Class 12 NCERT Solutions – Mathematics Part I – Chapter 4 Determinants – Exercise 4.6 | Set 2
Last Updated :
03 Apr, 2024
Note: This exercise has been renumbered as
Exercise 4.5 in the updated NCERT syllabus.
x – 2y – z = 3/2
3y – 5z = 9
Solution:
Matrix form of the given equation is AX = B
i.e.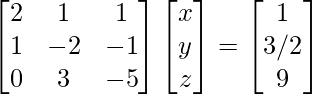
∴ |A| =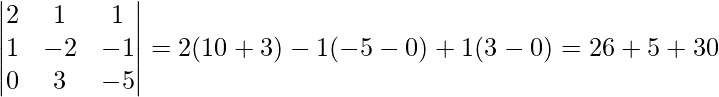
∴ Solution is unique.
Now, X = A-1B =  (adj.A)B
(adj.A)B

Therefore, x=1, y=1/2, z=3/2
Question 12. x – y + z = 4
2x + y – 3z = 0
x + y + z = 2
Solution:
Matrix form of the given equation is AX = B
i.e
∴ |A| =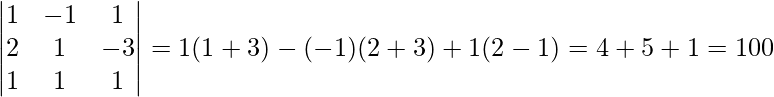
∴ Solution is unique.
Now, X = A-1B =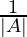 (adj.A)B
(adj.A)B
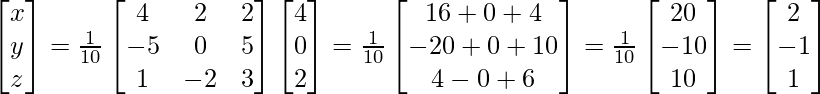
Therefore, x = 2, y = -1, z = 1
Question 13. 2x + 3y +3 z = 5
x – 2y + z = – 4
3x – y – 2z = 3
Solution:
Matrix form of given equation is AX = B
i.e.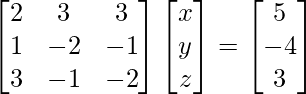
∴ |A| =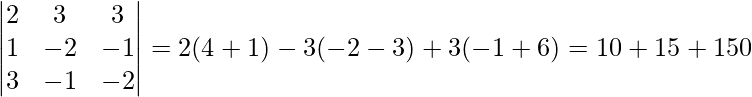
∴ Solution is unique.
Now, X = A-1B = 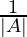 (adj.A)B
(adj.A)B

Therefore, x = 1, y = 2, z = -1
Question 14. x – y + 2z = 7
3x + 4y – 5z = – 5
2x – y + 3z = 12
Solution:
Matrix form of given equation is AX = B
i.e.
∴ |A| =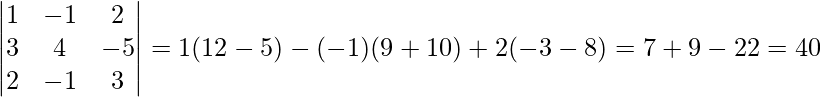
∴ Solution is unique.
Now, X = A-1B =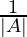 (adj.A)B
(adj.A)B
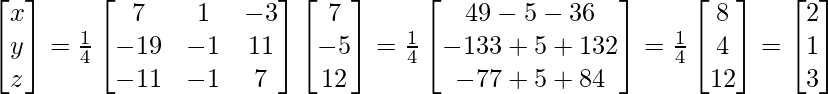
Therefore, x = 2, y = 1, z = 3
Question 15. If A=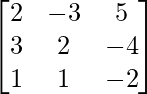 , find A–1. Using A–1 solve the system of equations
, find A–1. Using A–1 solve the system of equations
2x – 3y + 5z = 11
3x + 2y – 4z = – 5
x + y – 2z = – 3
Solution:
Given: A=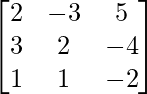
Now, |A|= 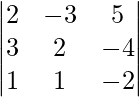
∴ |A|= 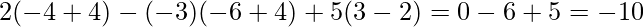
Means, A-1 exists.
And A-1 =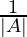 (adj.A)……(1)
(adj.A)……(1)
Now,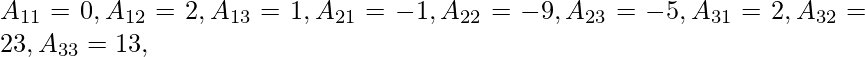
∴ adj. A =
From eq. (1),
A-1=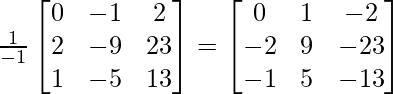
Now, Matrix form of given equation is AX = B
i.e.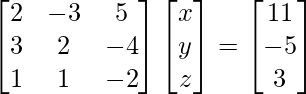
∵ Solution is unique.
∴ X=A-1B
⇒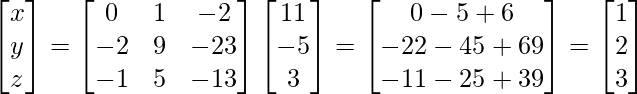
Therefore, x = 1, y = 2, z = 3
Question 16. The cost of 4 kg onion, 3 kg wheat and 2 kg rice is 60 rupees. The cost of 2 kg onion, 4 kg wheat and 6 kg rice is 90 rupees. The cost of 6 kg onion 2 kg wheat and 3 kg rice is 70 rupees. Find cost of each item per kg by matrix method.
Solution:
Let Rs x, Rs y, Rs z per kg be the prices of onion, wheat and rice respectively.
A.T.Q.
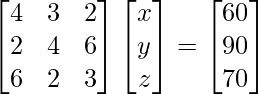
4x+3y+2z=60
2x+4y+6z=90
6x+2y+3z=70
Matrix form of equation is AX = B
where, A=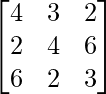 ,B=
,B= and X=
and X=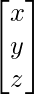
=> 
Now, |A|=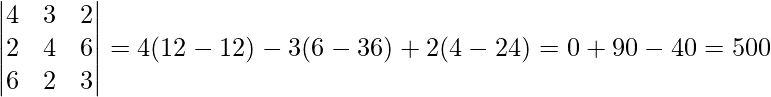
∴ Solution is unique
Now, X=A-1B= (adj. A)B……(1)
(adj. A)B……(1)
Now, 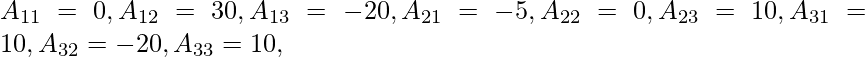
∴ (adj.A)= 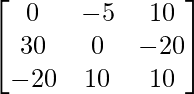
From eqn.(1)
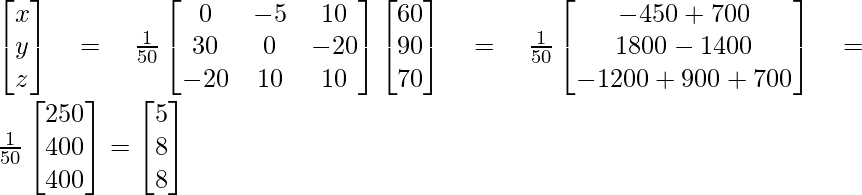
Therefore, x = 5, y = 8, z = 8
Hence, the cost of onion, wheat and rice are Rs. 5, Rs 8 and Rs 8 per kg.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...