Class 12 NCERT Solutions – Mathematics Part I – Chapter 4 Determinants – Exercise 4.1
Last Updated :
04 Mar, 2021
Evaluate the determinants from the following Questions.
Question 1. 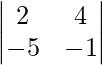
Solution:
The determinant of a 2 x 2 matrix 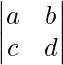
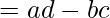
Hence, 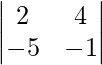
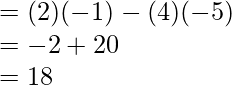
Question 2. (i) 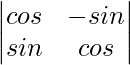
Solution:
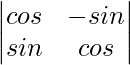
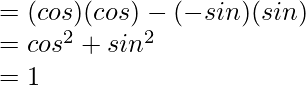 from trigonometric identities
from trigonometric identities
(ii) 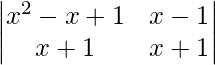
Solution:
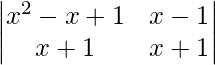
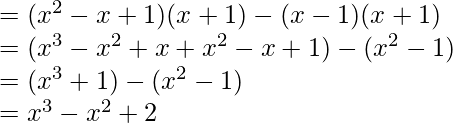
Question 3. If 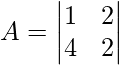 show that
show that 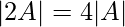
Solution:
LHS=>
Matrix, 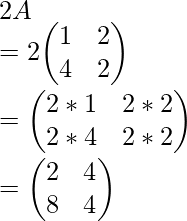
Hence, determinant, 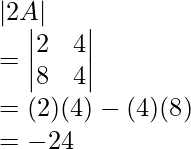
RHS=>
Determinant, 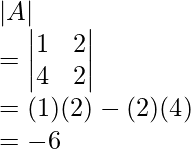
Now, 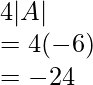
Hence, proved, LHS = RHS
Question 4. If 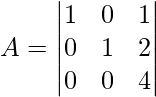 then show that |
then show that |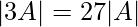
Solution:
LHS=>
Matrix, 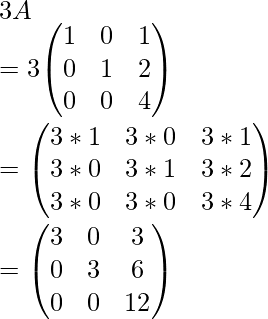
Hence, determinant, 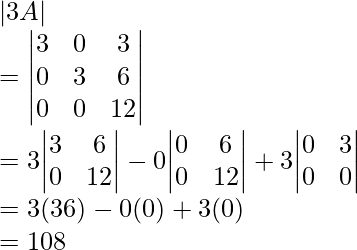
RHS =>
Determinant, 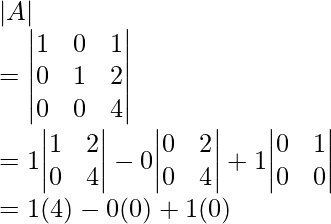
Now, 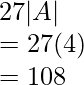
Hence, proved, LHS = RHS
Question 5. Evaluate the determinants
(i) 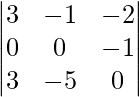
Solution:
Since the maximum number of zeroes are in the second row, we will expand the determinant along row 2.
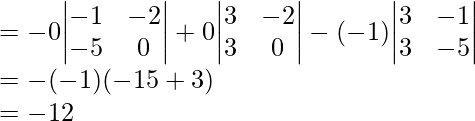
(ii) 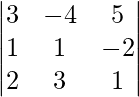
Solution:
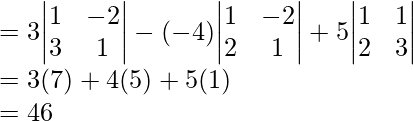
(iii) 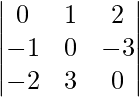
Solution:
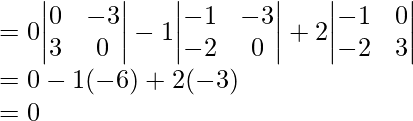
Note: This matrix is skew symmetric i.e. 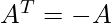
For every skew symmetric matrix of “odd dimension”, the determinant vanishes i.e. determinant is zero.
(iv) 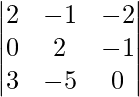
Solution:
Since the maximum number of zeroes are in the second row, we will expand the determinant along row 2.
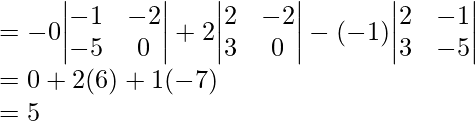
Question 6. If 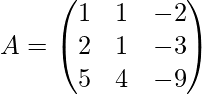 find |A|
find |A|
Solution:
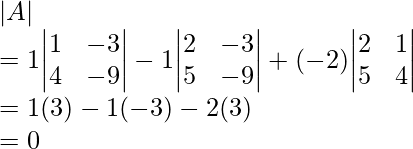
Question 7. Find the values of x if
(i) 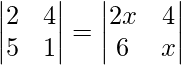
Solution:
Solving determinants on both sides,
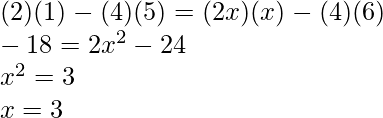
(ii) 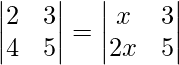
Solution:
Solving determinants on both sides
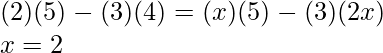
Question 8. If 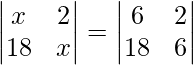 then x is equal to
then x is equal to
(A) 6 (B) ±6 (C) -6 (D) 0
Solution:
Solving determinants on both sides
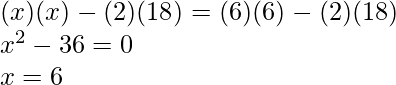
Hence, Option (B)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...