Write a program to Calculate Size of a tree | Recursion
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2023
Size of a tree is the number of elements present in the tree. Size of the below tree is 5.
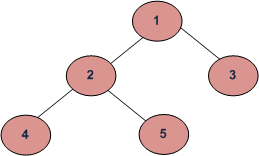
Size() function recursively calculates the size of a tree. It works as follows:
Size of a tree = Size of left subtree + 1 + Size of right subtree.
Algorithm:
size(tree)
1. If tree is empty then return 0
2. Else
(a) Get the size of left subtree recursively i.e., call
size( tree->left-subtree)
(a) Get the size of right subtree recursively i.e., call
size( tree->right-subtree)
(c) Calculate size of the tree as following:
tree_size = size(left-subtree) + size(right-
subtree) + 1
(d) Return tree_size
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
int size(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else
return(size(node->left) + 1 + size(node->right));
}
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Size of the tree is " << size(root);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
int size(struct node* node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return 0;
else
return(size(node->left) + 1 + size(node->right));
}
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Size of the tree is %d", size(root));
getchar();
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
int size() { return size(root); }
int size(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else
return (size(node.left) + 1 + size(node.right));
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("The size of binary tree is : "
+ tree.size());
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def size(node):
if node is None:
return 0
else:
return (size(node.left)+ 1 + size(node.right))
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print("Size of the tree is %d" %(size(root)))
|
C#
using System;
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
public virtual int size()
{
return size(root);
}
public virtual int size(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return (size(node.left) + 1 + size(node.right));
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("The size of binary tree is : " + tree.size());
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(item) {
this.data = item;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
size(node = this.root) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return this.size(node.left) + 1 + this.size(node.right);
}
}
}
var tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
document.write("Size of the tree is " + tree.size() + "<br>");
</script>
|
Output:
Size of the tree is 5
Time Complexity: O(N)
As every node is visited once.
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
The extra space is due to the recursion call stack and the worst case occurs when the tree is either left skewed or right skewed.
Since this program is similar to traversal of tree, time and space complexities will be same as Tree traversal (Please see our Tree Traversal post for details)
Using Morris Traversal:
The basic idea of Morris traversal is to use the empty right child of a node to store a temporary link to the next node in the inorder traversal. By using this link, we can traverse the binary tree without using any extra space for a stack or recursion.
Follow the steps to solve the problem:
- Initialize a counter variable to 0 and a current pointer to the root of the binary tree.
- While the current pointer is not NULL:
a. If the current node has no left child, increment the counter and move the current pointer to its right child.
b. Otherwise, find the rightmost node in the left subtree of the current node.
i. If this node does not have a right child, set its right child to the current node and move the current pointer to its left child.
ii. Otherwise, the right child of this node already points to the current node, so we have visited all the nodes in the left subtree of the current node. Set the right child of this node to NULL, increment the counter, and move the current pointer to its right child.
- When the current pointer becomes NULL, we have visited all the nodes in the binary tree. Return the counter variable.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
int countNodes(Node* root) {
int count = 0;
Node* current = root;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->left == NULL) {
count++;
current = current->right;
}
else {
Node* predecessor = current->left;
while (predecessor->right != NULL && predecessor->right != current) {
predecessor = predecessor->right;
}
if (predecessor->right == NULL) {
predecessor->right = current;
current = current->left;
}
else {
predecessor->right = NULL;
count++;
current = current->right;
}
}
}
return count;
}
int main() {
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(10);
root->right = new Node(39);
root->left->left = new Node(5);
int nodeCount = countNodes(root);
cout << "The size of binary tree is: " << nodeCount << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int val;
Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
val = x;
left = right = null;
}
}
class MorrisTraversal {
public static int countNodes(Node root) {
int count = 0;
Node current = root;
while (current != null) {
if (current.left == null) {
count++;
current = current.right;
} else {
Node predecessor = current.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != current) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
if (predecessor.right == null) {
predecessor.right = current;
current = current.left;
} else {
predecessor.right = null;
count++;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(10);
root.right = new Node(39);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
int nodeCount = countNodes(root);
System.out.println("The size of binary tree is: " + nodeCount);
}
}
|
Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def countNodes(root):
count = 0
current = root
while current is not None:
if current.left is None:
count += 1
current = current.right
else:
predecessor = current.left
while predecessor.right is not None and predecessor.right != current:
predecessor = predecessor.right
if predecessor.right is None:
predecessor.right = current
current = current.left
else:
predecessor.right = None
count += 1
current = current.right
return count
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(10)
root.right = Node(39)
root.left.left = Node(5)
nodeCount = countNodes(root)
print("The size of binary tree is:", nodeCount)
|
C#
using System;
class Node
{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
class GFG
{
public static int CountNodes(Node root)
{
int count = 0;
Node current = root;
while (current != null)
{
if (current.left == null)
{
count++;
current = current.right;
}
else
{
Node predecessor = current.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != current)
{
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
if (predecessor.right == null)
{
predecessor.right = current;
current = current.left;
}
else
{
predecessor.right = null;
count++;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
return count;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(10);
root.right = new Node(39);
root.left.left = new Node(5);
int nodeCount = CountNodes(root);
Console.WriteLine("The size of the binary tree is: " + nodeCount);
}
}
|
Javascript
class TreeNode {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function countNodes(root) {
let count = 0;
let current = root;
while (current !== null) {
if (current.left === null) {
count++;
current = current.right;
} else {
let predecessor = current.left;
while (predecessor.right !== null && predecessor.right !== current) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
if (predecessor.right === null) {
predecessor.right = current;
current = current.left;
} else {
predecessor.right = null;
count++;
current = current.right;
}
}
}
return count;
}
const root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(10);
root.right = new TreeNode(39);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(5);
const nodeCount = countNodes(root);
console.log("The size of binary tree is: " + nodeCount);
|
Output
The size of binary tree is: 4
Time Complexity: O(N) , since traversing all the nodes in the tree only once.
Auxiliary Space: O(1) , No extra space is required.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...