Convert PyMongo Cursor to JSON
Last Updated :
26 May, 2020
Prerequisites: MongoDB Python Basics
This article is about converting the PyMongo Cursor to JSON. Functions like find() and find_one() returns the Cursor instance.
Let’s begin:
- Importing Required Modules: Import the required module using the command:
from pymongo import MongoClient
from bson.json_util import dumps
If MongoDB is already not installed on your machine you can refer to the guide: Guide to Install MongoDB with Python
- Creating a Connection: Now we had already imported the module, its time to establish a connection to the MongoDB server, presumably which is running on localhost (host name) at port 27017 (port number).
client = MongoClient(‘localhost’, 27017)
- Accessing the Database: Since the connection to the MongoDB server is established. We can now create or use the existing database.
mydatabase = client.name_of_the_database
- Accessing the Collection: We now select the collection from the database using the following syntax:
collection_name = mydatabase.name_of_collection
- Getting the documents: Getting all the documents from the collection using find() method. It returns the instance of the Cursor.
cursor = collection_name.find()
- Converting the Cursor to JSON: Converting the Cursor to the JSON.
First, we will convert the Cursor to the list of dictionary.
list_cur = list(cursor)
Now, converting the list_cur to the JSON using the method dumps() from bson.json_util
json_data = dumps(list_cur)
You can now save it to the file or can use it in the program using loads() function.
Below is the implementation.
from pymongo import MongoClient
from bson.json_util import dumps, loads
client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
mydatabase = client.GFG
mycollection = mydatabase.College
cursor = mycollection.find()
list_cur = list(cursor)
json_data = dumps(list_cur, indent = 2)
with open('data.json', 'w') as file:
file.write(json_data)
|
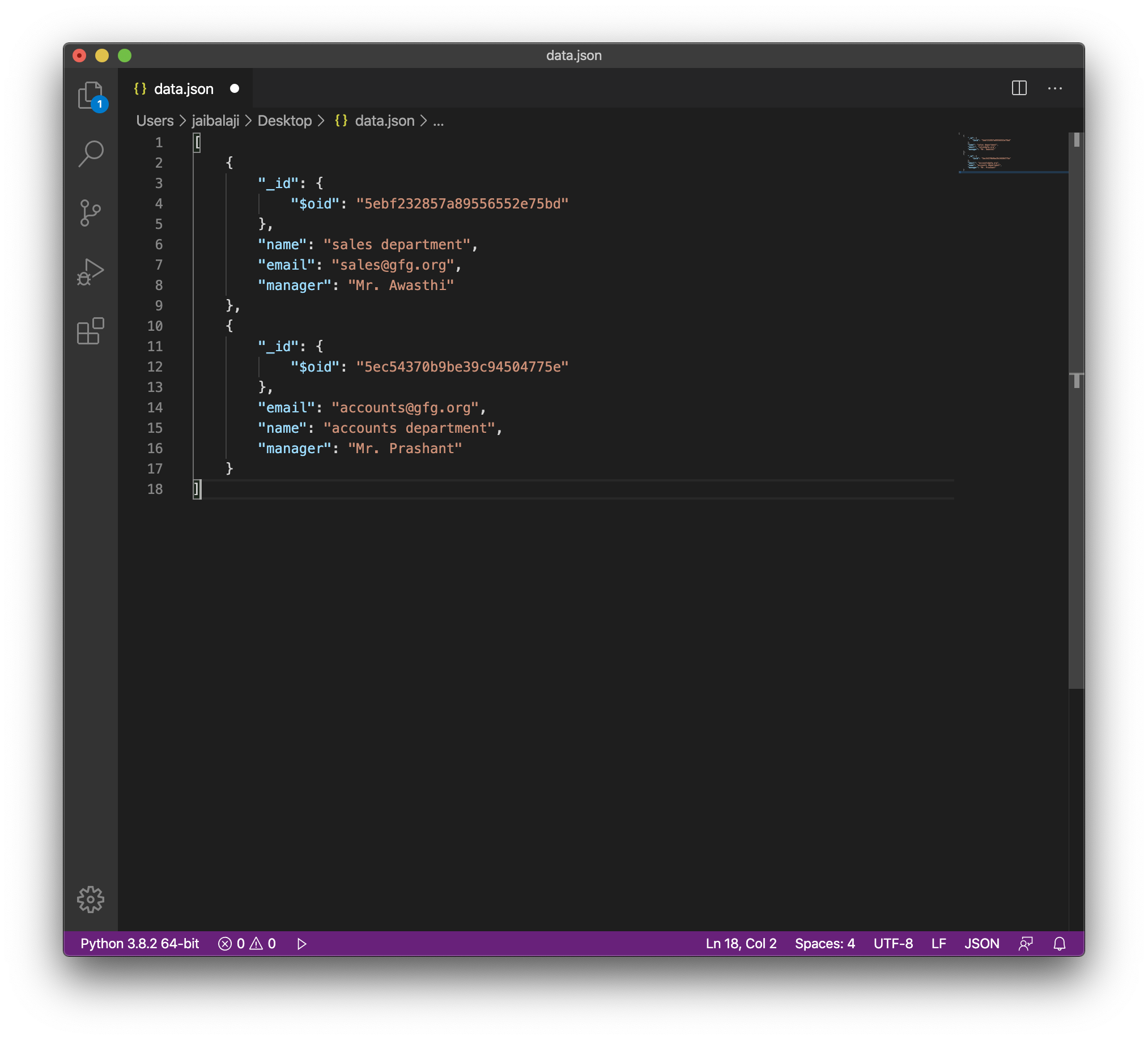
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...