ReactJS State
Last Updated :
14 Mar, 2024
The State is a way to store and manage the information or data while creating a React Application. The state is a JavaScript object that contains the real-time data or information on the webpage.
What is a React State?
The state in React is an instance of the React Component Class that can be defined as an object of a set of observable properties that control the behavior of the component.
In other words, the State of a component is an object that holds some information that may change over the lifetime of the component.
Creating State Object
Creating a state is essential to building dynamic and interactive components.
We can create a state object within the constructor of the class component.
JavaScript
import React from 'react';
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
brand: 'Ford', // Example property in the state
};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>My Car</h1>
{/* Other component content */}
</div>
);
}
}
export default MyComponent;
Conventions of Using State in React
- The state of a component should prevail throughout its lifetime, thus we must first have some initial state, to do so we should define the State in the constructor of the component’s class.
- The state should never be updated explicitly. React uses an observable object as the state that observes what changes are made to the state and helps the component behave accordingly.
- React provides its own method setState(). setState() method takes a single parameter and expects an object which should contain the set of values to be updated. Once the update is done the method implicitly calls the render() method to repaint the page. Hence, the correct method of updating the value of a state will be similar to the code below.
- State updates should be independent. The state object of a component may contain multiple attributes and React allows to use setState() function to update only a subset of those attributes as well as using multiple setState() methods to update each attribute value independently.
- The only time we are allowed to define the state explicitly is in the constructor to provide the initial state.
Updating State in React
In React, a State object can be updated using setState() method.
React may update multiple setState() updates in a single go. Thus using the value of the current state may not always generate the desired result.
For example, let us take a case where we must keep a count (Likes of a Post). Many developers may miswrite the code as below.
this.setState({counter: this.state.count + this.props.diff});Correct Method to Update State
In the below code, we are using the ES6 thick arrow function format to take the previous state and props of the component as parameters and are updating the counter. The same can be written using the default functional way as follows.
this.setState((prevState, props) => ({
counter: prevState.count + props.diff
}));Now let us see an example where we will implement state in React and use the state to create a counter
Example
This example demonstrates the use of React JS state creating a simple counter application.
JavaScript
// Filename - index.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0,
};
}
increment = () => {
this.setState((prevState) => ({
count: prevState.count + 1,
}));
};
decrement = () => {
this.setState((prevState) => ({
count: prevState.count - 1,
}));
};
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>
The current count is :{" "}
{this.state.count}
</h1>
<button onClick={this.increment}>
Increase
</button>
<button onClick={this.decrement}>
Decrease
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(
document.getElementById("root")
);
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
Output:
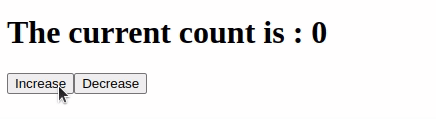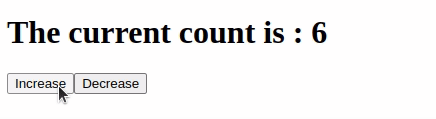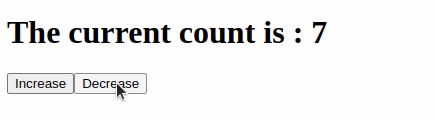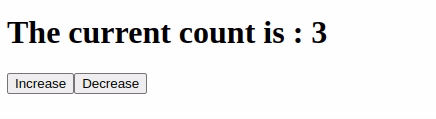
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...