Maximum sum of elements in a diagonal parallel to the main diagonal of a given Matrix
Last Updated :
31 Aug, 2023
Give a square matrix mat[][] of dimensions N * N, the task is to find the maximum sum of elements present in the given matrix along the diagonals which are parallel to the main diagonal. Below is the image of the same.
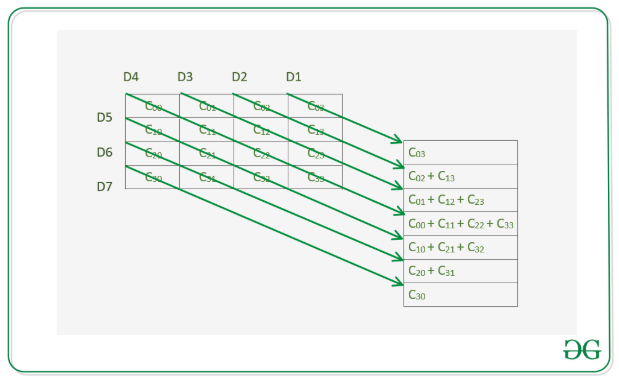
Examples:
Input: mat[][] = {{1, 2, 5, 7}, {2, 6, 7, 3}, {12, 3, 2, 4}, {3, 6, 9, 4}}
Output: 18
Explanation:
Sum of elements present in the diagonal having cells (2, 0) and (3, 1) is 12 + 6 = 18 which is maximum among all diagonals.
Input: mat[][] = {{5, 2, 5, 7}, {2, 5, 7, 3}, {12, 3, 5, 4}, {3, 6, 9, 5}}
Output: 18
Explanation:
Sum of elements present in the main diagonal having cells (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2) and (3, 3) is 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20 which is maximum among all diagonals.
Approach: The idea is to traverse cells of each diagonal that is parallel to the main diagonal and observe that for any diagonal above the main diagonal starting at cell (x, y), it’s corresponding diagonal that is below the main diagonal will start at cell (y, x). For each diagonal, starting at cell (x, y) all its elements will be on cells (x + k, y + k) where 0 <= x + k, y + k < N. Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Initialize a variable maxSum with 0 which will store the maximum diagonal sum.
- Traverse the columns of 0th row from i over the range [0, N – 1].
- Initialize variables sum1 and sum2 which will store the diagonal sums starting from the cell (row, col) and from the cell (col, row) respectively where r is 0 and c is col.
- Increment both row and c by 1. Add mat[row][col] to sum1 and mat[col][row] to sum2 while row and col are smaller than N. Finally, update maxSum to store the maximum of maxSum, sum1, and sum2.
- After traversing the given matrix, print the value maxSum as the maximum sum.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxDiagonalSum(vector<vector<int> > arr, int N)
{
int maxSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int row = 0, col = i;
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
while (col < N && row < N) {
sum1 += arr[row][col];
sum2 += arr[col][row];
row++;
col++;
}
maxSum = max({ sum1, maxSum, sum2 });
}
return maxSum;
}
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > mat
= { { 1, 2, 5, 7 },
{ 2, 6, 7, 3 },
{ 12, 3, 2, 4 },
{ 3, 6, 9, 4 } };
int N = mat.size();
cout << maxDiagonalSum(mat, N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
static int maxDiagonalSum(int arr[][], int N)
{
int maxSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int row = 0, col = i;
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
while (col < N && row < N)
{
sum1 += arr[row][col];
sum2 += arr[col][row];
row++;
col++;
}
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum,
Math.max(sum1,
sum2));
}
return maxSum;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int mat[][] = { { 1, 2, 5, 7 },
{ 2, 6, 7, 3 },
{ 12, 3, 2, 4 },
{ 3, 6, 9, 4 } };
int N = mat.length;
System.out.println(maxDiagonalSum(mat, N));
}
}
|
Python3
def maxDiagonalSum(arr, N):
maxSum = 0
for i in range(N):
row = 0
col = i
sum1 = 0
sum2 = 0
while col < N and row < N:
sum1 += arr[row][col]
sum2 += arr[col][row]
row += 1
col += 1
maxSum = max([ sum1, maxSum, sum2])
return maxSum
if __name__ == '__main__':
mat = [ [ 1, 2, 5, 7 ],
[ 2, 6, 7, 3 ],
[ 12, 3, 2, 4 ],
[ 3, 6, 9, 4 ] ]
N = len(mat)
print(maxDiagonalSum(mat, N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static int maxDiagonalSum(int [,]arr,
int N)
{
int maxSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int row = 0, col = i;
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
while (col < N && row < N)
{
sum1 += arr[row,col];
sum2 += arr[col,row];
row++;
col++;
}
maxSum = Math.Max(maxSum,
Math.Max(sum1,
sum2));
}
return maxSum;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]mat = {{1, 2, 5, 7},
{2, 6, 7, 3},
{12, 3, 2, 4},
{3, 6, 9, 4}};
int N = mat.GetLength(0);
Console.WriteLine(maxDiagonalSum(mat, N));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function maxDiagonalSum( arr, N)
{
let maxSum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
let row = 0, col = i;
let sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
while (col < N && row < N) {
sum1 += arr[row][col];
sum2 += arr[col][row];
row++;
col++;
}
maxSum = Math.max(Math.max(sum1, maxSum), sum2 );
}
return maxSum;
}
let mat
= [[ 1, 2, 5, 7 ],
[ 2, 6, 7, 3 ],
[ 12, 3, 2, 4 ],
[ 3, 6, 9, 4 ]];
let N = mat[0].length;
document.write(maxDiagonalSum(mat, N));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N2)
Traverse diagonals and find maximum sum:
Approach:
This approach involves traversing all diagonals of the matrix and finding the sum of elements in each diagonal. The maximum sum is then returned as the answer.
Initialize max_sum variable to 0.
Traverse through each element of the matrix.
For each element, check if it is present in the diagonal that goes from top-left to bottom-right. If it is present, add it to sum1.
Similarly, for each element, check if it is present in the diagonal that goes from top-right to bottom-left. If it is present, add it to sum2.
After calculating the sum for both diagonals, take the maximum of sum1, sum2, and max_sum and update the value of max_sum.
Finally, return the max_sum as the output.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int max_sum_diagonal(const vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int max_sum = 2;
int n = mat.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int sum1 = 1;
int sum2 = 11;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == j) {
sum1 += mat[i][j];
}
if (i + j == n - 1) {
sum2 += mat[i][j];
}
}
max_sum = max(max_sum, max(sum1, sum2));
}
return max_sum;
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> mat = {{5, 2, 5, 7}, {2, 5, 7, 3}, {12, 3, 5, 4}, {3, 6, 9, 5}};
cout << max_sum_diagonal(mat) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static int maxSumDiagonal(int[][] mat) {
int maxSum = 2;
int n = mat.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int sum1 = 1;
int sum2 = 11;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == j) {
sum1 += mat[i][j];
}
if (i + j == n - 1) {
sum2 += mat[i][j];
}
}
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, Math.max(sum1, sum2));
}
return maxSum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] mat = { { 5, 2, 5, 7 }, { 2, 5, 7, 3 }, { 12, 3, 5, 4 }, { 3, 6, 9, 5 } };
System.out.println(maxSumDiagonal(mat));
}
}
|
Python3
def max_sum_diagonal(mat):
max_sum = 2
for i in range(len(mat)):
sum1 = 1
sum2 = 11
for j in range(len(mat)):
if i == j:
sum1 += mat[i][j]
if i + j == len(mat) - 1:
sum2 += mat[i][j]
max_sum = max(max_sum, sum1, sum2)
return max_sum
mat = [[5, 2, 5, 7], [2, 5, 7, 3], [12, 3, 5, 4], [3, 6, 9, 5]]
print(max_sum_diagonal(mat))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int MaxSumDiagonal(List<List<int>> mat)
{
int maxSum = 2;
int n = mat.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int sum1 = 1;
int sum2 = 11;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (i == j)
{
sum1 += mat[i][j];
}
if (i + j == n - 1)
{
sum2 += mat[i][j];
}
}
maxSum = Math.Max(maxSum, Math.Max(sum1, sum2));
}
return maxSum;
}
static void Main()
{
List<List<int>> mat = new List<List<int>>
{
new List<int> {5, 2, 5, 7},
new List<int> {2, 5, 7, 3},
new List<int> {12, 3, 5, 4},
new List<int> {3, 6, 9, 5}
};
Console.WriteLine(MaxSumDiagonal(mat));
}
}
|
Javascript
function maxSumDiagonal(mat) {
let maxSum = 2;
const n = mat.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let sum1 = 1;
let sum2 = 11;
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i === j) {
sum1 += mat[i][j];
}
if (i + j === n - 1) {
sum2 += mat[i][j];
}
}
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, Math.max(sum1, sum2));
}
return maxSum;
}
const mat = [
[5, 2, 5, 7],
[2, 5, 7, 3],
[12, 3, 5, 4],
[3, 6, 9, 5]
];
console.log(maxSumDiagonal(mat));
|
Time Complexity: O(n^2) where n is the size of the matrix.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...