The Blockchain is a decentralized database that means authority is not associated with one person, it will be shared among the people. Hence, changing and modifying the data is near to impossible in the blockchain database. That’s why it’s the most trustworthy. It came in the 1990s when the research was going on but was actually implemented in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto. The digital cryptocurrency Bitcoin is made by an anonymous developer (Satoshi Nakamoto) with the help of blockchain. Bitcoin has been a trending topic in the world ever since.

What is inside a Blockchain?
Blockchain is a chain of blocks or records. In each block it contains 3 things:
- Relevant Information (Eg. Bitcoin —> transaction information means source and destination)
- Hash (it is a unique code for each block)
- Previous Block Hash
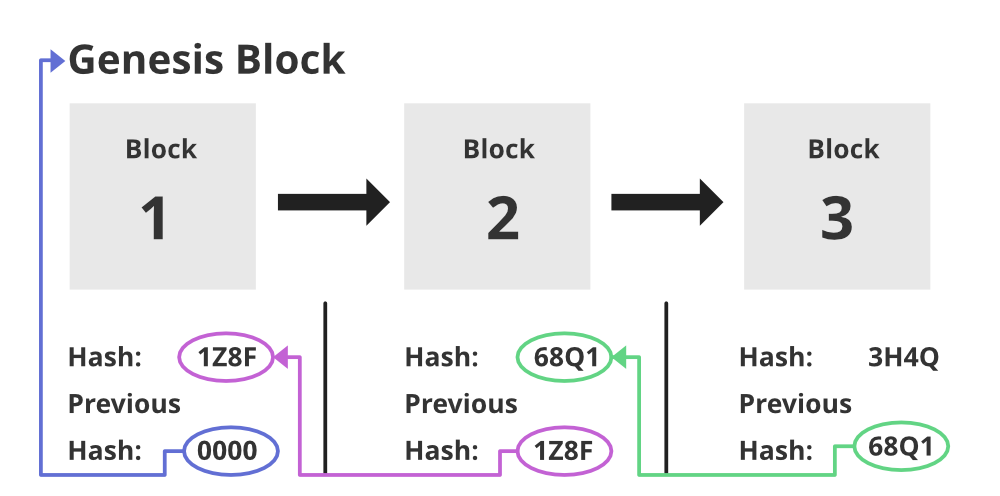
What will happen if anyone tries to change the data?
If anyone tries to change any block data, then the block hash will be changed. It is reflected in the next block as irrelevant data means an invalid hash will come. Similarly, it happens with all connected blocks in that chain. So that chain data will be invalid. If anyone thinks that it will change all the hashes in the chain, it will take too much time to change all the block’s hash. To change the hash of one block it will take 10 minutes (1 Block = 10 mins). For E.g. If we consider 1 crore blocks in the chain, it will take 200 years to change all the blocks’ hash. So, the conclusion is, changing the data is near to impossible on the blockchain.
The concept used to implement this time constraint is called Proof of Work. Anyone who makes changes to blockchain will have to prove that he has given x minutes of time. Here is one more added layer of security – everyone in the network has a copy of the blockchain. If you try to change the data into one copy, you can’t do that. The block you have modified has to be shared with everyone in the network. Then that block will get votes from everyone (meaning the change is valid or not). If the majority of people give the vote as invalid, then your change will be rejected, else change will be accepted. This type of voting system is called the Consensus Rule.
If you want to harm the blockchain, you have to spend a lot of time and get 50% of the votes on the network. So, hampering data is near too impossible on the blockchain.
How Blockchain is useful for Sustainable Development?
1. Healthcare
Healthcare will change in 3 ways by using the blockchain:
I. Health Records: Every modern healthcare system is built on the foundation of electronic medical records. With each visit to the doctor, however, patient medical records grow longer and more complex. And because each hospital and doctor’s office stores them differently, it’s not always straightforward for healthcare providers to acquire them. There are a few firms out there that are attempting to tackle this problem with the help of blockchain.
- Medicalchain
- IBM Digital Health Pass
- Patientory
- Medibloc, etc.
The goal is to give patients control over their whole medical history and to provide patients and physicians with one-stop access to it. Blockchain would not only make access easier and more efficient, but it would also bring data security to the field.
II. Supply Chains: The pharmaceutical business has some of the strictest product safety, security, and stability standards, and it’s ripe for disruption. Supply chain management, for example, maybe securely and openly tracked using blockchain. This can help to cut down on time delays and human errors. At any stage in the supply chain, it may be used to track expenses, labor, and even waste in emissions. It may be used to check the validity of items by following them back to their source, battling the counterfeit medication business, which loses $200 billion each year. Companies like Chronicled, Blockpharma, Modum, etc. are already working on making blockchain logistics more efficient. Modum complies with EU regulations that demand verification that pharmaceutical items have not been subjected to conditions, particularly extreme temperatures, that could compromise their quality. Modum’s answer was to create a sensor that records environmental variables while physical goods are in transit and stores them on the blockchain indefinitely.
III. Genomics Market:
Companies like Encrypgen, Nebula Genomics, etc. are working to build blockchain technologies that allow people to safely and securely share genetic data in a new developing industry. They believe that future potential in personal genome sequencing will generate a billion-dollar data business. And the blockchain is the ideal solution for resolving data security challenges and ensuring that data is delivered directly from the source to the end-user. These businesses want to leverage blockchain technology to improve genomic data security, make it easier for purchasers to obtain genomic data, and handle the issues of genomic large data. These are just a few of the dozens of firms attempting to disrupt healthcare with blockchain technology.
2. Government Records
Suppose, a working woman has just found out about her pregnancy and wants to take advantage of the government services that are needed and available for her. If these services/facilities are to be provided by three or four separate departments, then the same information will have to be given to each department separately for each woman. Because of that, she will spend a lot of time in the offices of that department. Well, there is no guarantee that all the work will be done in one visit. If she is going to spend most of her time doing this, it is also likely to drown out her daily routine and increase her physical and mental stress. Despite being eligible for the necessary medical support from financial aid, there is no doubt that many will be deprived of such a complicated, time-consuming process of getting such services/facilities.
But suppose, at such a time, on one visit to any one department, all the systems are working and the services/facilities are received at home and the financial help is deposited directly in the bank account? For this, the archives of various service providers should be linked in such a way that anyone’s information will create many ‘triggers’. This ‘trigger’ will automatically provide information to the officers of the various departments by providing information as per the need. How will these triggers work?
There are four main triggers for becoming more active in government services/facilities: (1) birth or age increase, (2) death, (3) marriage, and (4) migration. If these four main incidents are monitored digitally and their records are linked to the archives of each concerned department, then the government may be forced to come to the doorsteps of the citizens instead of going to court. For example, if there is a payment plan for his / her spouse after death, then the spouse will be registered for that pay plan at the very next moment after making the death certificate or hospital certificate, the salary will be credited directly to the account from the same month using the official bank account number of the concerned person.
This problem is solved perfectly with the help of the blockchain.
3. Agriculture
The annual global output of agriculture is close to 5 Trillion USD, which is approximately 7% of total production. Almost 40% of the global workforce is involved in agriculture-related activities. The consumer wants to know the provenance of the food they are consuming, including the various claims made on the label e.g. organic, allergen-free, etc. For suppliers and manufacturers, there is an onus to increase transparency as well as to identify and isolate contaminated and adulterated farm and food products in the chain. All this combined poses huge challenges for reliably tracking food origination. Consumers want more accountability and higher levels of transparency from corporations.
From food provenance to commodity tracking and trading, the projected role of blockchain in agricultural supply chains is significant. Linking agricultural shipping and monitoring processes adds value to agricultural products because it can be traced by the recipient to prove authenticity and therefore assign greater premium value. Manage warehouses, silos, and supply chains more intelligently, or utilize it in the field as a tool to transmit in real-time data about crops and livestock. IOT-linked technologies, such as sensors and machine learning, provide greater insight into the conditions that are inclusive to high yields, smooth operations, and risk mitigation. Incentivize environmentally friendly and sustainable practices to create a premium value for farm produce. Food waste can be minimized through sensor-based crop quality tracking. Facilitate payments more cost-effectively, including for agricultural subsidies and trade financing. Information & commodity prices and fluctuations and data about market demand and global trends will enable fairer pricing and risk mitigation. Companies/platforms that are working with these ideas – AgroTrust, Digital Green, Arthanium, etc.
4. Education System
The blockchain helps educational institutions keep digital records such as transcripts, badges, student records, identity, attendance and assignment completion tracking, infrastructure security and, efficient data storage. Also, the integration of blockchain in the teaching process can make the learning experience much better for the students.
5. Cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency. Many cryptocurrencies are decentralized networks based on blockchain technology, a distributed ledger enforced by a disparate network of computers. Blockchain is the technology that enables the existence of cryptocurrencies. A cryptocurrency is a medium of exchange for money. Some of these are – Ethereum (ETH), Tether (USDT), Binance Coin (BNB), Dogecoin (DOGE), etc.
What is the current status of various countries on Blockchain for Sustainable Development?
- Blockchain technology is widely accepted in Estonia.
- Estonia is followed by Dubai. To date, Dubai has conducted over 24 successful experiments in eight areas: education, finance, land or property, tourism, commerce, medical services, transportation, and security. Dubai aims to make all operations in the sector “100% paperless” by 2021 and to conduct all transactions through blockchain technology platforms.
- In the Australian state of Tasmania, a system called ‘Adapt (Administrative Data Exchange Protocol for Tasmania)’ has been in operation for several years. Its purpose is to securely pass information from one department to another.
- In the European Union, a project called ‘My-Data‘ is working in the same direction as Tasmania.
- Finland has a national information exchange system, the main function of which is to make all the services/facilities easily available to the citizens by using their information in a more efficient manner.
- In Taiwan, too, the ‘government calls the citizens to itself’ has been scrapped, leading to the idea of ‘the government itself will provide help or services/facilities to the citizens’.
- Mexico, USA, South Korea, and Spain! Former Mexican President Vincent Fox Keysada is currently implementing a number of projects at the national level to use “blockchain technology” to curb corruption in the country.
- The U.S. Air Force is using blockchain technology to verify the validity of the mechanical equipment they require.
- Denmark and Estonia are using blockchain technology to bring security and transparency to the voting process.
- The small country of Luxembourg has undertaken a grand initiative called ‘Infrachain’, in which government and private information will be made available from a ‘blockchain technology platform’.
- Ukraine has launched a campaign to bring its government machinery to the blockchain technology platform with the help of a company called BitFury.
- What is the situation in India in this regard? The Niti Commission announced a national project called Indiachain two years ago and the Reserve Bank of India has from time to time adopted a positive policy on blockchain technology (there is a separate policy for blockchain-based currencies). However, it will be easier to use blockchain technology at the state level in India than at the national level.
- Andhra Pradesh has tried out a limited number of blockchain-based projects in the land and transport sector. But it can be said that Tamil Nadu has taken the responsibility of inspiring other states. Recently, the ‘Tamil Nadu Blockchain Strategy – 2020′ was announced.
- Expansive technologies like blockchain need to be implemented at the state level, which requires a clear strategy. Otherwise, it will be very difficult for any project to go on the net. It is clear that this pragmatic policy presented by Tamil Nadu has taken care of these matters.
Undoubtedly, India is also taking the required steps towards blockchain – because blockchain is the future!!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...