An index is a disk-based structure linked to a table or view that facilitates quicker row retrieval. A table or view’s table or view’s columns are used to create keys in an index. These keys are kept in a structure (B-tree) that enables SQL Server to quickly and effectively locate the row or rows that correspond to the key values.
Clustered Index
A clustered index is created only when both the following conditions are satisfied:
- The data or file, that you are moving into secondary memory should be in sequential or sorted order.
- There should be a key value, meaning it can not have repeated values.
Whenever you apply clustered indexing in a table, it will perform sorting in that table only. You can create only one clustered index in a table like a primary key. A clustered index is as same as a dictionary where the data is arranged in alphabetical order.
In a clustered index, the index contains a pointer to block but not direct data.
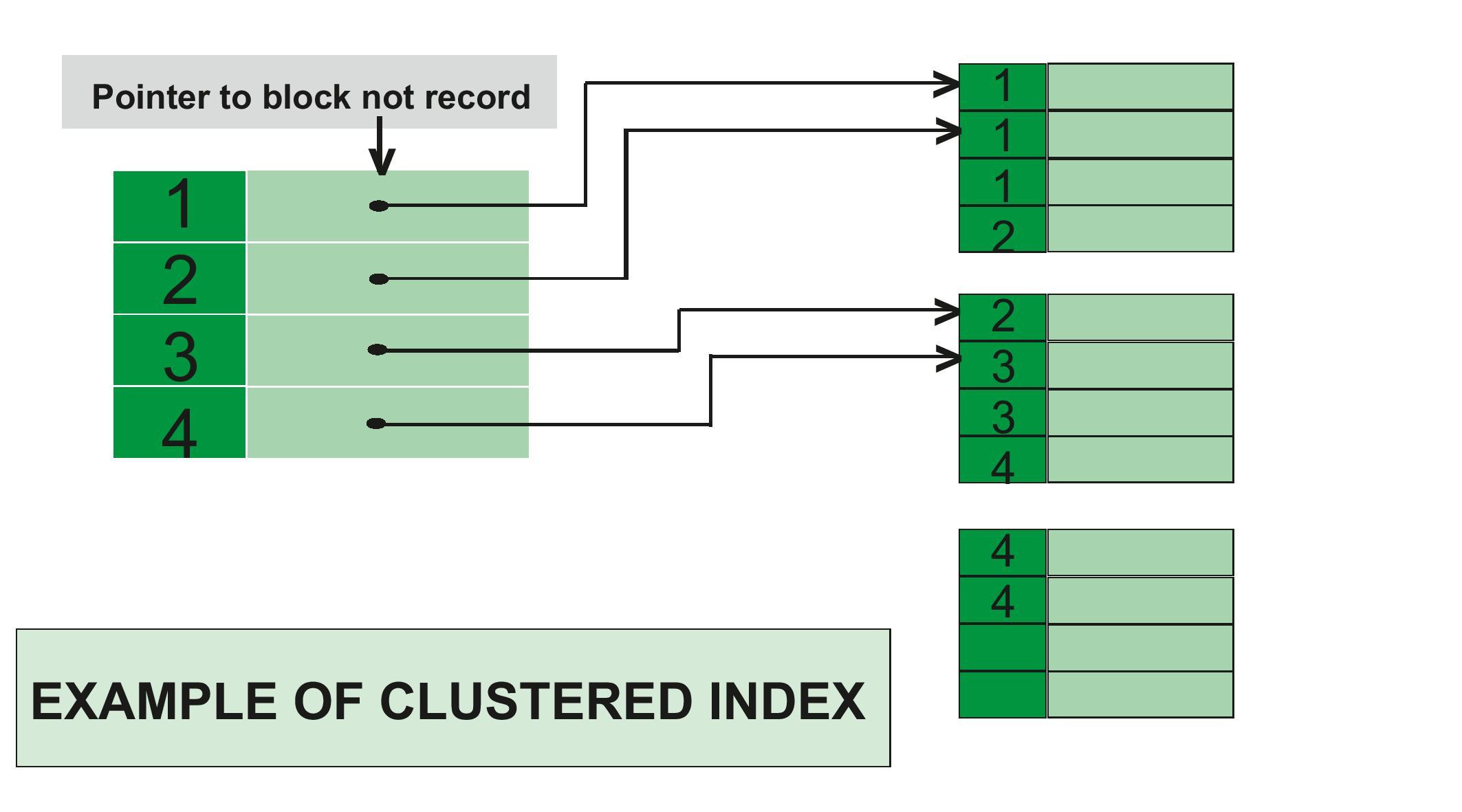
Example of Clustered Index
Example of Clustered Index
If you apply the primary key to any column, then automatically it will become a clustered index.
Create Table
Create table Student
( Roll_No int primary key,
Name varchar(50),
Gender varchar(30),
Mob_No bigint );
insert into Student
values (4, 'ankita', 'female', 9876543210 );
insert into Student
values (3, 'anita', 'female', 9675432890 );
insert into Student
values (5, 'mahima', 'female', 8976453201 );
In this example, Roll no is a primary key, it will automatically act as a clustered index. The output of this code will produce in increasing order of roll no.
Output
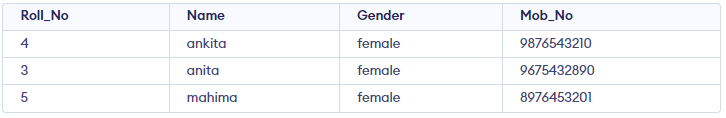
Student table
You can have only one clustered index in one table, but you can have one clustered index on multiple columns, and that type of index is called a composite index.
Non-Clustered Index
The non-Clustered Index is similar to the index of a book. The index of a book consists of a chapter name and page number, if you want to read any topic or chapter then you can directly go to that page by using the index of that book. No need to go through each and every page of a book.
The data is stored in one place, and the index is stored in another place. Since the data and non-clustered index is stored separately, then you can have multiple non-clustered indexes in a table.
In a non-clustered index, the index contains the pointer to data.
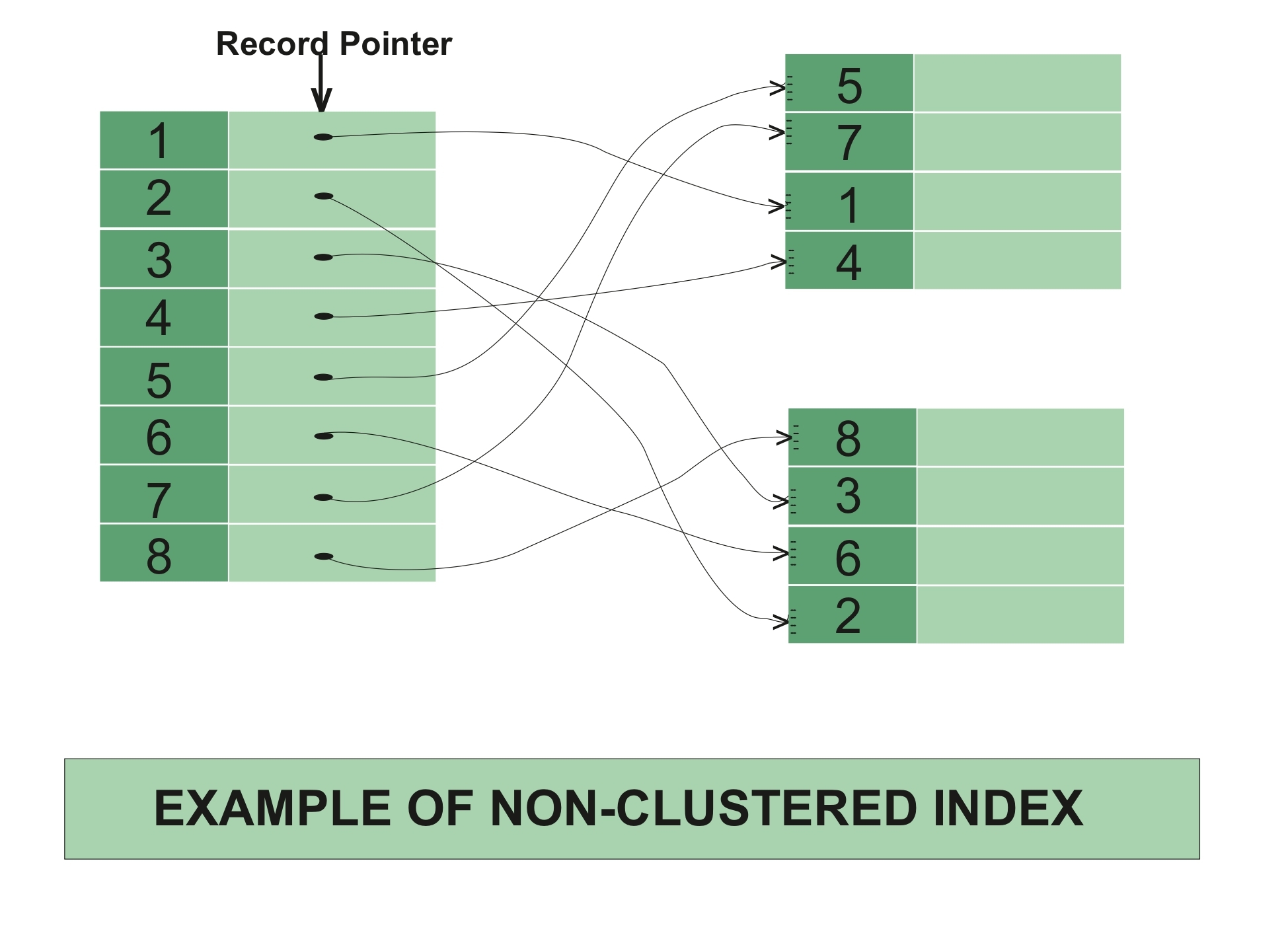
Example of Non Clustered Index
Example of Non-Clustered Index
The given code creates a table “Student” with columns “Roll_No”, “Name”, “Gender”, and “Mob_No”. The primary key is defined on the “Roll_No” column. Three rows are inserted into the “Student” table with different values for the columns. Finally, a nonclustered index “NIX_FTE_Name” is created on the “Name” column in ascending order.
The “CREATE TABLE” statement is used to create a new table “Student” with four columns “Roll_No”, “Name”, “Gender”, and “Mob_No”. The “Roll_No” column is defined as the primary key of the table.
The “INSERT INTO” statements are used to insert three rows of data into the “Student” table. Each row contains values for all the columns of the table. The first row has a roll number of 4, the name of “Afzal”, the gender of “male”, and a mobile number of 9876543210. The second row has a roll number of 3, the name of “Sudhir”, the gender of “male”, and a mobile number of 9675432890. The third row has a roll number of 5, name of “zoya”, the gender of “female”, and a mobile number of 8976453201.
Query:
Create table Student
( Roll_No int primary key,
Name varchar(50),
Gender varchar(30),
Mob_No bigint );
insert into Student
values (4, 'afzal', 'male', 9876543210 );
insert into Student
values (3, 'sudhir', 'male', 9675432890 );
insert into Student
values (5, 'zoya', 'female', 8976453201 );
create nonclustered index NIX_FTE_Name
on Student (Name ASC);
Here, roll no is a primary key, hence there is automatically a clustered index. If we want to apply a non-clustered index in the NAME column (in ascending order), then a new table will be created for that column.
Output:

Student table
The row address is used because, if someone wants to search the data for Sudhir, then by using the row address he/she will directly go to that row address and can fetch the data directly.
Difference Between Clustered and Non-Clustered Index
| A clustered index is faster. |
A non-clustered index is slower. |
| The clustered index requires less memory for operations. |
A non-Clustered index requires more memory for operations. |
| In a clustered index, the clustered index is the main data. |
In the Non-Clustered index, the index is the copy of data. |
| A table can have only one clustered index. |
A table can have multiple non-clustered indexes. |
| The clustered index has the inherent ability to store data on the disk. |
A non-Clustered index does not have the inherent ability to store data on the disk. |
| Clustered index store pointers to block not data. |
The non-clustered index stores both the value and a pointer to the actual row that holds the data |
| In Clustered index leaf nodes are actual data itself. |
In Non-Clustered index leaf nodes are not the actual data itself rather they only contain included columns. |
| In a Clustered index, Clustered key defines the order of data within a table. |
In a Non-Clustered index, the index key defines the order of data within the index. |
| A Clustered index is a type of index in which table records are physically reordered to match the index. |
A Non-Clustered index is a special type of index in which the logical order of the index does not match the physical stored order of the rows on the disk. |
| The size of The primary clustered index is large. |
The size of the non-clustered index is compared relativelyThe composite is smaller. |
| Primary Keys of the table by default are clustered indexes. |
The composite key when used with unique constraints of the table act as the non-clustered index. |
Conclusion
In Conclusion, the decision between clustered and non-clustered indexes primarily depends on the particular requirements of your database.
Index Clustering
- Perfect for tables where range queries, in particular, place a high value on data retrieval efficiency.
- Ideal for tables with few updates or relatively static data because moving data around can slow down insert and update operations.
Non-Clustered index
- allows for the optimization of various query types without changing the data’s physical order on disk.
- Ideal for tables where data changes often since inserts and updates are typically quicker than with clustered indexes.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...