Before we begin learning about the Google Cloud Platform, we will talk about what is Cloud Computing. Basically, it is using someone else’s computer over the internet. Examples- GCP, AWS, IBM Cloud, etc. Some interesting features of cloud computing are as follows:
- You get computing resources on-demand and self-service. The customer has to use a simple User Interface and they get the computing power, storage requirements, and network you need, without human intervention.
- You can access these cloud resources over the internet from anywhere on the globe.
- The provider of these resources has a huge collection of these resources and allocates them to customers out of that collection.
- The resources are elastic. If you need more resources you can get more, rapidly. If you need less, you can scale down back.
- The customers pay only for what they use or reserve. If they stop using resources, they stop paying.
What is Google Cloud Platform(GCP)?
Starting from 1998 with the launch of Google Search. google has developed one of the largest and most powerful IT Infrastructures in the world. Today, this infrastructure is used by billions of users to use services such as Gmail, YouTube, Google Photos, and Maps. In 2008, Google decided to open its network and IT infrastructure to business customers, taking an infrastructure that was initially developed for consumers’ applications to public service and launching the Google Cloud platform.
All the services listed above are provided by Google hence the name Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Apart from these, there are many other services provided by GCP and also many concepts related to it that we are going to discuss in this article.
Regions and zones
Let’s start at the finest grain level (i.e. the smallest or first step in the hierarchy), the Zone. A zone is an area where Google Cloud Platform Resources like virtual machines or storage are deployed.
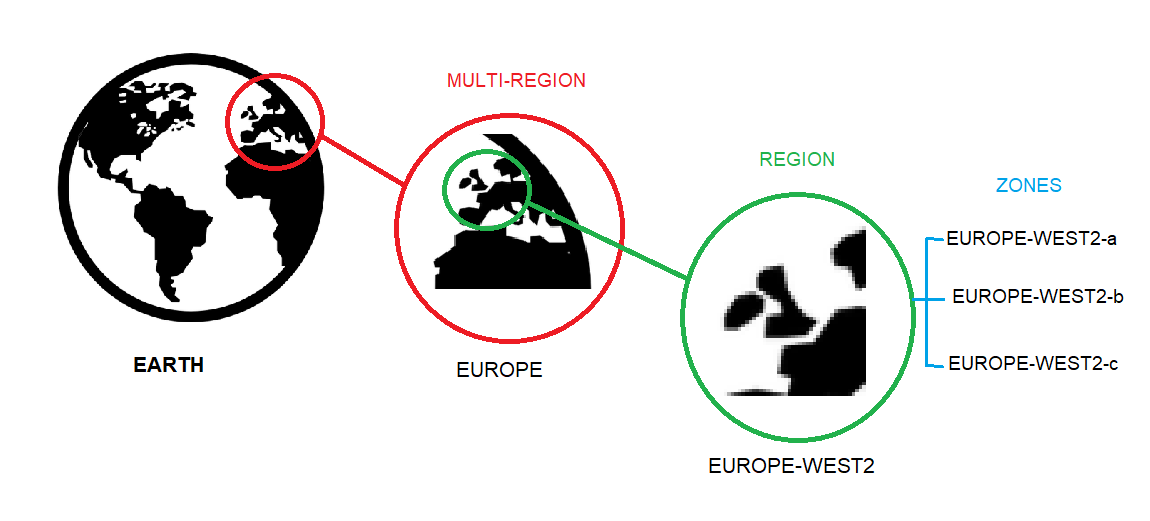
For example, when you launch a virtual machine in GCP using Compute Engine, it runs in a zone you specify (suppose Europe-west2-a). Although people consider a zone as being sort of a GCP Data Center, that’s not strictly accurate because a zone doesn’t always correspond to one physical building. You can still visualize the zone that way, though.
Zones are grouped into regions which are independent geographic areas and much larger than zones (for example- all zones shown above are grouped into a single region Europe-west2) and you can choose what regions you want your GCP resources to be placed in. All the zones within a neighborhood have fast network connectivity among them. Locations within regions usually have trip network latencies of under five milliseconds.
As a part of developing a fault-tolerant application, you’ll need to spread your resources across multiple zones in a region. That helps protect against unexpected failures. You can run resources in different regions too. Lots of GCP customers do this, both to bring their applications closer to users around the world, and also to guard against the loss of a whole region, say, due to a natural disaster.
A few GCP Services supports deploying resources in what we call a Multi-Region. For example, Google Cloud Storage, lets you place data within the Europe Multi-Region. What that means is that it is stored redundantly in a minimum of two different geographic locations, separated by at least 160 kilometers within Europe. Previously, GCP had 15 regions. Visit cloud.google.com to ascertain what the entire is up to today.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Google Cloud Platform?
Following are some use cases of google cloud platform.
- Scalability and flexibility: You can scale the servers based up on the load if there is high incoming traffic then you can scale up and if the traffic is less then you can scale down which make it flexible and mostly suited for the business use cases.
- Cost-effectiveness: Google Cloud Platform follows the pay-as-you-go model which it will charge only for the how much time you use service and at level you are going to use the services.
- High performance: You can highly reliable on the infrastructure of the google cloud because they are highly available and spread across the multiple regions around the world.
- Security: Google Cloud Platform is more secure you can trust the service offered by the gcp for the security options such as encryption, access control, and data loss prevention.
What are the different types of Google Cloud Platform services?
Overview of Google Cloud offerings
Following are the some of the services offered by the GCP.
Compute
- Compute Engine: It is used to provision the virtual machine machines to deploy the application with the need of your required ram,rom and security groups.
- Google Kubernetes Engine(GKE): Google cloud provide kubernetes(GKE) as an service where you can deploy the application and restof the things like autoscaling and load balancing will be taken care by the google cloud.
- App Engine: A scalable runtime environment, Google App Engine is mostly used to run Web applications. These dynamic scales as demand change over time because of Google’s vast computing infrastructure. Because it offers a secure execution environment in addition to a number of services, App Engine makes it easier to develop scalable and high-performance Web apps.
Storage
- Cloud Storage: You can store the data which is required to be highly available and which is in large amount.
- Persistent Disk: Presistent disk is an storage disk which can be attached to the virtual machine and can be reused for the another virtual machine.
- Cloud SQL: Cloud SQL is an fully managed service by the google cloud platform and it offers services like MySQL, PostgreSQL and SQL Server.
Networking
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): You can deploy your application in the private network which can be achieved by the google cloud.
- Cloud Load Balancing: This is most important service in the google cloud which is used to distribute the cloud across the multiple replicas of the applications.
- Cloud CDN: This is the service which will cache the content and delivers to the end users with the help of edge locations.
Data analytics
- Bigquery: All organizations look for unlocking business insights from their data. But it can be hard to scalably ingest, store, and analyze that data as it rapidly grows. Google’s enterprise data warehouse called BigQuery, was designed to make large-scale data analysis accessible to everyone.
- Dataflow: It is the analysis of flow of data in control flow graph, i.e., the analysis that determines the information regarding the definition and use of data in program. With the help of this analysis, optimization can be done.
- Pub/Sub: Pub/sub Consider a scenario of synchronous message passing. You have two components in your system that communicate with each other. LeLet’ss call the sender and receiver. The receiver asks for a service from the sender and the sender serves the request and waits for an acknowledgment from the receiver. There is another receiver that requests a service from the sender. The sender is blocked since it hasn’t yet received any acknowledgment from the first receiver. The sender isn’t able to serve the second receiver which can create problems. To solve this drawback, the Pub-Sub model was introduced.
Machine learning
- Vertex AI Platform: As we know Artificial Intelligence (AI) has undergone advancements throughout the years leading to a transformation of industries and reshaping how businesses operate. The emergence of cloud-based AI platforms has further accelerated this revolution enabling organizations to leverage the potential of AI.
- AI Platform Training: You can train the AI model with the help of AI Platform Training in google cloud.
- AI Platform Prediction: You can make the predictions by using the your machine learning models.
Productivity and collaboration
- Google Workspace: Most of us are familiar with various Google Workspace products(also called G Suite) like Calendar, Drive, and Gmail, etc.
- Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM): Identity Access Management is used by the root user (administrator) of the organization. The users represent one person within the organization, and the users can be grouped in that all the users will have the same privileges to the services.
How to get started with Google Cloud Platform?
Follow the steps mentioned below to get started with the Google Cloud Platform.
Step 1: Create an account in google cloud platform depending on your business need select the plan if you want to learn the service the create free account gcp will provide the $300 free credit to get you started.
Step 2: After creating free account it will validate till 90n days know you can start using by creating the project which means all the resources can be tracked under this project.
Step 3: Know you need to start the billing then only you can start use the service and also the billing will be on pay-as-you-go model you will be charged for the amount of resources you are going to use.
Step 4: You need to be careful while choosing the services. You must select the service according to need of you application.
Step 5: Once you have choosen the service know you can deploy you application into the cloud.
Step 6: After deploying the application know you can monitor you resource usage by using the services available in the gcp.
Google Cloud Platform use cases
Google Cloud Platform is well suited for the build and deploy and manage the applications.
- E-commerce: You deploy and manage the e-commerce websites by autoscaling and load balancing you can manage the millions of users and transactions.
- Media and entertainment: You can store the static and dynamic data can deliver it to the across the world with out any latency to the end users.
- Financial services: Google Cloud Platform is well suited for the sinical application because of the level of security it is offering.
- Healthcare: You can store the data of patient and take care the outcomes of the health of patient.
Google Cloud Platform security
Google Cloud Platform offers following security options.
- Encryption: Google cloud platform offers security like encryption at rest and in transit for all of your data.
- Access control: You can control the access to the individual users like which services they can access and which service they can’t depending on the use cases.
- Network Security: You can create the VPC where you can secure the application by deploying the application in the private network and also you can configure the firewalls andsecurity groups etc.
- Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP): With IAP, users may manage application access according to their context and identity. It aids in preventing unwanted access.
Google Cloud Platform Future
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is evolving constantly by expanding its resources and increasing its regions and availability zone across the world which make it mote available for the users to use reduces the latency. GCP is upgrading itself according to the market trends gcp play an major role in the upcoming years it will play major role it will helps for the businesses to thrive in the increasingly data-driven and interconnected world.
Google Cloud Platform pricing(GCP)
Google was the primary major Cloud provider to bill by the second instead of rounding up to greater units of your time for its virtual machines as a service offering. This may not sound like a big deal, but charges for rounding up can really add up for customers who are creating and running lots of virtual machines. Per second billing is obtainable for a virtual machine use through Compute Engine and for several other services too.
Compute Engine provides automatically applied use discounts which are discounts that you simply get for running a virtual machine for a big portion of the billing month. When you run an instance for at least 25% of a month, Compute Engine automatically gives you a reduction for each incremental minute you employ it. Here’s one more way Compute Engine saves you money.
Normally, you choose a virtual machine type from a typical set of those values, but Compute Engine also offers custom virtual machine types, in order that you’ll fine-tune the sizes of the virtual machines you use. That way, you’ll tailor your pricing for your workloads.
Google Cloud Platform Open API’s(GCP)
Some people are afraid to bring their workloads to the cloud because they’re afraid they’ll get locked into a specific vendor. But in many ways, Google gives customers the power to run their applications elsewhere, if Google becomes not the simplest provider for his or her needs. Here are some samples of how Google helps its customers avoid feeling locked in. GCP services are compatible with open source products. For example, take Cloud Bigtable, a database that uses the interface of the open-source database Apache HBase, which provides customers the advantage of code portability. Another example, Cloud Dataproc provides the open-source big data environment Hadoop, as a managed service, etc.
Google Cloud Platform Certification(GCP)
Google Cloud Platform offers wide range of certifications to validate you skills some of the certifications as mentioned follows.
- Foundational: It is an basic certification to test your basics on google cloud platform like features,benefits and use cases of google cloud.
- Associate Cloud Enginee: Associate Cloud Enginee this certification will test your fundamentals on google cloud platform which are like deploying and maintaining the projects.
- Professional Cloud Architect: Professional Cloud Architect will test you depth knowledge on the complete overview of the services implementation of and managing the services of google cloud.
- Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer: Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer will test you knowledge on the services like deployment automation and scaling the application at the sudden loads.
- Professional Cloud Network Engineer: Professional Cloud Network Engineer will validates the you ability on the desging of the networks for the business use in cloud environments.
Why choose GCP?
- GCP allows you to choose between computing, storage, big data, machine learning, and application services for your web, mobile, analytics, and, back-end solutions.
- It’s global and it is cost-effective.
- It’s open-source friendly.
- It’s designed for security.
Advantages of Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Good documentation: We are talking about many pages in total, including a reasonably detailed API Reference guide.
- Different storage classes for every necessity: Regional (frequent use), Nearline (infrequent use), and Coldline (long-term storage).
- High durability: This suggests that data survives even within the event of the simultaneous loss of two disks.
- Many regions available to store your data: North Ameria, South America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
- The “Console” tab within the documentation allows you to try for free of charge different SDKs. It’s incredibly useful for developers
- One of the simplest free layers within the industry. $300 free credit to start with any GCP product during the primary year. Afterward, 5 GB of Storage to use forever without any charges.
Disadvantages of Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- The support fee is sort of hefty: Around 150 USD per month for the foremost basic service (Silver class).
- Downloading data from Google Cloud Storage is expensive. 0, 12 USD per GB.
- Google Cloud Platform web interface is somewhat confusing. Sometimes I am lost while browsing around the menus.
- Prices in both Microsoft Azure (around 0.018 USD per GB/month) or Backblaze B2 (about 0.005 USD per GB/month) are less than Google Cloud Storage.
- It has a high pricing schema, almost like AWS S3, so it’s easy to urge unexpected costs (e.g. number of requests, transfers, etc.).
Three Categories of Cloud Services
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): It provides you with all the hardware components you require such as computing power, storage, network, etc.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): It provides you with a platform that you can use to develop applications, software, and other projects.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): It provides you with complete software to use like Gmail, Google Drive, etc.
FAQs On GCP Cloud
1. Is Google Cloud platform same as AWS?
Google Cloud Platform and AWS are two different cloud service providers with wide range of services for the businesses of all sizes. There are lots of key difference between themand similarities also.
2. Is Google cloud storage for free?
Yes, there is a free tier available with Google Cloud Storage that gives you 5GB of free US regional storage each month without deducting from your credit limit. This implies that there are no fees associated with storing and retrieving up to 5GB of data from Cloud Storage at any time.
3. What is Google Cloud Platform database?
The database services provided by Google Cloud Platform (GCP) give you a variety of choices for managing and storing data for your apps. These databases are made to accommodate the requirements of enterprises of all sizes and are extremely scalable, dependable, and secure.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...