Spring Security – Registration and Login Process
Last Updated :
03 Sep, 2023
Spring Security is a framework that allows a programmer to use JEE components to set security limitations on Spring-framework-based Web applications. In this article, we are going to explain how to perform the complete registration and login process by using Spring Security and Spring MVC. The main purpose is to add a full registration process that allows a user to sign up, as well as validates and persists user data. And after that, we are also going to perform the login process for the registered users.
Example Project
Step 1: Create Your Project and Configure Apache Tomcat Server
Note: We are going to use Spring Tool Suite 4 IDE for this project. Please refer to this article to install STS in your local machine How to Download and Install Spring Tool Suite (Spring Tools 4 for Eclipse) IDE.
Step 2: Create Schema and Tables in MySQL Workbench and Put Some Sample Data
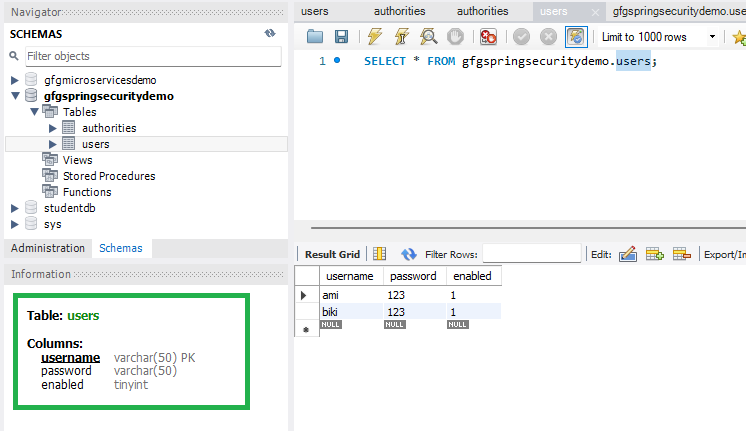
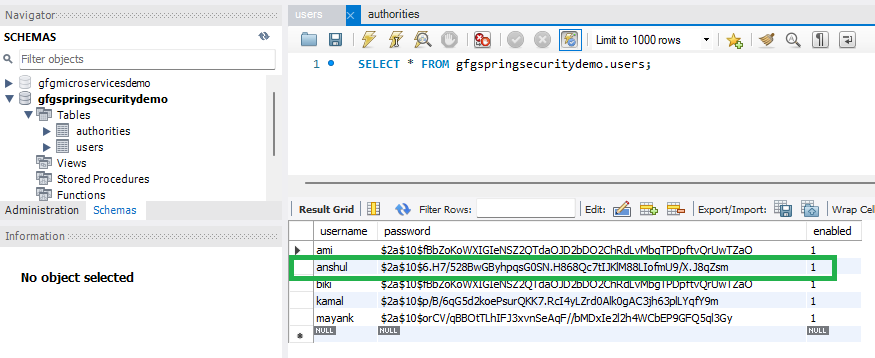
Go to your MySQL Workbench and create a schema named gfgspringsecuritydemo and inside that create two tables users and authorities and put some sample data as shown in the below image.
Note: It is strictly recommended that (recommended by spring official docs) you should create the tables as per the schema. The column name must be the same. You may put some sample data or we are going to take the data from the users through the registration form.
users Table:
Here is the users Table Schema
- username varchar_ignorecase(50) not null primary key,
- password varchar_ignorecase(50) not null,
- enabled boolean not null
Please refer to the below image for reference.
authorities Table:
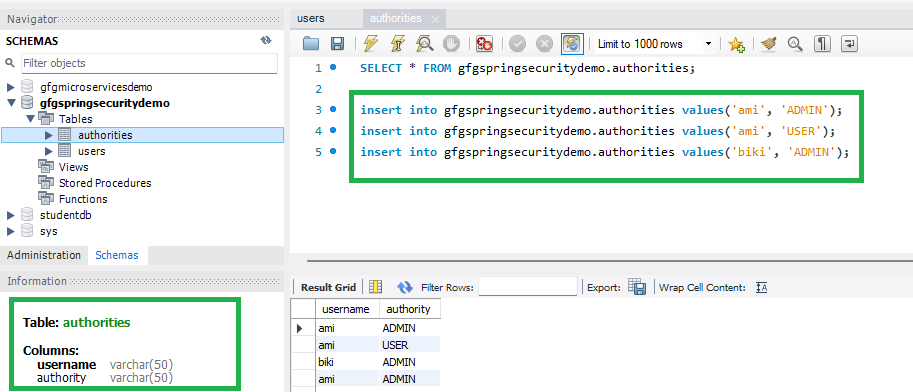
Here is the authorities Table Schema
- username varchar_ignorecase(50) not null,
- authority varchar_ignorecase(50) not null,
- constraint fk_authorities_users foreign key(username) references users(username)
Please refer to the below image for reference.
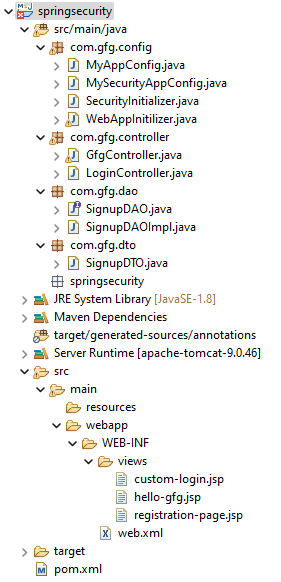
Step 3: Folder Structure
Before moving to the project let’s have a look at the complete project structure for our Spring MVC application.
Step 4: Add Dependencies to pom.xml File
Add the following dependencies to your pom.xml file
- Spring Web MVC
- Java Servlet API
- Spring Security Config
- Spring Security Web
- Spring JDBC
- MySQL Connector Java
XML
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.24</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId>
<version>5.7.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-web</artifactId>
<version>5.7.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.24</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
Below is the complete pom.xml file. Please cross-verify if you have missed some dependencies.
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.gfg.springsecurity</groupId>
<artifactId>springsecurity</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>springsecurity Maven Webapp</name>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.24</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId>
<version>5.7.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-web</artifactId>
<version>5.7.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.24</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>springsecurity</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
|
Step 5: Configuring Dispatcher Servlet
Please refer to this article What is Dispatcher Servlet in Spring? and read more about Dispatcher Servlet which is a very very important concept to understand. Now we are going to configure Dispatcher Servlet with our Spring MVC application. Go to the src > main > java and create a class WebAppInitilizer. Below is the code for the WebAppInitilizer.java file.
File: WebAppInitilizer.java
Java
package com.gfg.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class WebAppInitilizer extends
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
Class[] configFiles = {MyAppConfig.class};
return configFiles;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
String[] mappings = {"/"};
return mappings;
}
}
|
Create another class in the same location (src > main > java) and name it MyAppConfig. Below is the code for the MyAppConfig.java file.
File: MyAppConfig.java
Java
package com.gfg.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan("com")
public class MyAppConfig {
}
|
Reference Article: Spring – Configure Dispatcher Servlet in Three Different Ways
Step 6: Create Your Spring MVC Controller
Go to the src > main > java and create a class LoginController. Below is the code for the LoginController.java file.
File: LoginController.java
Java
package com.gfg.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import com.gfg.dao.SignupDAO;
import com.gfg.dto.SignupDTO;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Autowired
private SignupDAO signupDAO;
@GetMapping("/customLogin")
public String customLogin() {
return "custom-login";
}
@GetMapping("/userRegister")
public String userRegistration(@ModelAttribute("signupdto") SignupDTO signupDTO) {
return "registration-page";
}
@PostMapping("/process-registration")
public String processRegistration(SignupDTO signupDTO) {
signupDTO.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(signupDTO.getPassword()));
signupDAO.saveUser(signupDTO);
return "redirect:/customLogin";
}
}
|
Reference Article: Create and Run Your First Spring MVC Controller in Eclipse/Spring Tool Suite
Step 7: Create Your Spring MVC View
Go to the src > main > webapp > WEB-INF > right-click > New > Folder and name the folder as views. Then views > right-click > New > JSP File and name your view. Here we have named it as registration-page.jsp file. Below is the code for the registration-page.jsp file. We have created the registration form inside that file.
File: registration-page.jsp
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>GFG Registration Page</title>
<body bgcolor="green">
<h1>Register Here !!</h1>
<form:form action="process-registration" method="POST" modelAttribute="signupDTO">
Username : <input type="text" name="username" path="username">
<br/>
Password : <input type="password" name="password" path="password">
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="Register">
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
Also, create another view named custom-login.jsp file. Below is the code for the custom-login.jsp file. We have created a simple login form inside that file.
File: custom-login.jsp
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>GFG Login Page</title>
<body bgcolor="green">
<h1>Custom Login Page</h1>
<form:form>
Username : <input type="text" name="username">
<br/>
Password : <input type="password" name="password">
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="Login">
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
Reference Articles:
Step 8: Setting Up ViewResolver in Spring MVC
Go to the src > main > java > MyAppConfig and set your ViewResolver like this
File: MyAppConfig.java
Java
package com.gfg.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan("com")
public class MyAppConfig {
@Bean
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
}
|
Reference Article: ViewResolver in Spring MVC
Step 9: Setting Up Spring Security Filter Chain
Go to the src > main > java and create a class MySecurityAppConfig and annotate the class with @EnableWebSecurity annotation. This class will help to create the spring security filter chain. Below is the code for the MySecurityAppConfig.java file.
File: MySecurityAppConfig.java
Java
package com.gfg.config;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
@EnableWebSecurity
public class MySecurityAppConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}
|
Step 10: Create Spring Security Initilizer
Go to the src > main > java and create a class SecurityInitializer. This class will help to register the spring security filter chain with our application. Below is the code for the SecurityInitializer.java file.
File: SecurityInitializer.java
Java
package com.gfg.config;
import org.springframework.security.web.context.AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer;
public class SecurityInitializer extends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer {
}
|
Now we are done with setting up our Spring Security Filter Chain.
Step 11: Required Files for Registration Process
Create a DTO class and name it SignupDTO. Below is the code for the SignupDTO.java file.
File: SignupDTO.java
Java
package com.gfg.dto;
public class SignupDTO {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SignupDTO [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}
|
Create a DAO layer and inside this layer, there is one interface named SignupDAO and its implementation class SignupDAOImpl. Below is the code for both files.
File: SignupDAO.java Interface
Java
package com.gfg.dao;
import com.gfg.dto.SignupDTO;
public interface SignupDAO {
void saveUser(SignupDTO signupDTO);
}
|
File: SignupDAOImpl.java Class
Java
package com.gfg.dao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.gfg.dto.SignupDTO;
@Repository
public class SignupDAOImpl implements SignupDAO {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void saveUser(SignupDTO signupDTO) {
String sql = "insert into users values(?,?,?)";
String sql2 = "insert into authorities values(?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, signupDTO.getUsername(), signupDTO.getPassword(), 1);
jdbcTemplate.update(sql2, signupDTO.getUsername(), "USER");
}
}
|
Step 12: Required Files for Login Process
Modify the MyAppConfig file. Here we are going to create the DataSource Bean. That means we are going to write the code for the MySQL Database connection. We have also defined other required beans. Below is the complete code for the MyAppConfig file.
File: MyAppConfig.java
Java
package com.gfg.config;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan("com")
public class MyAppConfig {
@Bean
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean
DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
driverManagerDataSource.setUsername("root");
driverManagerDataSource.setPassword("143@Arpilu");
driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
return driverManagerDataSource;
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder getPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
|
Modify the MySecurityAppConfig file. Here we are going to implement the JDBC Authentication by overriding the configure() method. Below is the complete code for the MySecurityAppConfig file.
File: MySecurityAppConfig.java
Java
package com.gfg.config;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@EnableWebSecurity
public class MySecurityAppConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private DataSource datasource;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.jdbcAuthentication()
.dataSource(datasource)
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.antMatchers("/gfg").authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin().loginPage("/customLogin")
.and()
.httpBasic();
}
}
|
Now, let’s run the application and test it out.
Step 13: Run Your Spring MVC Application
To run our Spring MVC Application right-click on your project > Run As > Run on Server. After that use the following URL to run your controller.
http://localhost:8080/springsecurity/userRegister
And now you can see the registration page has been shown. Put some sample data and register yourself.
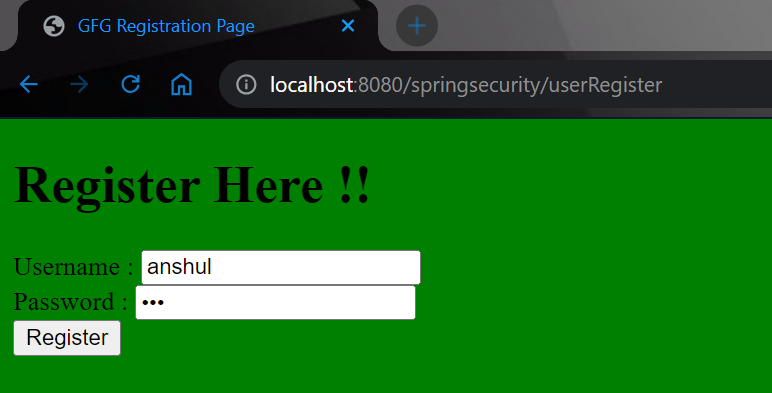
After clicking the registration button you can see the username and password have been stored in our database. You may notice that we are storing the password in an encrypted format.
And it will redirect you to the login page. Refer to the below image.
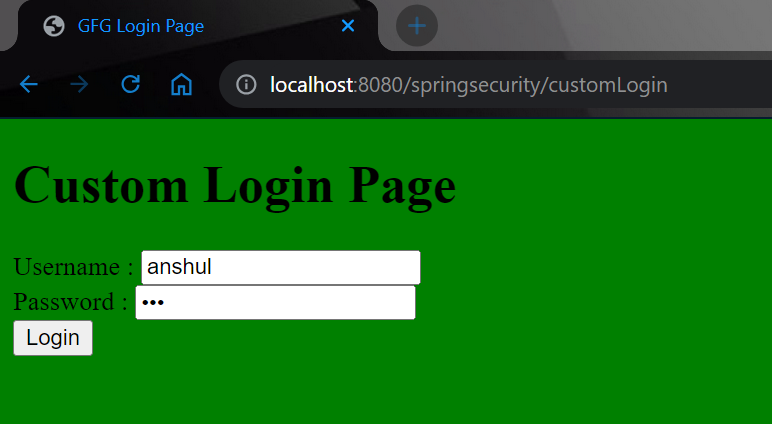
Now login with your database credentials
- Username: anshul
- Password: 123
So this is the complete registration and login process by using Spring Security and Spring MVC.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...