How to rebuild all the indexes of a collection using PyMongo?
Last Updated :
20 Jun, 2022
According to MongoDB documentation, normally, MongoDB compacts indexes during routine updates. For most users, the reIndex command is unnecessary. However, it may be worth running if the collection size has changed significantly or if the indexes are consuming a disproportionate amount of disk space.
Prerequisites: MongoDB Python Basics This article is about rebuilding the indexes of the collection in MongoDB using PyMongo reindex() function.
The collection indexes may take more than a disproportionate amount of disk space, and this problem can be solved by rebuilding the index of the collection. Let’s begin with rebuilding the index of Collection:
Importing Required Modules: Import the required module using the command:
from pymongo import MongoClient
If MongoDB is already not installed on your machine you can refer to the guide: Guide to Install MongoDB with Python
Creating a Connection: Now we had already imported the module, it’s time to establish a connection to the MongoDB server, presumably which is running on localhost (host name) at port 27017 (port number).
client = MongoClient(‘localhost’, 27017)
Accessing the Database: Since the connection to the MongoDB server is established. We can now create or use the existing database.
mydatabase = client.name_of_the_database
Accessing the Collection: We now select the collection from the database using the following syntax:
collection_name = mydatabase.name_of_collection
Rebuilding Index:
collection_name.reindex()
- The above statement rebuilds all the indexes. Please use the above statement with caution as the rebuilding of indexes takes place in the foreground that blocks all the operations on the MongoDB server.
- reindex() is deprecated in 3.11.
- Starting from 4.0, use the following command to rebuild the index.
<db object>.command('reIndex', <collection name>)
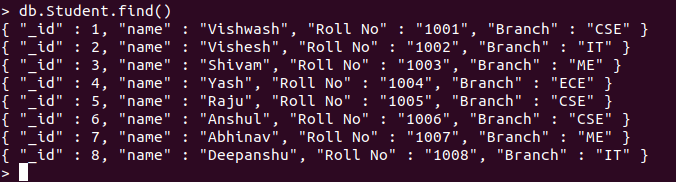
Example: Sample Database
Python3
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
mydatabase = client.GFG
mycollection = mydatabase.Student
mycollection.reindex()
|
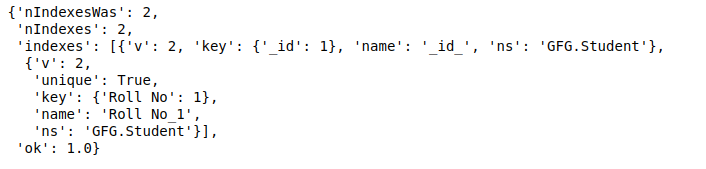
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...