Types of Cloud
Last Updated :
24 Jan, 2023
Cloud computing is Internet-based computing in which a shared pool of resources is available over broad network access, these resources can be provisioned or released with minimum management efforts and service-provider interaction.
Types of Cloud
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
- Community cloud
- Multicloud
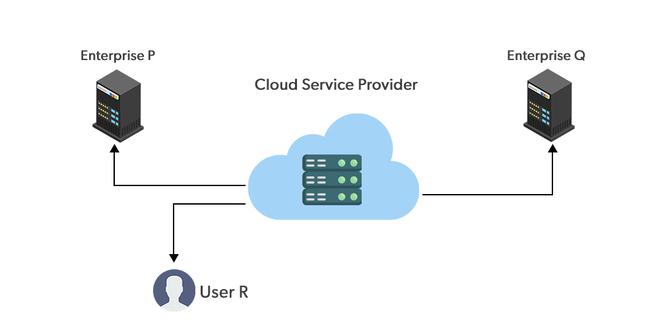
Public Cloud
Public clouds are managed by third parties which provide cloud services over the internet to the public, these services are available as pay-as-you-go billing models.
They offer solutions for minimizing IT infrastructure costs and become a good option for handling peak loads on the local infrastructure. Public clouds are the go-to option for small enterprises, which can start their businesses without large upfront investments by completely relying on public infrastructure for their IT needs.
The fundamental characteristics of public clouds are multitenancy. A public cloud is meant to serve multiple users, not a single customer. A user requires a virtual computing environment that is separated, and most likely isolated, from other users.
Public cloud
Advantages of using a Public cloud are:
- High Scalability
- Cost Reduction
- Reliability and flexibility
- Disaster Recovery
Disadvantages of using a Public cloud are:
- Loss of control over data
- Data security and privacy
- Limited Visibility
- Unpredictable cost
Private cloud
Private clouds are distributed systems that work on private infrastructure and provide the users with dynamic provisioning of computing resources. Instead of a pay-as-you-go model in private clouds, there could be other schemes that manage the usage of the cloud and proportionally billing of the different departments or sections of an enterprise. Private cloud providers are HP Data Centers, Ubuntu, Elastic-Private cloud, Microsoft, etc.

Private Cloud
The advantages of using a private cloud are as follows:
- Customer information protection: In the private cloud security concerns are less since customer data and other sensitive information do not flow out of private infrastructure.
- Infrastructure ensuring SLAs: Private cloud provides specific operations such as appropriate clustering, data replication, system monitoring, and maintenance, disaster recovery, and other uptime services.
- Compliance with standard procedures and operations: Specific procedures have to be put in place when deploying and executing applications according to third-party compliance standards. This is not possible in the case of the public cloud.
Disadvantages of using a private cloud are:
- The restricted area of operations: Private cloud is accessible within a particular area. So the area of accessibility is restricted.
- Expertise requires: In the private cloud security concerns are less since customer data and other sensitive information do not flow out of private infrastructure. Hence skilled people are required to manage & operate cloud services.
Hybrid cloud:
A hybrid cloud is a heterogeneous distributed system formed by combining facilities of the public cloud and private cloud. For this reason, they are also called heterogeneous clouds.
A major drawback of private deployments is the inability to scale on-demand and efficiently address peak loads. Here public clouds are needed. Hence, a hybrid cloud takes advantage of both public and private clouds.

Hybrid Cloud
Advantages of using a Hybrid cloud are:
1) Cost: Available at a cheap cost than other clouds because it is formed by a distributed system.
2) Speed: It is efficiently fast with lower cost, It reduces the latency of the data transfer process.
3) Security: Most important thing is security. A hybrid cloud is totally safe and secure because it works on the distributed system network.
Disadvantages of using a Hybrid cloud are:
- It’s possible that businesses lack the internal knowledge necessary to create such a hybrid environment. Managing security may also be more challenging. Different access levels and security considerations may apply in each environment.
- Managing a hybrid cloud may be more difficult. With all of the alternatives and choices available today, not to mention the new PaaS components and technologies that will be released every day going forward, public cloud and migration to public cloud are already complicated enough. It could just feel like a step too far to include hybrid.
Community cloud:
Community clouds are distributed systems created by integrating the services of different clouds to address the specific needs of an industry, a community, or a business sector. But sharing responsibilities among the organizations is difficult.
In the community cloud, the infrastructure is shared between organizations that have shared concerns or tasks. An organization or a third party may manage the cloud.

Community Cloud
Advantages of using Community cloud are:
- Because the entire cloud is shared by numerous enterprises or a community, community clouds are cost-effective.
- Because it works with every user, the community cloud is adaptable and scalable. Users can alter the documents according to their needs and requirements.
- Public cloud is less secure than the community cloud, which is more secure than private cloud.
- Thanks to community clouds, we may share cloud resources, infrastructure, and other capabilities between different enterprises.
Disadvantages of using Community cloud are:
- Not all businesses should choose community cloud.
- gradual adoption of data
- It’s challenging for corporations to share duties.
Sectors that use community clouds are:
1. Media industry: Media companies are looking for quick, simple, low-cost ways for increasing the efficiency of content generation. Most media productions involve an extended ecosystem of partners. In particular, the creation of digital content is the outcome of a collaborative process that includes the movement of large data, massive compute-intensive rendering tasks, and complex workflow executions.
2. Healthcare industry: In the healthcare industry community clouds are used to share information and knowledge on the global level with sensitive data in the private infrastructure.
3. Energy and core industry: In these sectors, the community cloud is used to cluster a set of solution which collectively addresses the management, deployment, and orchestration of services and operations.
4. Scientific research: In this organization with common interests in science share a large distributed infrastructure for scientific computing.
Multicloud
Multicloud is the use of multiple cloud computing services from different providers, which allows organizations to use the best-suited services for their specific needs and avoid vendor lock-in.
This allows organizations to take advantage of the different features and capabilities offered by different cloud providers.
Advantages of using multi-cloud:
- Flexibility: Using multiple cloud providers allows organizations to choose the best-suited services for their specific needs, and avoid vendor lock-in.
- Cost-effectiveness: Organizations can take advantage of the cost savings and pricing benefits offered by different cloud providers for different services.
- Improved performance: By distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers, organizations can improve the performance and availability of their applications and services.
- Increased security: Organizations can increase the security of their data and applications by spreading them across multiple cloud providers and implementing different security strategies for each.
Disadvantages of using multi-cloud:
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud providers and services can be complex and require specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Increased costs: The cost of managing multiple cloud providers and services can be higher than using a single provider.
- Compatibility issues: Different cloud providers may use different technologies and standards, which can cause compatibility issues and require additional resources to resolve.
- Limited interoperability: Different cloud providers may not be able to interoperate seamlessly, which can limit the ability to move data and applications between them.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...