How to Use the Tracert (Traceroute) Command in Windows?
Last Updated :
19 Oct, 2023
When your internet isn’t working right, knowing how your data travels can be useful. Tracert, also called traceroute, is a helpful tool on your computer. In this article, we’ll show you How to Use the Tracert (Traceroute) Command in Windows in simple steps, without any confusing terms. Let’s get started.
-Command-in-Windows.webp)
Understanding the Basics of Tracert
In the big world of the internet, data packets travel through a series of routers before reaching their destination. Tracert traceroute is a command that allows you to trace this path, providing valuable insights into your network connection.
What is Tracert?
Tracert, short for traceroute, is like a digital detective. It traces the route taken by your data, revealing each hop (router) it encounters and the time it takes to reach it. This information is crucial for diagnosing network issues.
Executing Tracert: Step-by-Step Guide
1. Open the Command Prompt
Simply type ‘cmd’ in the search bar and hit Enter. The Command Prompt window will open.
2. Execute the Tracert Command
To trace the route to a specific website, type ‘tracert’ followed by the domain or IP address i.e. tracert [hostname or IP address]
For instance, ‘tracert www.geeksforgeeks.org‘. Hit Enter, and Tracert will start its journey, displaying a list of hops and the time taken for your data to reach each one.
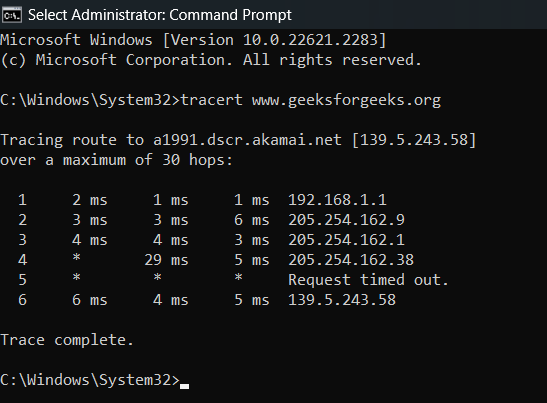
Basic Tracert Command
What Do the Results Mean?
After running the Tracert command, you’ll be presented with a list of hops, each showing the time taken for your data to travel.
- IP Addresses: The series of numbers represents the routers your data passes through.
- Response Times: The time displayed (in milliseconds) indicates how long it took for your data to reach each router. Higher times might indicate network congestion or other issues.
Different Commands & Options for Tracert Traceroute in Windows:
|
`tracert`
|
tracert [hostname or IP address]
|
Displays the list of hops (routers) and the time taken for data packets to reach each hop.
|
|
`-h [max_hops]`
|
tracert -h [max_hops] [hostname/IP]
|
Limits the number of hops in the route to the specified value.
|
|
`-w [timeout]`
|
tracert -w [timeout] [hostname/IP]
|
Adjusts the time Tracert waits for a response from each router.
|
|
`-d`
|
tracert -d [hostname/IP]
|
Displays only the IP addresses of routers, not their hostnames.
|
|
`-t`
|
tracert -t [hostname/IP]
|
Displays the time when data packets reach each router.
|
|
`-6`
|
tracert -6 [hostname/IPv6 address]
|
Traces the route using IPv6, the latest version of the Internet Protocol.
|
|
`/?`
|
tracert /?
|
It provides a list of available options, commands, and their descriptions.
|
These options provide users with flexibility in customizing Tracert’s behavior for effective network troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting with Tracert Traceroute
Tracert Traceroute isn’t just about tracking data; it’s a strong tool for identifying and fixing network problems.
- Finding Slow Connections: If a certain step takes a long time in Tracert, it’s like finding a traffic jam on the internet highway. This helps you know where the problem might be and fix it.
- Spotting Network Breaks: When a step doesn’t respond at all, it’s like finding a roadblock. Tracert traceroute shows you exactly where the internet connection is broken, so you can figure out what’s wrong.
Using Tracert traceroute in these ways makes fixing internet issues much easier!
Conclusion
Understanding computer networks might seem difficult, but tools like Tracert make it easier to fix problems and have a smooth time online.
In this guide, we’ve explained Tracert, making it easier to understand network issues. Now, you can fix problems with confidence. Enjoy using Tracert!
Also Read
FAQs on How to Use the Tracert (Traceroute) Command in Windows
1. Can Tracert Traceroute be used for both websites and IP addresses?
Absolutely! Whether you’re troubleshooting a website or an IP address, Tracert can trace the path your data takes, providing valuable insights into network performance.
2. What Should I Do if a Hop Doesn’t Respond?
If a hop doesn’t respond, it could indicate a network issue or a misconfiguration. Contact your internet service provider (ISP) and share the Tracert traceroute results. They can help you diagnose and resolve the problem.
3. Why Do Some Hops Have Longer Response Times?
Longer response times at specific hops might indicate network congestion or slower connections at those points. These insights can help you pinpoint and address the issue effectively.
4. Can Tracert Command Identify Wi-Fi Problems?
While Tracert can’t specifically diagnose Wi-Fi issues, it can identify network problems affecting your overall internet connection. If you suspect Wi-Fi problems, consider checking your router, signal strength, or contacting your ISP.
5. Is Tracert Command Safe to Use?
Absolutely! Tracert is a non-intrusive diagnostic tool commonly used by IT professionals and enthusiasts. It only traces the route data packets take and doesn’t interfere with your network’s operation.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...