Introduction to Red-Black Tree
Last Updated :
15 Mar, 2023
Introduction:
When it comes to searching and sorting data, one of the most fundamental data structures is the binary search tree. However, the performance of a binary search tree is highly dependent on its shape, and in the worst case, it can degenerate into a linear structure with a time complexity of O(n). This is where Red Black Trees come in, they are a type of balanced binary search tree that use a specific set of rules to ensure that the tree is always balanced. This balance guarantees that the time complexity for operations such as insertion, deletion, and searching is always O(log n), regardless of the initial shape of the tree.
Red Black Trees are self-balancing, meaning that the tree adjusts itself automatically after each insertion or deletion operation. It uses a simple but powerful mechanism to maintain balance, by coloring each node in the tree either red or black.
Red Black Tree-
Red-Black tree is a binary search tree in which every node is colored with either red or black. It is a type of self balancing binary search tree. It has a good efficient worst case running time complexity.
Properties of Red Black Tree:
The Red-Black tree satisfies all the properties of binary search tree in addition to that it satisfies following additional properties –
1. Root property: The root is black.
2. External property: Every leaf (Leaf is a NULL child of a node) is black in Red-Black tree.
3. Internal property: The children of a red node are black. Hence possible parent of red node is a black node.
4. Depth property: All the leaves have the same black depth.
5. Path property: Every simple path from root to descendant leaf node contains same number of black nodes.
The result of all these above-mentioned properties is that the Red-Black tree is roughly balanced.
Rules That Every Red-Black Tree Follows:
- Every node has a color either red or black.
- The root of the tree is always black.
- There are no two adjacent red nodes (A red node cannot have a red parent or red child).
- Every path from a node (including root) to any of its descendants NULL nodes has the same number of black nodes.
- Every leaf (e.i. NULL node) must be colored BLACK.
Why Red-Black Trees?
Most of the BST operations (e.g., search, max, min, insert, delete.. etc) take O(h) time where h is the height of the BST. The cost of these operations may become O(n) for a skewed Binary tree. If we make sure that the height of the tree remains O(log n) after every insertion and deletion, then we can guarantee an upper bound of O(log n) for all these operations. The height of a Red-Black tree is always O(log n) where n is the number of nodes in the tree.
| Sr. No. |
Algorithm |
Time Complexity |
| 1. |
Search |
O(log n) |
| 2. |
Insert |
O(log n) |
| 3. |
Delete |
O(log n) |
“n” is the total number of elements in the red-black tree.
Comparison with AVL Tree:
The AVL trees are more balanced compared to Red-Black Trees, but they may cause more rotations during insertion and deletion. So if your application involves frequent insertions and deletions, then Red-Black trees should be preferred. And if the insertions and deletions are less frequent and search is a more frequent operation, then AVL tree should be preferred over the Red-Black Tree.
How does a Red-Black Tree ensure balance?
A simple example to understand balancing is, that a chain of 3 nodes is not possible in the Red-Black tree. We can try any combination of colors and see if all of them violate the Red-Black tree property.
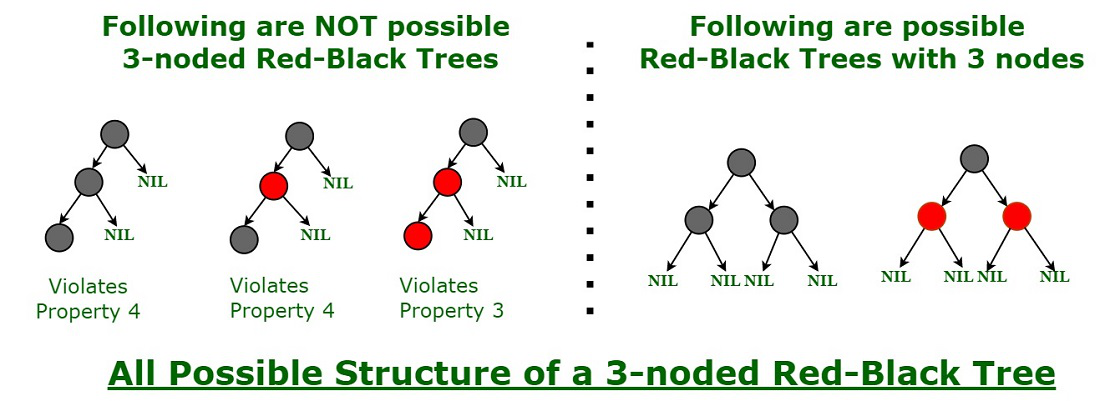
Proper structure of three noded Red-black tree
Interesting points about Red-Black Tree:
- The black height of the red-black tree is the number of black nodes on a path from the root node to a leaf node. Leaf nodes are also counted as black nodes. So, a red-black tree of height h has black height >= h/2.
- Height of a red-black tree with n nodes is h<= 2 log2(n + 1).
- All leaves (NIL) are black.
- The black depth of a node is defined as the number of black nodes from the root to that node i.e the number of black ancestors.
- Every red-black tree is a special case of a binary tree.
Black Height of a Red-Black Tree :
Black height is the number of black nodes on a path from the root to a leaf. Leaf nodes are also counted black nodes. From the above properties 3 and 4, we can derive, a Red-Black Tree of height h has black-height >= h/2.
Number of nodes from a node to its farthest descendant leaf is no more than twice as the number of nodes to the nearest descendant leaf.
Every Red Black Tree with n nodes has height <= 2Log2(n+1)
This can be proved using the following facts:
- For a general Binary Tree, let k be the minimum number of nodes on all root to NULL paths, then n >= 2k – 1 (Ex. If k is 3, then n is at least 7). This expression can also be written as k <= Log2(n+1).
- From property 4 of Red-Black trees and above claim, we can say in a Red-Black Tree with n nodes, there is a root to leaf path with at-most Log2(n+1) black nodes.
- From properties 3 and 5 of Red-Black trees, we can claim that the number of black nodes in a Red-Black tree is at least ⌊ n/2 ⌋ where n is the total number of nodes.
From the above points, we can conclude the fact that Red Black Tree with n nodes has a height <= 2Log2(n+1)
Search Operation in Red-black Tree:
As every red-black tree is a special case of a binary tree so the searching algorithm of a red-black tree is similar to that of a binary tree.
Algorithm:
searchElement (tree, val)
Step 1:
If tree -> data = val OR tree = NULL
Return tree
Else
If val < data
Return searchElement (tree -> left, val)
Else
Return searchElement (tree -> right, val)
[ End of if ]
[ End of if ]
Step 2: END
For the program, you can refer it for AVL tree.
Example: Searching 11 in the following red-black tree.

Solution:
- Start from the root.
- Compare the inserting element with root, if less than root, then recurse for left, else recurse for right.
- If the element to search is found anywhere, return true, else return false.

Just follow the blue bubble.
In this post, we introduced Red-Black trees and discussed how balance is ensured. The hard part is to maintain balance when keys are added and removed. We have also seen how to search an element from the red-black tree. We will soon be discussing insertion and deletion operations in coming posts on the Red-Black tree.
Exercise:
1) Is it possible to have all black nodes in a Red-Black tree?
2) Draw a Red-Black Tree that is not an AVL tree structure-wise?
Insertion and Deletion
Red-Black Tree Insertion
Red-Black Tree Deletion
Applications:
- Most of the self-balancing BST library functions like map, multiset, and multimap in C++ ( or java packages like java.util.TreeMap and java.util.TreeSet ) use Red-Black Trees.
- It is used to implement CPU Scheduling Linux. Completely Fair Scheduler uses it.
- It is also used in the K-mean clustering algorithm in machine learning for reducing time complexity.
- Moreover, MySQL also uses the Red-Black tree for indexes on tables in order to reduce the searching and insertion time.
- Red Black Trees are used in the implementation of the virtual memory manager in some operating systems, to keep track of memory pages and their usage.
- Many programming languages such as Java, C++, and Python have implemented Red Black Trees as a built-in data structure for efficient searching and sorting of data.
- Red Black Trees are used in the implementation of graph algorithms such as Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm and Prim’s minimum spanning tree algorithm.
- Red Black Trees are used in the implementation of game engines.
Advantages:
- Red Black Trees have a guaranteed time complexity of O(log n) for basic operations like insertion, deletion, and searching.
- Red Black Trees are self-balancing.
- Red Black Trees can be used in a wide range of applications due to their efficient performance and versatility.
- The mechanism used to maintain balance in Red Black Trees is relatively simple and easy to understand.
Disadvantages:
- Red Black Trees require one extra bit of storage for each node to store the color of the node (red or black).
- Complexity of Implementation.
- Although Red Black Trees provide efficient performance for basic operations, they may not be the best choice for certain types of data or specific use cases.
References:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...