How to Create a 3D Cube in React ?
Last Updated :
18 Mar, 2024
Creating a 3D cube in a web application can add a visually appealing element to the user interface. A 3D cube is a six-sided geometric shape that can be rotated and manipulated in 3D space.
In this article, we will be creating a 3D cube using the Three.js library
What is the Three.js library?
Three.js is a popular JavaScript library used for creating and displaying 3D graphics in a web browser. It provides a wide range of features for building 3D animations, games, visualizations, and interactive experiences.
Approach to Create a 3D Cube in React:
- Set up a Three.js scene, camera, and renderer using useRef to reference the DOM element.
- Defined materials for each face of the cube and created a cube mesh with BoxGeometry.
- Positioned the camera to view the scene.
- Implemented continuous cube rotation based on mouse movement using requestAnimationFrame.
- Tracked mouse movement and normalized coordinates for cube rotation.
- Added a mouse move event listener for tracking and cleaned up on unmount by removing the event listener and renderer’s DOM element.
Steps to Create a 3D Cube in React:
Step 1: Create a React Project.
npx create-react-app cube
Step 2: Navigate to the project directory.
cd cube
Step 3: Installing required modules
npm install three
The updated dependencies in package.json file will look like:
"dependencies": {
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.17.0",
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"three": "^0.162.0",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
}Example of 3D Cube in React
Example: Below code snippet provides the implementation of 3D cube
Javascript
// App.js
import React, {
useEffect,
useRef
} from 'react';
import * as THREE from 'three';
const ThreeDCube = () => {
const ref = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
let mouseX = 0;
let mouseY = 0;
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
ref.current.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
const materials = [
// Front face (red)
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff0000 }),
// Back face (green)
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }),
// Top face (blue)
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff }),
// Bottom face (yellow)
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffff00 }),
// Right face (magenta)
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff00ff }),
// Left face (cyan)
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ffff })
];
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.BoxGeometry(), materials);
scene.add(cube);
camera.position.z = 5;
const animate = () => {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
cube.rotation.x += (mouseY - cube.rotation.x) * 0.05;
cube.rotation.y += (mouseX - cube.rotation.y) * 0.05;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
};
const onMouseMove = (event) => {
mouseX = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1;
mouseY = -(event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1;
};
animate();
window.addEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
ref.current.removeChild(renderer.domElement);
};
}, []);
return <div ref={ref}></div>;
};
export default ThreeDCube;
Output:
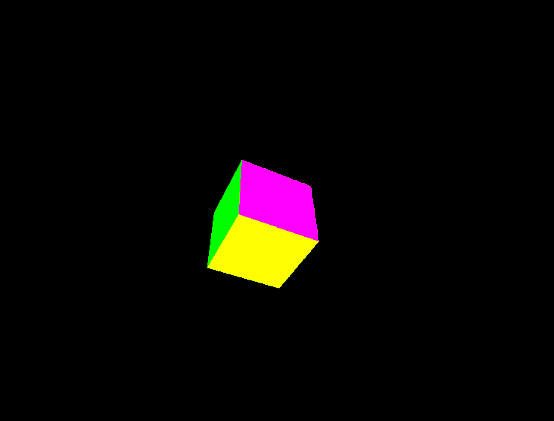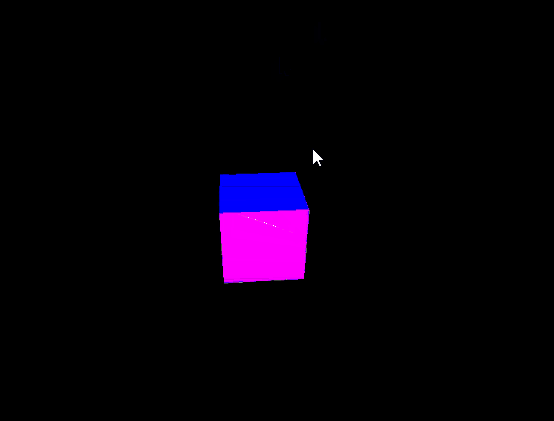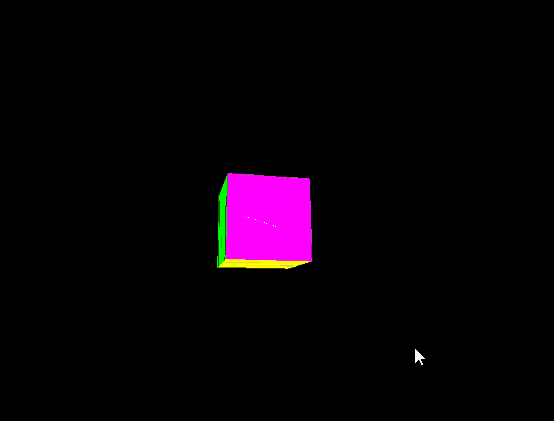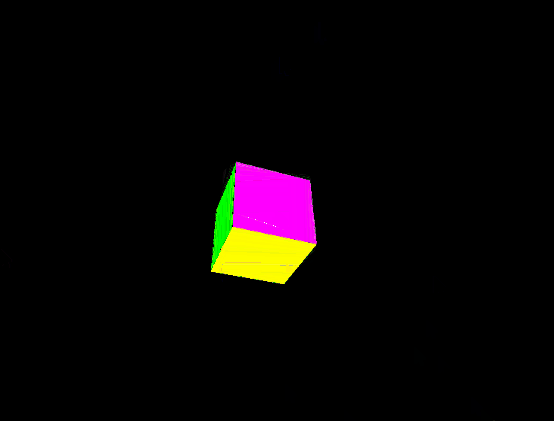
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...