An Operating System acts as a communication bridge (interface) between the user and computer hardware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide a platform on which a user can execute programs conveniently and efficiently.
An operating system is a piece of software that manages the allocation of Computer Hardware. The coordination of the hardware must be appropriate to ensure the correct working of the computer system and to prevent user programs from interfering with the proper working of the system.
The main goal of the Operating System is to make the computer environment more convenient to use and the Secondary goal is to use the resources most efficiently.
What is an Operating System?
An operating system is a program that manages a computer’s hardware. It also provides a basis for application programs and acts as an intermediary between the computer user and computer hardware. The main task an operating system carries out is the allocation of resources and services, such as the allocation of memory, devices, processors, and information. The operating system also includes programs to manage these resources, such as a traffic controller, a scheduler, a memory management module, I/O programs, and a file system. The operating system simply provides an environment within which other programs can do useful work.
Why are Operating Systems Used?
Operating System is used as a communication channel between the Computer hardware and the user. It works as an intermediate between System Hardware and End-User. Operating System handles the following responsibilities:
- It controls all the computer resources.
- It provides valuable services to user programs.
- It coordinates the execution of user programs.
- It provides resources for user programs.
- It provides an interface (virtual machine) to the user.
- It hides the complexity of software.
- It supports multiple execution modes.
- It monitors the execution of user programs to prevent errors.
Functions of an Operating System
Memory Management
The operating system manages the Primary Memory or Main Memory. Main memory is made up of a large array of bytes or words where each byte or word is assigned a certain address. Main memory is fast storage and it can be accessed directly by the CPU. For a program to be executed, it should be first loaded in the main memory. An operating system manages the allocation and deallocation of memory to various processes and ensures that the other process does not consume the memory allocated to one process. An Operating System performs the following activities for Memory Management:
- It keeps track of primary memory, i.e., which bytes of memory are used by which user program. The memory addresses that have already been allocated and the memory addresses of the memory that has not yet been used.
- In multiprogramming, the OS decides the order in which processes are granted memory access, and for how long.
- It Allocates the memory to a process when the process requests it and deallocates the memory when the process has terminated or is performing an I/O operation.

Memory Management
Processor Management
In a multi-programming environment, the OS decides the order in which processes have access to the processor, and how much processing time each process has. This function of OS is called Process Scheduling. An Operating System performs the following activities for Processor Management.
An operating system manages the processor’s work by allocating various jobs to it and ensuring that each process receives enough time from the processor to function properly.
Keeps track of the status of processes. The program which performs this task is known as a traffic controller. Allocates the CPU that is a processor to a process. De-allocates processor when a process is no longer required.
.webp)
Processor Management
Device Management
An OS manages device communication via its respective drivers. It performs the following activities for device management.
- Keeps track of all devices connected to the system. Designates a program responsible for every device known as the Input/Output controller.
- Decide which process gets access to a certain device and for how long.
- Allocates devices effectively and efficiently. Deallocates devices when they are no longer required.
- There are various input and output devices. An OS controls the working of these input-output devices.
- It receives the requests from these devices, performs a specific task, and communicates back to the requesting process.
File Management
A file system is organized into directories for efficient or easy navigation and usage. These directories may contain other directories and other files. An Operating System carries out the following file management activities. It keeps track of where information is stored, user access settings, the status of every file, and more. These facilities are collectively known as the file system. An OS keeps track of information regarding the creation, deletion, transfer, copy, and storage of files in an organized way. It also maintains the integrity of the data stored in these files, including the file directory structure, by protecting against unauthorized access.

File Management
User Interface or Command Interpreter
The user interacts with the computer system through the operating system. Hence OS acts as an interface between the user and the computer hardware. This user interface is offered through a set of commands or a graphical user interface (GUI). Through this interface, the user makes interacts with the applications and the machine hardware.

Command Interpreter
Booting the Computer
The process of starting or restarting the computer is known as booting. If the computer is switched off completely and if turned on then it is called cold booting. Warm booting is a process of using the operating system to restart the computer.
Security
The operating system uses password protection to protect user data and similar other techniques. it also prevents unauthorized access to programs and user data. The operating system provides various techniques which assure the integrity and confidentiality of user data. The following security measures are used to protect user data:
- Protection against unauthorized access through login.
- Protection against intrusion by keeping the firewall active.
- Protecting the system memory against malicious access.
- Displaying messages related to system vulnerabilities.
Control Over System Performance
Operating systems play a pivotal role in controlling and optimizing system performance. They act as intermediaries between hardware and software, ensuring that computing resources are efficiently utilized. One fundamental aspect is resource allocation, where the OS allocates CPU time, memory, and I/O devices to different processes, striving to provide fair and optimal resource utilization. Process scheduling, a critical function, helps decide which processes or threads should run when preventing any single task from monopolizing the CPU and enabling effective multitasking.
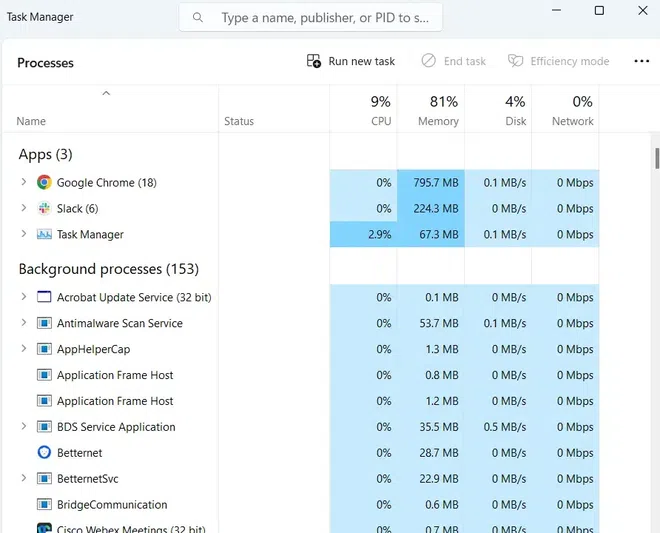
Control Over System Performance
Job Accounting
The operating system Keeps track of time and resources used by various tasks and users, this information can be used to track resource usage for a particular user or group of users. In a multitasking OS where multiple programs run simultaneously, the OS determines which applications should run in which order and how time should be allocated to each application.
Error-Detecting Aids
The operating system constantly monitors the system to detect errors and avoid malfunctioning computer systems. From time to time, the operating system checks the system for any external threat or malicious software activity. It also checks the hardware for any type of damage. This process displays several alerts to the user so that the appropriate action can be taken against any damage caused to the system.
Coordination Between Other Software and Users
Operating systems also coordinate and assign interpreters, compilers, assemblers, and other software to the various users of the computer systems. In simpler terms, think of the operating system as the traffic cop of your computer. It directs and manages how different software programs can share your computer’s resources without causing chaos. It ensures that when you want to use a program, it runs smoothly without crashing or causing problems for others. So, it’s like the friendly officer ensuring a smooth flow of traffic on a busy road, making sure everyone gets where they need to go without any accidents or jams.
Performs Basic Computer Tasks
The management of various peripheral devices such as the mouse, keyboard, and printer is carried out by the operating system. Today most operating systems are plug-and-play. These operating systems automatically recognize and configure the devices with no user interference.
Network Management
- Network Communication: Think of them as traffic cops for your internet traffic. Operating systems help computers talk to each other and the internet. They manage how data is packaged and sent over the network, making sure it arrives safely and in the right order.
- Settings and Monitoring: Think of them as the settings and security guard for your internet connection. They also let you set up your network connections, like Wi-Fi or Ethernet, and keep an eye on how your network is doing. They make sure your computer is using the network efficiently and securely, like adjusting the speed of your internet or protecting your computer from online threats.
Services Provided by an Operating System
The Operating System provides certain services to the users which can be listed in the following manner:
- User Interface: Almost all operating systems have a user interface (UI). This interface can take several forms. One is a command-line interface(CLI), which uses text commands and a method for entering them (say, a keyboard for typing in commands in a specific format with specific options). Another is a batch interface, in which commands and directives to control those commands are entered into files, and those files are executed. Most commonly, a graphical user interface (GUI) is used. the interface is a window system with a pointing device to direct I/O, choose from menus, and make selections and a keyboard to enter text.
- Program Execution: The Operating System is responsible for the execution of all types of programs whether it be user programs or system programs. The Operating System utilizes various resources available for the efficient running of all types of functionalities.
- Handling Input/Output Operations: The Operating System is responsible for handling all sorts of inputs, i.e., from the keyboard, mouse, desktop, etc. The Operating System does all interfacing most appropriately regarding all kinds of Inputs and Outputs.
For example, there is a difference between all types of peripheral devices such as mice or keyboards, the Operating System is responsible for handling data between them.
- Manipulation of File System: The Operating System is responsible for making decisions regarding the storage of all types of data or files, i.e., floppy disk/hard disk/pen drive, etc. The Operating System decides how the data should be manipulated and stored.
- Resource Allocation: The Operating System ensures the proper use of all the resources available by deciding which resource to be used by whom for how much time. All the decisions are taken by the Operating System.
- Accounting: The Operating System tracks an account of all the functionalities taking place in the computer system at a time. All the details such as the types of errors that occurred are recorded by the Operating System.
- Information and Resource Protection: The Operating System is responsible for using all the information and resources available on the machine in the most protected way. The Operating System must foil an attempt from any external resource to hamper any sort of data or information.
- Communication: The operating system implements communication between one process to another process to exchange information. Such communication may occur between processes that are executing on the same computer or between processes that are executing on different computer systems tied together by a computer network.
- System Services: The operating system provides various system services, such as printing, time and date management, and event logging.
- Error Detection: The operating system needs to be detecting and correcting errors constantly. Errors may occur in the CPU and memory hardware ( for eg. a memory error or a power failure), in I/O devices (such as a parity error on disk, a connection failure on a network, or a lack of paper in the printer), and in the user program ( an arithmetic overflow, an attempt to access an illegal memory location or a too-great use of CPU time). For each type of error, the operating system should take the appropriate action to ensure correct and consistent computing.
All these services are ensured by the Operating System for the convenience of the users to make the programming task easier. All different kinds of Operating Systems more or less provide the same services.
Characteristics of Operating System
- Virtualization: Operating systems can provide Virtualization capabilities, allowing multiple operating systems or instances of an operating system to run on a single physical machine. This can improve resource utilization and provide isolation between different operating systems or applications.
- Networking: Operating systems provide networking capabilities, allowing the computer system to connect to other systems and devices over a network. This can include features such as network protocols, network interfaces, and network security.
- Scheduling: Operating systems provide scheduling algorithms that determine the order in which tasks are executed on the system. These algorithms prioritize tasks based on their resource requirements and other factors to optimize system performance.
- Interprocess Communication: Operating systems provide mechanisms for applications to communicate with each other, allowing them to share data and coordinate their activities.
- Performance Monitoring: Operating systems provide tools for monitoring system performance, including CPU usage, memory usage, disk usage, and network activity. This can help identify performance bottlenecks and optimize system performance.
- Backup and Recovery: Operating systems provide backup and recovery mechanisms to protect data in the event of system failure or data loss.
- Debugging: Operating systems provide debugging tools that allow developers to identify and fix software bugs and other issues in the system.

Share of characteristics of an OS
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...