The `mv` command in Linux is like a superhero tool that can do a bunch of cool stuff with your files and folders. Think of it as a digital moving truck that helps you shift things around in your computer. Whether you want to tidy up your folders, give your files new names, or send them to different places, `mv` is the go-to friend for the job. It’s a basic tool that every person using Linux should know about. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how you can use the mv command for different tasks, and I’ll show you step-by-step examples to make it super easy to understand. So, buckle up, and let’s explore the many tricks the mv command has up its sleeve!
In UNIX-based operating systems like Linux and macOS, `mv` stands for “move”. But in this article, we will be talking about the “mv command in Linux”. As its name suggests this command is used to rename file directories and move files from one location to another within a file system.
How to Move File in Linux | mv Command
Syntax of mv command in Linux
The Basic Syntax for mv command in linux is mentioned below.
mv [options(s)] [source_file_name(s)] [Destination_file_name]
Here,
- source_file_name(s) = The name of the files that we want to rename or move.
- Destination_file_name = The name of the new location or the name of the file.
Examples of mv Command
1. How to Rename a file in Linux Using mv Command
Syntax:
mv [source_file_name(s)] [Destination_file_name]
Enter your source file name in place of [source_file_name(s)] and your destination file name in place of [Destination_file_name].
For Example:
If we have a file “name = jayesh_gfg” and want to rename it to “name = geeksforgeeks”.
mv jayesh_gfg geeksforgeeks
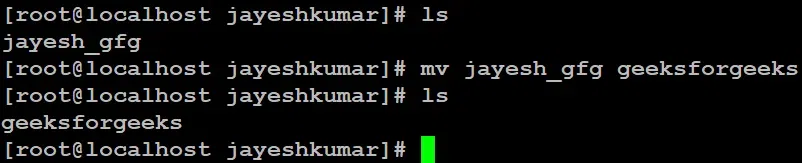
mv jayesh_gfg geeksforgeeks
Here we used the `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
This command is renamed `jayesh_gfg` to `geeksforgeeks`. If `geeksforgeeks` already exists, in that case, it will be overwritten without prompting for confirmation.
2. How to Move a File in Linux Using mv Command
Syntax:
mv [source_file_name(s)] [Destination_path]
Enter your source file name in place of [source_file_name(s)] and your destination path in place of [Destination_path].
For Example:
If we have a file “name = geeksforgeeks” and want to move it to location “name = /home/jayeshkumar/jkj”.
mv geeksforgeeks /home/jayeshkumar/jkj/

mv geeksforgeeks /home/jayeshkumar/jkj/
Here we used the `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
This command moved file “name = `geeksforgeeks`” to the destination “name = “/home.jayeshkumar/jkj/”.
3. How to Move Multiple files in Linux Using mv Command
Syntax:
mv [source_file_name_1] [source_file_name_2] [source_file_name_ .....] [Destination_path]
Enter your source file names in place of [source_file_name_1…..] and your destination path in place of [Destination_path].
For Example:
If we have a file “name = gfg_1 , gfg_2” and want to move it to location “name = /home/jayeshkumar/jkj”.
mv gfg_1 gfg_2 /home/jayeshkumar/jkj/

mv gfg_1 gfg_2 /home/jayeshkumar/jkj/
Here we used the `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
This command moved file “name = `gfg_1 and gfg_2`” to the destination “name = “/home.jayeshkumar/jkj/”.
4. How to Rename a directory in Linux Using mv Command in Linux
Syntax:
mv [source_directory_name(s)] [Destination_directory_name]
Enter your source directory name in place of [source_directory_name(s)] and your destination directory name in place of [Destination_directory_name].
For Example:
If we have a directory “name = jkj” and want to rename it to “name = new_gfg”.
mv jkj new_gfg

mv jkj new_gfg
Here we used `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
This command renames `jkj` to `new_gfg`. If `new_gfg` already exists, in that case it will be overwritten without prompting for confirmation.
Options Available in mv Command
1. -i (interactive)
The “-i” option makes the “mv” command ask for confirmation before overwriting an existing file. If the file doesn’t exist, it will simply rename or move it without prompting.
Syntax:
mv -i [source_file/directory_name(s)] [Destination_file/directory_name/path]
Enter your source file/directory name in place of [source_file/directory_name(s)] and your destination file/directory name/path in place of [Destination_file/directory_name/path].
For Example:
If we have a file “name = jayesh_gfg” and want to rename it to existing file “name = geeksforgeeks”.
mv -i jayesh_gfg geeksforgeeks

mv -i jayesh_gfg geeksforgeeks
Here we used `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
Here we have to give permission by typing yes = `y` and no =`n`.
2. -f (Force)
mv prompts for confirmation overwriting the destination file if a file is write-protected. The -f option overrides this minor protection and overwrites the destination file forcefully and deletes the source file.
Syntax:
mv -f [source_file/directory_name(s)] [Destination_file/directory_name/path]
Enter your source file/directory name in place of [source_file/directory_name(s)] and your destination file/directory name/path in place of [Destination_file/directory_name/path].
For Example:
If we have a file “name = gfg” and want to rename it to existing file “name = geeksforgeeks”.
mv -f gfg geeksforgeeks
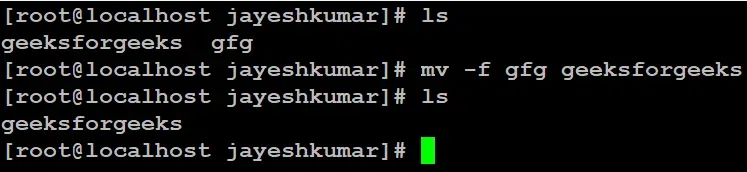
mv -f gfg geeksforgeeks
Here we used `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
3. -n (no-clobber)
With -n option, mv prevents an existing file from being overwritten.
Syntax:
mv -n [source_file/directory_name(s)] [Destination_file/directory_name/path]
Enter your source file/directory name in place of [source_file/directory_name(s)] and your destination file/directory name/path in place of [Destination_file/directory_name/path].
For Example:
If we have a file “name = oldfile” and want to rename it to existing file “name = newfile”.
mv -n oldfile newfile

mv -n oldfile newfile
Here we used `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
4. -b(backup)
With this option, it is easier to take a backup of an existing file that will be overwritten as a result of the mv command. This will create a backup file with the tilde character (~) appended to it.
Syntax:
mv -b [source_file/directory_name(s)] [Destination_file/directory_name/path]
Enter your source file/directory name in place of [source_file/directory_name(s)] and your destination file/directory name/path in place of [Destination_file/directory_name/path].
For Example:
If we have a file “name = first_file” and want to rename it to existing file “name = second_file”.
mv -b first_file second_file

mv -b first_file second_file
Here we used `ls` command to see the files and directories in the following location.
5. –version
This option is used to display the version of mv which is currently running on your system.
Syntax:
mv --version

mv –version
How to Move File in Linux | mv Command – FAQs
How do I move a file from one folder to another using the mv command in Linux?
To move a file from one folder to another, you can use the mv command followed by the source file name and the destination folder. For example:
mv filename /path/to/destination/
Can I use the mv command to rename a file in Linux?
Absolutely! The mv command is not only for moving files but also for renaming them. Just provide the current filename and the desired new name as the destination:
mv old_filename new_filename
How can I move an entire directory in Linux with the mv command?
Moving a directory is as simple as moving a file. Use the mv command with the source directory name and the destination directory:
mv directory_name /path/to/destination/
What should I do if a file with the same name already exists in the destination folder when using mv?
If a file with the same name is present in the destination folder, mv will prompt you for confirmation before overwriting. To bypass the confirmation and overwrite without asking, you can use the -f (force) option:
mv -f source destination
Can I move multiple files at once using the mv command in Linux?
Absolutely! You can move multiple files in a single command by providing all the file names followed by the destination folder:
mv file1 file2 file3 /path/to/destination/
Conclusion
The `mv` command is a useful tool for managing directories and files in Linux-based Operating Systems. We have discussed two distinct functions of `mv` command they are: renaming or moving files or directories from one location to another. Overall, we can say that `mv` command is an essential tool for managing files and directories efficiently in Linux.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...