echo command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
12 Mar, 2024
The echo command in Linux is a built-in command that allows users to display lines of text or strings that are passed as arguments. It is commonly used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to the screen or a file.
Syntax of `echo` command in Linux
echo [option] [string]
Here,
[options] = The various options available for modifying the behavior of the `echo` command
[string] = It is the string that we want to display.
Basic Usage: Displaying Text/String:
The most straightforward usage of the echo command is to display a text or string on the terminal. To do this, you simply provide the desired text or string as an argument to the echo command.
Syntax:
echo [string]
Example:
If we want to display “Geeks for Geeks”. We use the following command.
echo "Geeks for Geeks"
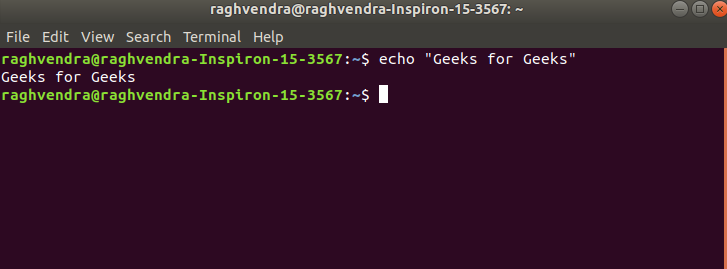
Display text
Options Available in `echo` command in Linux
NOTE :- -e here enables the interpretation of backslash escapes
1. \b : it removes all the spaces in between the text
Example:
echo -e "Geeks \bfor \bGeeks"
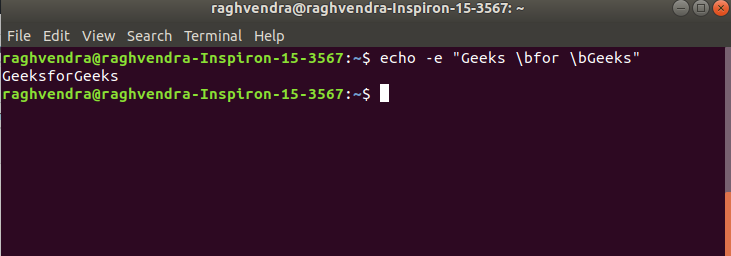
remove space
2. \c : suppress trailing new line with backspace interpreter ‘-e‘ to continue without emitting new line.
Example:
echo -e "Geeks \cfor Geeks"
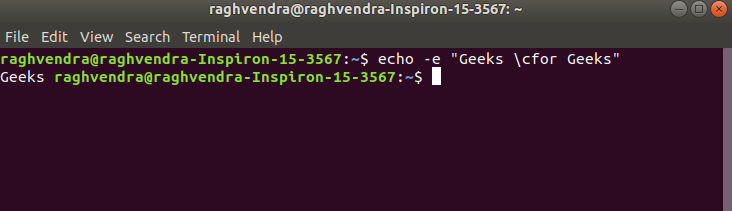
continue without emitting new line
In the above example, text after \c is not printed and omitted trailing new line.
3. \n : this option creates a new line from where it is used.
Example:
echo -e "Geeks \nfor \nGeeks"

create new line
4. \t : this option is used to create horizontal tab spaces.
Example:
echo -e "Geeks \tfor \tGeeks"

creating horizontal tab space
5. \r : carriage return with backspace interpreter ‘-e‘ to have specified carriage return in output.
Example:
echo -e "Geeks \rfor Geeks"

Carriage return
In the above example, text before \r is not printed.
6. \v : this option is used to create vertical tab spaces.
Example:
echo -e "Geeks \vfor \vGeeks
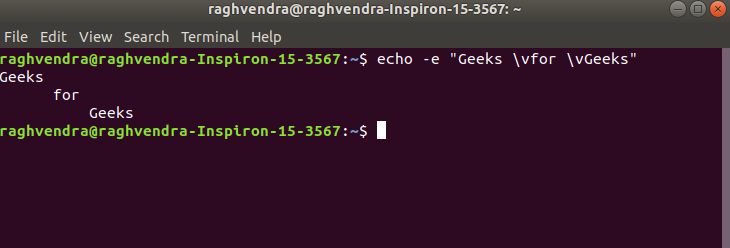
create vertical tab spaces
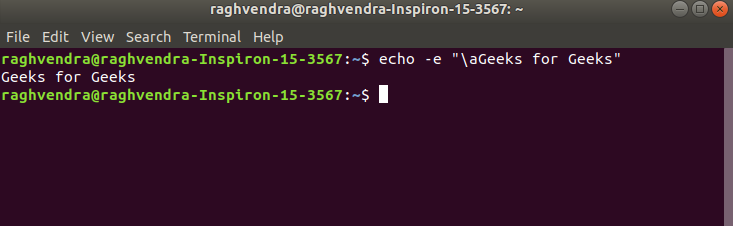
7. \a : alert return with backspace interpreter ‘-e‘ to have sound alert.
Example:
echo -e "\aGeeks for Geeks"
alert return
This command when executed, it will produce an alert sound or Bell.
8. echo *: this command will print all files/folders, similar to ls command.
Example:
echo *

similar to `ls` command
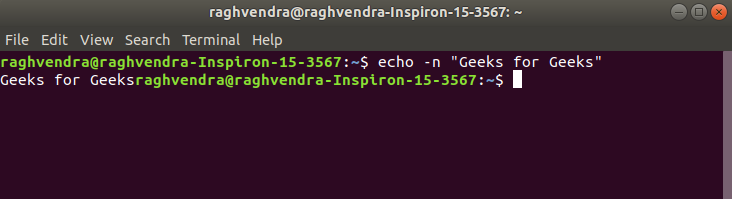
9. -n: this option is used to omit echoing trailing newline.
Example:
echo -n "Geeks for Geeks"
omit echoing trailing newline
10. Redirecting `echo` Output
The output of the `echo` can be redirected to a file instead of displaying it on the terminal. We can achive this by using the `>` or `>>` operators for output redirection.
Example:
echo "Welcome GFG" > output.txt
This will write the output of the echo command to the file name `output.txt`. File will be overwritten if it already exists.
If we want to append the output in an existing file, we use `>>` instead of `>`.
Conclusion
In this article we have discussed `echo` command in Linux which is a powerful and versatile tool and allows users to display lines of the text or strings on the terminal. Overall, we can say that by understanding the `echo` command experimenting with its features, we can effectively display message, variables, or any desired text in our Linux.
?t=153
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...