Python Falcon – Websocket
Last Updated :
19 Mar, 2024
Websockets provide a powerful mechanism for establishing bidirectional communication between a client and a server over a single, long-lived connection. Python Falcon, a lightweight and fast web framework, offers support for implementing websockets, enabling real-time communication between clients and servers.
What is a Websocket?
WebSocket is a protocol that provides full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection. It’s commonly used for real-time web applications such as chat applications, online gaming, and live updates. Falcon is a high-performance Python web framework for building RESTful APIs. While Falcon itself doesn’t have built-in WebSocket support, you can integrate WebSocket functionality into a Falcon application using libraries such as websocket-server or websockets.
Python Falcon – Websocket
Below is the step-by-step procedure to understand about websocket in Python Falcon:
Step 1: Installation
Here, we will install the following libraries and modules before starting:
- Install Python Falcon
- Install Python
Step 2: Setting Up the Environment
Before diving into the implementation, make sure you have the necessary dependencies installed. You’ll need falcon, falcon-asgi, jinja2, and uvicorn. You can install them via pip:
pip install falcon falcon-asgi jinja2 uvicorn
Step 3: Implementing WebSocket Chat in Falcon
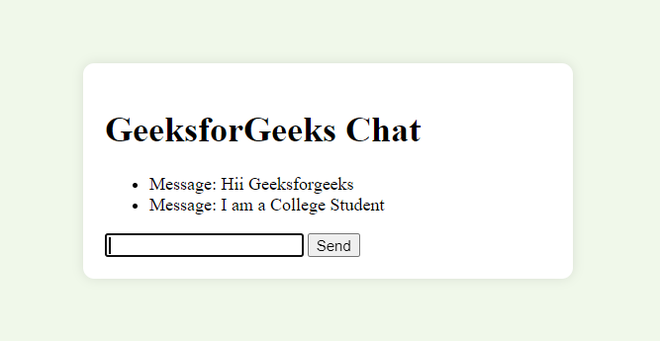
In this example, we define an HTML template for the chat interface with the title “GeeksforGeeks Chat” and a light green background color. The chat container is centered on the page using flexbox CSS. We implement a Falcon resource called ChatResource. The on_get method serves the HTML template, while the on_websocket method handles WebSocket connections. The WebSocket handler accepts incoming connections and echoes any received messages back to the client.
Python3
import uvicorn
import falcon
import falcon.asgi
import jinja2
html = """
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>GeeksforGeeks Chat</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: #f0f8ea;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
margin: 0;
}
#chat-container {
width: 400px;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #ffffff;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="chat-container">
<h1>GeeksforGeeks Chat</h1>
<ul id='messages'></ul>
<form action="" onsubmit="sendMessage(event)">
<input type="text" id="messageText" autocomplete="off"/>
<button>Send</button>
</form>
</div>
<script>
var ws = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8000/chat");
ws.onmessage = function(event) {
var messages = document.getElementById('messages');
var message = document.createElement('li');
var content = document.createTextNode(event.data);
message.appendChild(content);
messages.appendChild(message);
};
function sendMessage(event) {
var input = document.getElementById("messageText");
ws.send(input.value);
input.value = '';
event.preventDefault();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
"""
class ChatResource:
async def on_get(self, req, resp):
"""Handles GET requests"""
resp.status = falcon.HTTP_200
resp.content_type = 'text/html'
template = jinja2.Template(html)
resp.body = template.render()
async def on_websocket(self, req, websocket):
await websocket.accept()
while True:
data = await websocket.receive_text()
await websocket.send_text(f"Message: {data}")
app = falcon.asgi.App()
chat = ChatResource()
app.add_route('/chat', chat)
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("app:app", host="0.0.0.0", port=8000, reload=True)
Step 4: Running the Application
To run the Falcon application with WebSocket chat support, execute the script:
python app.py
This will start the Falcon application using the Uvicorn server, which supports ASGI and WebSocket protocols. You can then access the WebSocket chat interface by navigating to http://localhost:8000/chat in your web browser.
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...