How to Kill a Process in Linux | Kill Command
Last Updated :
23 Nov, 2023
kill command in Linux (located in /bin/kill), is a built-in command which is used to terminate processes manually. kill command sends a signal to a process that terminates the process. If the user doesn’t specify any signal that is to be sent along with the kill command, then a default TERM signal is sent that terminates the process.
Basic Syntax of `kill` command in Linux
The basic syntax of the `kill` command is as follows:
Syntax :
kill [signal] PID
Here,
- PID = The `kill` command requires the process ID (PID) of the process we want to terminate.
- [signal] = We have to specify the signal and if we don’t specify the signal, the default signal `TERM` is sent to terminate the process
Signals can be specified in three ways:
Signals can be specified in three ways; they are as follows:
1) By number:
We can specify a signal using a number. For example, we have a PID `1212` and want to send a `SIGKILL` signal to kill this PID. SIGKILL has a signal number of `9` (To find signal numbers run `kill -l` command).
Syntax:
kill -9 1212
2) With SIG prefix (e.g/ -SIGkill)
We can also specify signal using SIG prefix. For example, we need to send a signal `SIGTERM` and PID is `1432`. To just check signal number of `SIGTERM` signal we can use `kill -l` command.
Syntax:
kill -SIGTERM 1432
3) Without SIG prefix:
We can also specify signals without using SIG prefix. For example, if want to send signal `TERM` and PID `1234`. To just check signal number of `TERM` signal we can use `kill -l` command.
Syntax:
kill -TERM 1234
Some Common Signals in `kill` command in Linux
The table below shows some common signals and their corresponding numbers.
| SIGHUP |
1 |
It hangup detected on controlling terminals or death of controlling process. |
| SIGINT |
2 |
It interrupts from keyboard. |
| SIGKILL |
9 |
It kills signal. |
| SIGTERM |
15 |
It terminates signal. |
To check signal name and number we can use `kill -l` command.
Options and examples of `kill` command in Linux
1. `kill -l ` Options in`kill` command in Linux
To display all the available signals, you can use the below command option:
Syntax:
kill -l
.webp)
kill -l
Note:
- Negative PID values are used to indicate the process group ID. If you pass a process group ID then all the process within that group will receive the signal.
- A PID of -1 is very special as it indicates all the processes except kill and init, which is the parent process of all processes on the system.
- To display a list of running processes use the command ps and this will show you running processes with their PID number. To specify which process should receive the kill signal we need to provide the PID.
Syntax:
ps
.webp)
ps
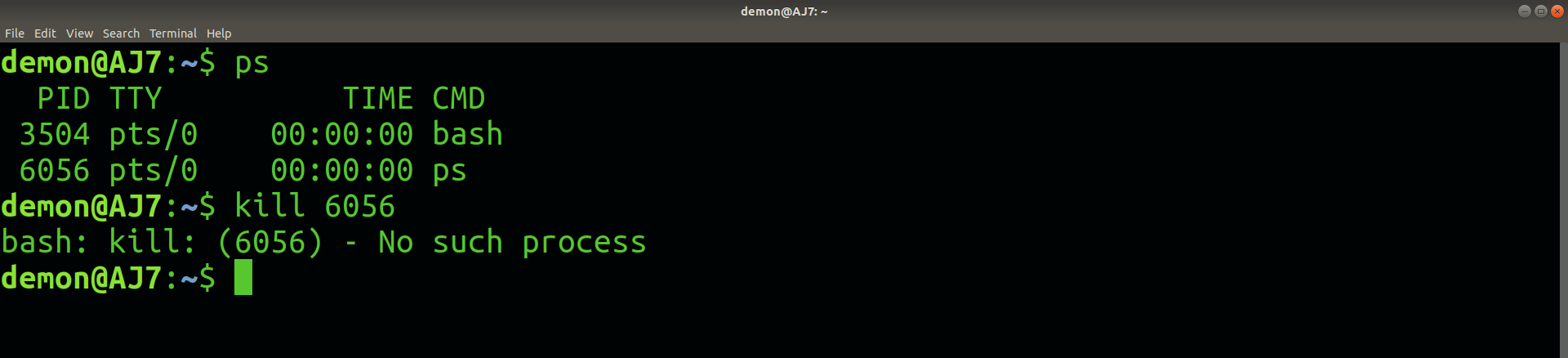
2. `kill PID` Options in`kill` command in Linux
This option specifies the process ID of the process to be killed.
Syntax:
kill pid
 3. `kill -s` Options in`kill` command in Linux
3. `kill -s` Options in`kill` command in Linux
This option specifies the signal to be sent to the process.
Syntax:
kill {-signal | -s signal} pid
Frequently Asked Questions on `kill` command in Linux
How to Kill a Process from the Linux Command Line?
To kill a process from the Linux command line, you can use the kill command followed by the process ID (PID) of the target process. For example, to terminate a process with PID 1234, you would use the following command:
kill 1234
By default, the kill command sends the SIGTERM signal, allowing the process to perform cleanup operations before termination. If the process doesn’t respond to SIGTERM or if immediate termination is required, you can use the SIGKILL signal with the -9 option:
kill -9 1234
It’s important to note that forcefully terminating a process with SIGKILL may result in data loss or corruption, so it’s recommended to try SIGTERM first and resort to SIGKILL only if necessary.
How to kill multiple processes at once?
We can use kill command to kill multiple processes at once. We just need to specify multiple PIDs separated by spaces, or we can also use `killall` command to kill all the processes with a specific name.
For Example:
If we want to kill processes PIDs like 1234, 4321, and 2342, we can we use the following command:
kill 1234 4321 2342
If we want to kill all the processes with the name “firefox”. We can use the following command.
killall firefox
Is it safe to kill the system processes?
No, it is important to note that only kill processes that we know are safe to kill and killing system processes can cause system instability. It is always better to use other methods like restarting the system or identifying the root cause of the issue and fixing it.
What is the difference between SIGTERM and SIGKILL in `kill` command in Linux?
SIGTERM, it sends a termination signal to the process which helps in exit gracefully. Whereas SIGKILL sends a kill signal to the process, which terminate the processes forcefully and immediately.
For Example:
To send signal `SIGTERM` and PID `4321`, we can use the following command.
kill -15 4321
To send signal `SIGKILL` and PID `4321`, we can use the following command.
kill -9 4321
How can I find the process ID (PID) of a specific program in Linux?
To find the PID of a specific program, you can use the pgrep command followed by the program’s name. For example, to find the PID of the “firefox” process, you would enter:
pgrep firefox
What is the purpose of the pkill command, and how does it differ from the kill command?
The pkill command is used to send signals to processes based on their name, providing a more convenient way to terminate processes. It differs from the kill command by allowing users to specify processes by name rather than PID.
How can I check the resource usage (CPU, memory) of a specific process in Linux?
To check the resource usage of a specific process, you can use the top command along with the process ID (PID). For instance, to monitor the resource usage of a process with PID 1234, you would run:
top -p 1234
Conclusion
The `kill` command in Linux is a very powerful utility for managing processes. We have understood the different ways to specify the signals and available options in the kill command which can help us to manage our system resources efficiently and resolve issues quickly and effectively.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...