Linux, renowned for its robust command-line interface, provides a suite of powerful tools for efficient file and directory management. Among these, the “find” command stands out as an indispensable asset, offering unparalleled versatility in searching for files based on diverse criteria. This article explores the prowess of the find command, shedding light on its capabilities and how it serves as a go-to tool for Linux users aiming to locate files swiftly and effectively.
What is the Find Command in Linux?
The find command in Linux is a dynamic utility designed for comprehensive file and directory searches within a hierarchical structure. Its adaptability allows users to search by name, size, modification time, or content, providing a flexible and potent solution. As a pivotal component of the Linux command-line toolkit, the find command caters to the nuanced needs of users, ensuring precision in file exploration and retrieval. Discover the diverse functionalities of the find command and enhance your file management efficiency on the Linux platform.
Syntax of Find Command in Linux :
Here is the syntax for the find command in Linux:
find [path] [options] [expression]
Here,
- path: Starting directory for the search.
- Example:
find /path/to/search
- options: Additional settings or conditions for the search.
- Example:
find /path/to/search -type f -name "*.txt"
- expression: Criteria for filtering and locating files.
- Example:
find /path/to/search -type d -name "docs"
This syntax allows you to customize your file search by specifying the path, adding options, and defining search criteria using expressions.
Options Available in Find Command in Linux
Here are the `find` command options along with brief descriptions of their purposes.
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
-name pattern
|
Searches for files with a specific name or pattern.
|
|
-type type
|
Specifies the type of file to search for (e.g., f for regular files, d for directories).
|
|
-size [+/-]n
|
Searches for files based on size. `+n` finds larger files, `-n` finds smaller files. ‘n‘ measures size in characters.
|
|
-mtime n
|
Finds files based on modification time. `n` represents the number of days ago.
|
|
-exec command {} \;
|
Executes a command on each file found.
|
|
-print
|
Displays the path names of files that match the specified criteria.
|
|
-maxdepth levels
|
Restricts the search to a specified directory depth.
|
|
-mindepth levels
|
Specifies the minimum directory depth for the search.
|
|
-empty
|
Finds empty files and directories.
|
|
-delete
|
Deletes files that match the specified criteria.
|
|
-execdir command {} \;
|
Executes a command on each file found, from the directory containing the matched file.
|
|
-iname pattern
|
Case-insensitive version of `-name`. Searches for files with a specific name or pattern, regardless of case.
|
How to Find a File in Linux from the Command Line
Using the find command is straightforward. To find a file in Linux, open a terminal and use the following basic syntax:
find /path/to/search -options criteria
Replace “/path/to/search" with the directory where you want to start the search and customize the options and criteria based on your requirements.
For example :
To find a file named “example.txt” in the home directory, you would use:
find ~ -name "example.txt"
This command will locate and display the path to the file if it exists in the specified directory or its subdirectories.
Examples of Find Command in Linux
1. How to Find A Specific File Using `find` Command in Linux
This query is designed to pinpoint a file within a designated directory. In the provided example, it seeks a file named “sample.txt” within the “GFG” directory.
find ./GFG -name sample.txt
The find command traverses the specified directory (./GFG) and looks for a file named “sample.txt.” If found, it displays the path to the file.
Output:
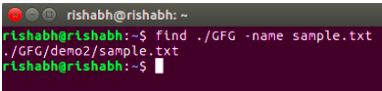 Search a file with specific name
Search a file with specific name
2. How to Search Files with a Pattern Using `find` Command in Linux
This command is tailored for discovering files within a directory that adhere to a specific naming pattern. In this case, it identifies files ending with ‘.txt’ within the “GFG” directory.
find ./GFG -name *.txt
The command looks for files with names ending in ‘.txt’ within the “GFG” directory, presenting a list of matching files.
Output:
 Search a file with pattern
Search a file with pattern
3. How to Find and Confirm File Deletion Using `find` Command in Linux
This command not only locates a specified file but also prompts the user for confirmation before initiating its removal. The example seeks to delete a file named “sample.txt” within the “GFG” directory.
find ./GFG -name sample.txt -exec rm -i {} \;
The -exec option executes the rm command on the located file, and the -i flag prompts the user for confirmation before deletion. When this command is entered, a prompt will come for confirmation, if you want to delete sample.txt or not. if you enter ‘Y/y’ it will delete the file.
Output :
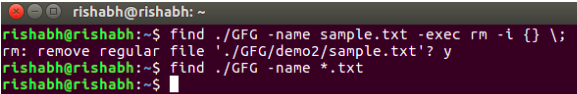 find and delete a file with confirmation
find and delete a file with confirmation
4. Search for Empty Files and Directories Using `find` Command in Linux
This query is tailored for discovering and listing empty files and directories within a specified directory.
find ./GFG -empty
The `find` command identifies and lists all empty folders and files within the “GFG” directory or its subdirectories.
Output:
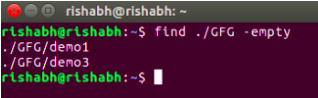 Search for empty files and directories
Search for empty files and directories
5. Search Files with Specific Permissions Using `find` Command in Linux
This command is used to locate files within a directory that have specific permissions. In the provided example, it identifies files with permissions set to 664 within the “GFG” directory.
find ./GFG -perm 664
The command searches for files within the “GFG” directory with the specified permissions (664) and displays the results.
Output:
 Search for file with entered permissions
Search for file with entered permissions
6. Display Repository Hierarchy Using `find` Command in Linux
This command is utilized to display the hierarchical structure of repositories and sub-repositories within a given directory.
find . -type d
This command displays all the repositories and sub-repositories present in the current repository. In the below example, we are currently in a repository namely “GeeksforGeeks” which contains a repo “Linux”, which contains sub-repo “LinuxCmds” which further contains a repo “FindCmd”. The ouput of below cmd is simply displaying this info. Please note that in this case if you will use “ls” cmd then it will only show “/Linux”.
Output:
.png)
7. Search Text Within Multiple Files Using `find` Command in Linux
This command is tailored for finding lines containing specific text within multiple files. The example looks for lines containing the word ‘Geek’ within all ‘.txt’ files in the current directory and its subdirectories.
find ./ -type f -name "*.txt" -exec grep 'Geek' {} \;
The command searches for ‘.txt’ files (-type f and -name "*.txt") and uses grep to print lines containing the specified text (‘Geek’).
Output:
 Search text within multiple files
Search text within multiple files
8. Find Files by When They Were Modified Using `find` Command in Linux
The -mtime option is handy for finding files based on their modification time. To find files modified within the last 7 days, you can use:
find /path/to/search -mtime -7
This command will list files modified in the last week.
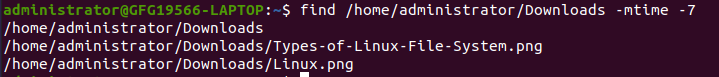 Finding Last modifications
Finding Last modifications
In this example we are searching changes in directory “/home/administrator/Downloads” which are done is past 7 days.
9. Use Grep to Find Files Based on Content Using `find` Command in Linux
Combining the find command with grep allows you to search for files based on their content. For example, to find files containing the word “pattern” in the current directory and its subdirectories, you can use:
find . -type f -exec grep -l "pattern" {} \;
This command will display the names of files containing the specified content.
Breakdown of the Command:
find .: Initiates the search from the current directory (.).-type f: Specifies that the search is for files only, excluding directories.-exec grep -l "pattern" {} \;: Executes the grep command on each found file ({}) to search for the specified content (“pattern”). The -l option in grep ensures that only the names of files containing the pattern are displayed.
Command Execution:
- The
find command starts the search from the current directory, including all its subdirectories.
- For each file (
-type f) found in the search, the -exec option executes the grep command.
- The
grep command searches for the specified content (“pattern”) in each file.
- If a file contains the specified content, its name is displayed due to the
-l option in grep.
Frequently Asked Questions in Find Command in Linux
Can I use the find command to search for files based on their content in Linux?
Yes, the find command can be combined with grep to search for files based on their content. The article provides an example of using this combination to locate files containing specific text.
How can I search for all directories in Linux using the find command?
Use the -type d option to specify that you are searching for directories. For example:
find /path/to/search -type d
The -type d flag instructs the find command to look for directories. This command will display a list of all directories within the specified path.
How can I search for files with a specific name using the find command in Linux?
To search for files with a specific name, you can use the -name option with the find command. The article includes an example syntax for finding a file named “example.txt” in the home directory.
Can I use the find command to search for files containing a specific text string within their contents?
Yes, you can combine the find command with grep to search for files based on their content. For example:
find /path/to/search -type f -exec grep -l "specific_text" {} \;
This command executes grep on each file found ({}) in the search, searching for the specified text (“specific_text”). The -l option in grep ensures that only the names of files containing the specified text are displayed.
Is the find command case-sensitive when searching for files in Linux?
By default, the find command is case-sensitive. However, the article introduces the -iname option as a case-insensitive version of -name, allowing users to search for files with a specific name or pattern regardless of case.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed the find command which is like a trusty guide for finding and managing files. This article explored how the find command can locate files based on different criteria, from names to content. It’s like having a superpower for organizing and searching through your files in a quick and flexible way. Whether you’re a seasoned Linux user or just starting out, mastering the find command is a game-changer for efficiently handling your files on the command line. It’s a must-have tool that makes navigating your computer’s files a breeze!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...