(root){
let diagonalVals = [];
if(root == null) return diagonalVals;
let leftQueue = [];
let node = root;
while(node != null){
diagonalVals.push(node.data);
if(node.left != null)
leftQueue.push(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
node = node.right;
else{
if(leftQueue.length > 0){
node = leftQueue.shift();
}
else{
node = null;
}
}
}
return diagonalVals;
}
function newNode(data){
node = new Node(data);
return node;
}
let root = newNode(8)
root.left = newNode(3)
root.right = newNode(10)
root.left.left = newNode(1)
root.left.right = newNode(6)
root.right.right = newNode(14)
root.right.right.left = newNode(13)
root.left.right.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right.right = newNode(7)
let diagonalValues = diagonal(root);
for(let i = 0; i<diagonalValues.length; i++){
console.log(diagonalValues[i] + " ");
}
|
Output
[8, 10, 14, 3, 6, 7, 13, 1, 4]
Time complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Approach 2: Using Queue:
Every node will contribute to the formation of the following diagonal. Only when the element’s left is available will we push it into the queue. We’ll process the node and then go to the right.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
vector<vector<int> > result;
void diagonalPrint(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
vector<int> answer;
while (size--) {
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
while (temp) {
answer.push_back(temp->data);
if (temp->left)
q.push(temp->left);
temp = temp->right;
}
}
result.push_back(answer);
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++)
cout << result[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
static class TNode {
Node node;
int level;
public TNode(Node n, int l){
this.node = n;
this.level = l;
}
}
public static void diagonalPrint(Node root){
if (root == null) return;
TreeMap<Integer, List<Integer> > map = new TreeMap<Integer, List<Integer> >();
Queue<TNode> q = new LinkedList<TNode>();
q.add(new TNode(root, 0));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TNode curr = q.poll();
map.putIfAbsent(curr.level, new ArrayList<>());
map.get(curr.level).add(curr.node.data);
if (curr.node.left != null)
q.add(new TNode(curr.node.left, curr.level + 1));
if (curr.node.right != null)
q.add(new TNode(curr.node.right, curr.level));
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<Integer> > entry : map.entrySet()) {
int k = entry.getKey();
List<Integer> l = map.get(k);
int size = l.size();
for (int i = 0; i < l.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(l.get(i));
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
return;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def diagonalPrint(root):
if root is None:
return
q = []
q.append(root)
while len(q) > 0:
size = len(q)
answer = []
while size > 0:
temp = q[0]
q.pop(0)
while temp is not None:
answer.append(temp.data)
if temp.left is not None:
q.append(temp.left)
temp = temp.right
size -= 1
result.append(answer)
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(8)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(10)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(14)
root.right.right.left = Node(13)
root.left.right.left = Node(4)
root.left.right.right = Node(7)
result = []
diagonalPrint(root)
for i in range(len(result)):
for j in range(len(result[i])):
print(result[i][j], end=" ")
print()
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
static List<List<int> > result = new List<List<int> >();
static void printLevelOrder(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
q.Enqueue(root);
while (q.Count != 0) {
int size = q.Count;
List<int> answer = new List<int>();
while (size-- != 0) {
Node temp = q.Dequeue();
while (temp != null) {
answer.Add(temp.data);
if (temp.left != null)
q.Enqueue(temp.left);
temp = temp.right;
}
}
result.Add(answer);
}
}
public static void Main()
{
Node root = new Node(8);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(10);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(14);
root.right.right.left = new Node(13);
root.left.right.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right.right = new Node(7);
printLevelOrder(root);
for (int i = 0; i < result.Count; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < result[i].Count; j++) {
Console.Write(result[i][j]);
Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function newNode(data){
return new Node(data);
}
let result = []
function diagonalPrint(root){
if(root == null) return;
q = [];
q.push(root);
while(q.length > 0){
let size = q.length;
answer = [];
while(size--){
let temp = q.shift();
while(temp != null){
answer.push(temp.data);
if(temp.left != null)
q.push(temp.left);
temp = temp.right;
}
}
result.push(answer);
}
}
let root = newNode(8);
root.left = newNode(3);
root.right = newNode(10);
root.left.left = newNode(1);
root.left.right = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(14);
root.right.right.left = newNode(13);
root.left.right.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right.right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
for(let i = 0; i < result.length; i++){
for(let j = 0; j < result[i].length; j++){
console.log(result[i][j] + " ");
}
}
|
Output
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4
Time Complexity: O(N), because we are visiting nodes once.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), because we are using a queue.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...