Trie Data Structure | Insert and Search
Last Updated :
17 Apr, 2024
The Trie data structure is a tree-like data structure used for storing a dynamic set of strings. It is commonly used for efficient retrieval and storage of keys in a large dataset. The structure supports operations such as insertion, search, and deletion of keys, making it a valuable tool in fields like computer science and information retrieval. In this article we are going to explore insertion and search operation in Trie Data Structure.
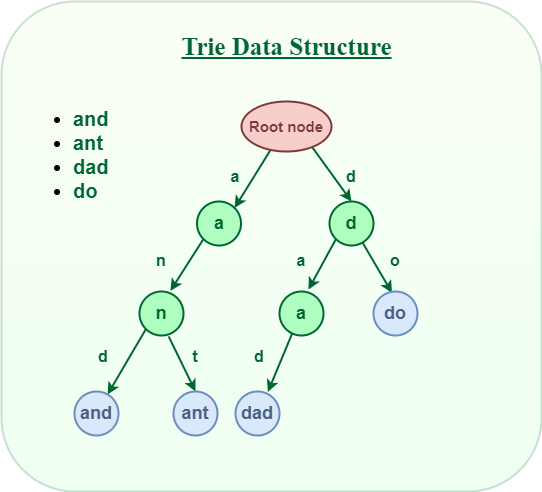 Trie data structure
Trie data structureRepresentation of of Trie Node:
A Trie data structure consists of nodes connected by edges. Each node represents a character or a part of a string. The root node, the starting point of the Trie, represents an empty string. Each edge emanating from a node signifies a specific character. The path from the root to a node represents the prefix of a string stored in the Trie.
A simple structure to represent nodes of the English alphabet can be as follows.
C++
struct TrieNode {
// pointer array for child nodes of each node
TrieNode* childNode[26];
// Used for indicating ending of string
bool wordEnd;
TrieNode()
{
// constructor
// initialize the wordEnd variable with false
// initialize every index of childNode array with
// NULL
wordEnd = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
childNode[i] = NULL;
}
}
};
Insertion in Trie Data Structure:
Let’s walk through the process of inserting the words into a Trie data structure. We have already cover the basics of Trie and its node structure.
Here’s a visual representation of inserting the words “and” and “ant” into a Trie data structure:
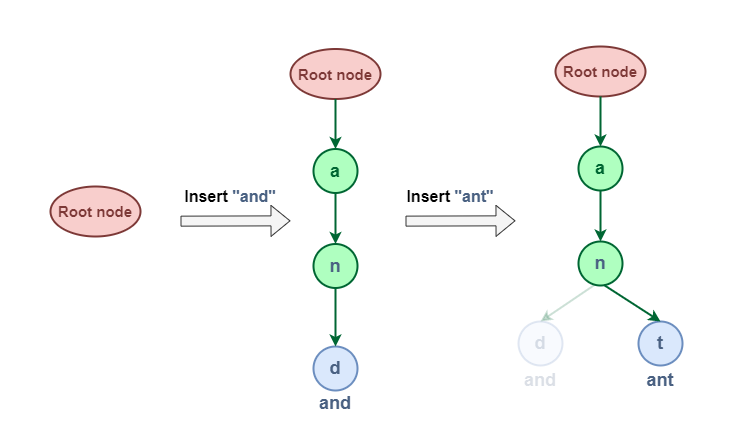 Insert Operation in Trie Data Structure
Insert Operation in Trie Data Structure
Inserting “and” in Trie data structure:
- Start at the root node: The root node has no character associated with it and its wordEnd value is 0, indicating no complete word ends at this point.
- First character “a”: Calculate the index using ‘a’ – ‘a’ = 0. Check if the childNode[0] is null. Since it is, create a new TrieNode with the character “a“, wordEnd set to 0, and an empty array of pointers. Move to this new node.
- Second character “n”: Calculate the index using ‘n’ – ‘a’ = 13. Check if childNode[13] is null. It is, so create a new TrieNode with the character “n“, wordEnd set to 0, and an empty array of pointers. Move to this new node.
- Third character “d”: Calculate the index using ‘d’ – ‘a’ = 3. Check if childNode[3] is null. It is, so create a new TrieNode with the character “d“, wordEnd set to 1 (indicating the word “and” ends here).
Inserting “ant” in Trie data structure:
- Start at the root node: Root node doesn’t contain any data but it keep track of every first character of every string that has been inserted.
- First character “a”: Calculate the index using ‘a’ – ‘a’ = 0. Check if the childNode[0] is null. We already have the “a” node created from the previous insertion. so move to the existing “a” node.
- First character “n”: Calculate the index using ‘n’ – ‘a’ = 13. Check if childNode[13] is null. It’s not, so move to the existing “n” node.
- Second character “t”: Calculate the index using ‘t’ – ‘a’ = 19. Check if childNode[19] is null. It is, so create a new TrieNode with the character “t“, wordEnd set to 1 (indicating the word “ant” ends here).
Below is the implementation of insertion of strings in Trie data structure:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TrieNode {
// pointer array for child nodes of each node
TrieNode* childNode[26];
// Used for indicating ending of string
bool wordEnd;
TrieNode()
{
// constructor
// initialize the wordEnd variable with false
// initialize every index of childNode array with
// NULL
wordEnd = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
childNode[i] = NULL;
}
}
};
void insert_key(TrieNode* root, string& key)
{
// Initialize the currentNode pointer
// with the root node
TrieNode* currentNode = root;
// Iterate across the length of the string
for (auto c : key) {
// Check if the node exist for the current
// character in the Trie.
if (currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'] == NULL) {
// If node for current character does not exist
// then make a new node
TrieNode* newNode = new TrieNode();
// Keep the reference for the newly created
// node.
currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'] = newNode;
}
// Now, move the current node pointer to the newly
// created node.
currentNode = currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'];
}
// Increment the wordEndCount for the last currentNode
// pointer this implies that there is a string ending at
// currentNode.
currentNode->wordEnd = 1;
}
Time Complexity: O(number of words * maxLengthOfWord)
Auxiliary Space: O(number of words * maxLengthOfWord)
Searching in Trie Data Structure:
Searching for a key in Trie data structure is similar to its insert operation. However, It only compares the characters and moves down. The search can terminate due to the end of a string or lack of key in the trie.
Steps by step approach for searching in Trie Data structure:
- Start at the root node. This is the starting point for all searches within the Trie.
- Traverse the Trie based on the characters of the word you are searching for. For each character, follow the corresponding branch in the Trie. If the branch doesn’t exist, the word is not present in the Trie.
- If you reach the end of the word and the wordEnd flag is set to 1, the word has been found.
- If you reach the end of the word and the wordEnd flag is 0, the word is not present in the Trie, even though it shares a prefix with an existing word.
Here’s a visual representation of searching word “dad” in Trie data structure:
Let’s assume that we have successfully inserted the words “and“, “ant“, and “dad” into our Trie, and we have to search for specific words within the Trie data structure. Let’s try searching for the word “dad“:
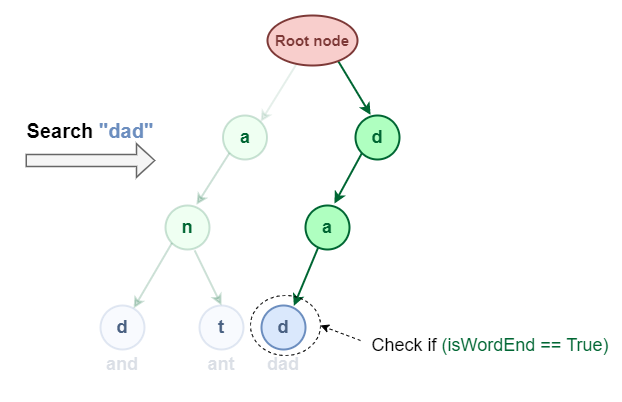 Search Operation in Trie Data Structure
Search Operation in Trie Data Structure
- We start at the root node.
- We follow the branch corresponding to the character ‘d’.
- We follow the branch corresponding to the character a’.
- We follow the branch corresponding to the character ‘d’.
- We reach the end of the word and wordEnd flag is 1. This means that “dad” is present in the Trie.
Below is the implementation of searching strings in Trie Data Structure:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TrieNode {
// pointer array for child nodes of each node
TrieNode* childNode[26];
// Used for indicating ending of string
bool wordEnd;
TrieNode()
{
// constructor
// initialize the wordEnd variable with false
// initialize every index of childNode array with
// NULL
wordEnd = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
childNode[i] = NULL;
}
}
};
bool search_key(TrieNode* root, string& key)
{
// Initialize the currentNode pointer
// with the root node
TrieNode* currentNode = root;
// Iterate across the length of the string
for (auto c : key) {
// Check if the node exist for the current
// character in the Trie.
if (currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'] == NULL) {
// Given word does not exist in Trie
return false;
}
// Move the currentNode pointer to the already
// existing node for current character.
currentNode = currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'];
}
return (currentNode->wordEnd == true);
}
Time Complexity: O(number of words * maxLengthOfWord)
Auxiliary Space: O(number of words * maxLengthOfWord)
Implementation of Insert and Search Operations in Trie Data Structure:
Steps-by-step approach:
- Create a root node with the help of TrieNode() constructor.
- Store a collection of strings that have to be inserted in the trie in a vector of strings say, arr.
- Inserting all strings in Trie with the help of the insert_key() function,
- Search strings with the help of search_key() function.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TrieNode {
// pointer array for child nodes of each node
TrieNode* childNode[26];
// Used for indicating ending of string
bool wordEnd;
TrieNode()
{
// constructor
// initialize the wordEnd variable with false
// initialize every index of childNode array with
// NULL
wordEnd = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
childNode[i] = NULL;
}
}
};
void insert_key(TrieNode* root, string& key)
{
// Initialize the currentNode pointer
// with the root node
TrieNode* currentNode = root;
// Iterate across the length of the string
for (auto c : key) {
// Check if the node exist for the current
// character in the Trie.
if (currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'] == NULL) {
// If node for current character does not exist
// then make a new node
TrieNode* newNode = new TrieNode();
// Keep the reference for the newly created
// node.
currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'] = newNode;
}
// Now, move the current node pointer to the newly
// created node.
currentNode = currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'];
}
// Increment the wordEndCount for the last currentNode
// pointer this implies that there is a string ending at
// currentNode.
currentNode->wordEnd = 1;
}
bool search_key(TrieNode* root, string& key)
{
// Initialize the currentNode pointer
// with the root node
TrieNode* currentNode = root;
// Iterate across the length of the string
for (auto c : key) {
// Check if the node exist for the current
// character in the Trie.
if (currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'] == NULL) {
// Given word does not exist in Trie
return false;
}
// Move the currentNode pointer to the already
// existing node for current character.
currentNode = currentNode->childNode[c - 'a'];
}
return (currentNode->wordEnd == true);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Make a root node for the Trie
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode();
// Stores the strings that we want to insert in the
// Trie
vector<string> inputStrings
= { "and", "ant", "do", "geek", "dad", "ball" };
// number of insert operations in the Trie
int n = inputStrings.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
insert_key(root, inputStrings[i]);
}
// Stores the strings that we want to search in the Trie
vector<string> searchQueryStrings
= { "do", "geek", "bat" };
// number of search operations in the Trie
int searchQueries = searchQueryStrings.size();
for (int i = 0; i < searchQueries; i++) {
cout << "Query String: " << searchQueryStrings[i]
<< "\n";
if (search_key(root, searchQueryStrings[i])) {
// the queryString is present in the Trie
cout << "The query string is present in the "
"Trie\n";
}
else {
// the queryString is not present in the Trie
cout << "The query string is not present in "
"the Trie\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
OutputQuery String: do
The query string is present in the Trie
Query String: geek
The query string is present in the Trie
Query String: bat
The query string is not present in the Trie
Complexity Analysis of Trie Data Structure:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Auxiliary Space |
|---|
| Insertion | O(n) | O(n*m) |
|---|
| Searching | O(n) | O(1) |
|---|
Related Articles:
Practice Problems:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...