In Spring MVC, the @ModelAttribute annotation binds a method parameter or method return value to a named model attribute and then exposes it to a web view. It refers to the property of the Model object. For example, if we have a form with a form backing object that is called “Student” then we can have Spring MVC supply this object to a Controller method by using the @ModelAttribute annotation:
@RequestMapping("/home")
public String showHomePage(@ModelAttribute("studentInfo") StudentInfoDTO studentInfoDTO) {
return "something";
}
So, let’s understand the whole concept of @ModelAttribute Annotation with an interesting example project. Before that, we suggest you please refer to these articles so that it’s going to be very easy for you to understand the concept of @ModelAttribute Annotation through an example project.
Example Project
We are going to use Spring Tool Suite 4 IDE for this project. Please refer to this article to install STS on your local machine How to Download and Install Spring Tool Suite (Spring Tools 4 for Eclipse) IDE? Go to your STS IDE then create a new maven project, File > New > Maven Project, and choose the following archetype as shown in the below image as follows:
Add the following maven dependencies and plugin to your pom.xml file.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- plugin -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Below is the complete code for the pom.xml file after adding these dependencies.
File: pom.xml
XML
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.geeksforgeeks</groupId>
<artifactId>simple-calculator</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>simple-calculator Maven Webapp</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>simple-calculator</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
Configuring Dispatcher Servlet
Before moving into the coding part let’s have a look at the file structure in the below image.
So at first create an src/main/java folder and inside this folder create a class named CalculatorAppIntilizer and put it inside the com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.config package and extends the AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer class. Refer to the below image.
And whenever you are extending this class, it has some pre abstract methods that we need to provide the implementation. Now inside this class, we have to just write two lines of code to Configure the Dispatcher Servlet. Before that, we have to create another class for the Spring configuration file. So, go to the src/main/java folder and inside this folder create a class named CalculatorAppConfig and put it inside the com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.config package. Below is the code for the CalculatorAppConfig.java file.
File: CalculatorAppConfig.java
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.controllers")
public class CalculatorAppConfig {
}
|
And below is the complete code for the CalculatorAppIntilizer.java file. Comments are added inside the code to understand the code in more detail.
File: CalculatorAppIntilizer.java
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class CalculatorAppIntilizer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
Class aClass[] = { CalculatorAppConfig.class };
return aClass;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
String arr[] = { "/geeksforgeeks.org/*" };
return arr;
}
}
|
Setup ViewResolver
Spring MVC is a Web MVC Framework for building web applications. In generic all MVC frameworks provide a way of working with views. Spring does that via the ViewResolvers, which enables you to render models in the browser without tying the implementation to specific view technology. Read more here: ViewResolver in Spring MVC. So for setting up ViewResolver go to the CalculatorAppConfig.java file and write down the code as follows
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/view/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
And below is the updated code for the CalculatorAppConfig.java file after writing the code for setting up the ViewResolver.
File: Updated CalculatorAppConfig.java
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.controllers")
public class CalculatorAppConfig {
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/view/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
}
|
Create DTO
Go to the src/main/java folder and inside this folder create a class named NameInfoDTO and put it inside the com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.dto package. Below is the code for the NameInfoDTO.java file. Comments are added inside the code to understand the code in more detail.
File: NameInfoDTO.java
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.dto;
public class NameInfoDTO {
private String firstName = "Anshul";
private String lastName = "Aggarwal";
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NameInfoDTO [firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + "]";
}
}
|
Create Controller
Go to the src/main/java folder and inside this folder create a class named AppController and put it inside the com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.controllers package. Below is the complete code for the AppController.java file.
File: AppController.java file
Java
package com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.controllers;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.geeksforgeeks.calculator.dto.NameInfoDTO;
@Controller
public class AppController {
@RequestMapping("/home")
public String showHomePage(Model model) {
NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO = new NameInfoDTO();
model.addAttribute("nameInfo", nameInfoDTO);
return "welcome-page";
}
@RequestMapping("/process-homepage")
public String showResultPage(NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("nameInfo", nameInfoDTO);
return "result-page";
}
}
|
Create View
Now we have to create a view named “welcome-page” inside the WEB-INF/view folder with the .jsp extension. So, go to the src > main > webapp > WEB-INF and create a folder view and inside that folder create a jsp file named welcome-page. So below is the code for the welcome-page.jsp file.
File: welcome-page.jsp
HTML
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<hr />
<form:form action="process-homepage" method="get" modelAttribute="nameInfo">
<div align="center">
<p>
<label for="name1">Enter First Name : </label>
<form:input id="name1" path="firstName" />
</p>
<p>
<label for="name2">Enter Last Name : </label>
<form:input id="name2" path="lastName" />
</p>
<input type="submit" value="Bind Data" />
</div>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
|
Now we have to create another view named “result-page” to display the captured values. So below is the code for the result-page.jsp file.
File: result-page.jsp
HTML
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<hr />
<p>First Name is: ${nameInfo.firstName}</p>
<p>Last Name is: ${nameInfo.lastName}</p>
</body>
</html>
|
So, now we have done with the coding part. And if you run your application it will work fine but now let’s come to the AppController.java file again to understand the concept of @ModelAttribute Annotation.
Understanding @ModelAttribute Annotation
So, in the AppController.java file, we have written so much code and we can do the same thing using the @ModelAttribute Annotation also. So let’s have a look at the code.
@RequestMapping("/home")
public String showHomePage(Model model) {
// Read the existing property by
// fetching it from the DTO
NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO = new NameInfoDTO();
model.addAttribute("nameInfo", nameInfoDTO);
return "welcome-page";
}
@RequestMapping("/process-homepage")
public String showResultPage(NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO, Model model) {
// writing the value to the properties
// by fetching from the URL
model.addAttribute("nameInfo", nameInfoDTO);
return "result-page";
}
And we can write this code using the @ModelAttribute annotation as follows:
@RequestMapping("/home")
public String showHomePage(@ModelAttribute("nameInfo") NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO) {
return "welcome-page";
}
@RequestMapping("/process-homepage")
public String showResultPage(@ModelAttribute("nameInfo") NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO) {
return "result-page";
}
So, we have noticed that we have converted this much of the code.
NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO = new NameInfoDTO();
model.addAttribute("nameInfo", nameInfoDTO);
To a single line of code using @ModelAttribute Annotation
@ModelAttribute("nameInfo") NameInfoDTO nameInfoDTO
So, as the definition says “@ModelAttribute is an annotation that binds a method parameter or method return value to a named model attribute and then exposes it to a web view.” Let’s now run our application and see if everything is working fine or not.
Run Your Application
To run our Spring MVC Application right-click on your project > Run As > Run on Server. And run your application as shown in the below image as depicted below as follows:
After that use the following URL to run your controller
http://localhost:8080/simple-calculator/geeksforgeeks.org/home
Output:
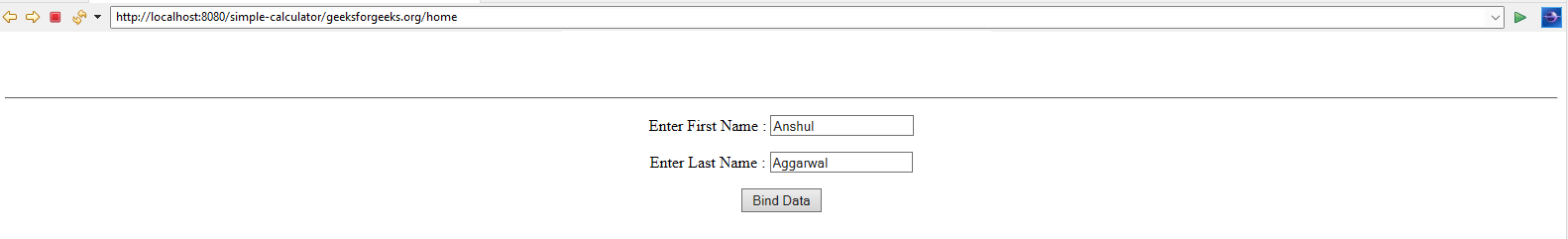
So, in the output, you can see whenever you hit the URL the values are already present which means spring successfully read the values from the variable. Now let’s put some values inside the label and click on the Bind Data. Suppose here we have put “Amiya” as First Name and “Rout” as Last Name and whenever we click on the “Bind Data” button an URL is generated as below
http://localhost:8080/simple-calculator/geeksforgeeks.org/process-homepage?firstName=Amiya&lastName=Rout
And you can see on the next page the values are displayed.
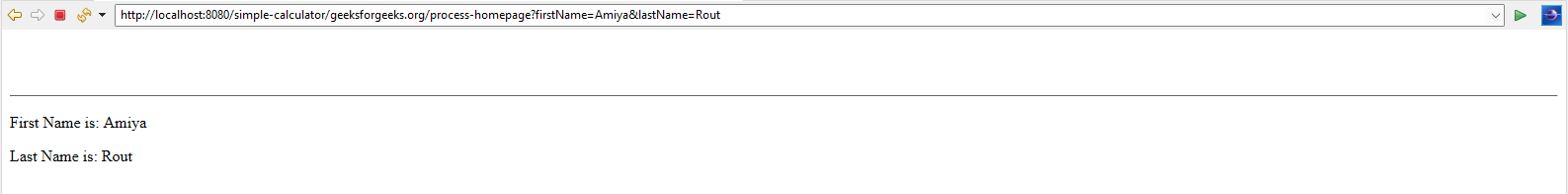
So, our application is working fine.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...