During 2013, the NSA (United States National Security Agency) scandal was leaked to the public, people started to opt for services that could provide a strong privacy for their data. Among the services people opted for, most particularly for Emails, were different plug-ins and extensions for their browsers. Interestingly, among the various plug-ins and extensions that people started to use, two main programs were solely responsible for the complete email security that the people needed. One was S/MIME which we will see later and the other was PGP.
What is PGP?
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is an encryption software program software designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of virtual communications and information. Developed with the aid of Phil Zimmermann in 1991, PGP has emerge as a cornerstone of present-day cryptography, notably regarded as one of the best methods for securing digital facts.
At its core, PGP employs a hybrid cryptographic method, combining symmetric-key and public-key cryptography techniques. Symmetric-key cryptography entails the use of a single mystery key to each encrypt and decrypt statistics. Conversely, public-key cryptography utilizes a pair of mathematically associated keys: a public key, that is freely shared and used for encryption, and a personal key, that is stored in mystery and used for decryption.
Evolution and Advancement of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) has undergone extensive evolution and advancement because its inception in 1991. Developed with the aid of Phil Zimmermann, PGP was to start with conceived as a tool to permit stable communique and protect man or woman privacy in the face of developing concerns approximately authorities surveillance and statistics interception.
- Early Development (1991-1996): PGP turned into first launched as freeware, allowing users to encrypt and decrypt e-mail messages and files the usage of public-key cryptography. This early version of PGP utilized the RSA algorithm for public-key encryption and the IDEA cipher for symmetric-key encryption. Despite its groundbreaking skills, PGP faced prison demanding situations due to export regulations on cryptographic software.
- International Expansion and Standardization (1996-2000): In 1997, PGP changed into acquired with the aid of Network Associates Inc. (NAI), which continued its improvement and improved its international presence. During this period, PGP have become a de facto preferred for e mail encryption and digital signatures, with support for multiple platforms and electronic mail customers. The OpenPGP standard, primarily based on the original PGP protocol, changed into established to make certain interoperability and compatibility among specific implementations of PGP.
- Open Source Development (2000-Present): In response to concerns about the proprietary nature of PGP and the need for transparency and security, the OpenPGP Working Group become shaped to increase an open-supply version of PGP. This caused the advent of GnuPG (GNU Privacy Guard), an open-supply implementation of the OpenPGP trendy. GnuPG remains actively maintained and widely used as a loose opportunity to industrial PGP software program.
- Modernization and Integration (2000s-Present): PGP has persisted to adapt in response to technological improvements and changing protection requirements. Modern versions of PGP provide stronger functions together with guide for elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), stepped forward key management, integration with cloud garage services, and compatibility with cellular gadgets. Additionally, PGP has been integrated into diverse encryption gear, steady e-mail customers, and agency safety answers, expanding its utility and reach.
The following are the services offered by PGP:
1. Authentication
2. Confidentiality
3. Email Compatibility
4. Segmentation
Authentication in PGP
Authentication basically means something that is used to validate something as true or real. To login into some sites sometimes we give our account name and password, that is an authentication verification procedure.
In the email world, checking the authenticity of an email is nothing but to check whether it actually came from the person it says. In emails, authentication has to be checked as there are some people who spoof the emails or some spams and sometimes it can cause a lot of inconvenience. The Authentication service in PGP is provided as follows:
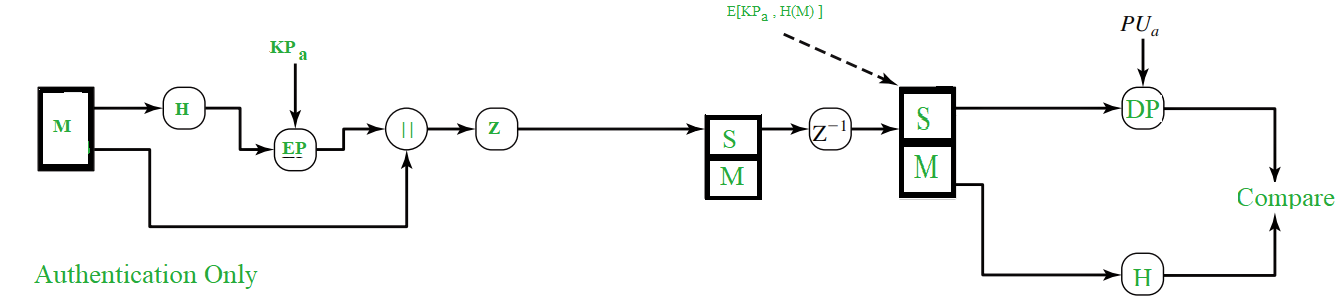
As shown in the above figure, the Hash Function (H) calculates the Hash Value of the message. For the hashing purpose, SHA-1 is used and it produces a 160 bit output hash value. Then, using the sender’s private key (KPa), it is encrypted and it’s called as Digital Signature. The Message is then appended to the signature. All the process happened till now, is sometimes described as signing the message . Then the message is compressed to reduce the transmission overhead and is sent over to the receiver.
At the receiver’s end, the data is decompressed and the message, signature are obtained. The signature is then decrypted using the sender’s public key(PUa) and the hash value is obtained. The message is again passed to hash function and it’s hash value is calculated and obtained.
Both the values, one from signature and another from the recent output of hash function are compared and if both are same, it means that the email is actually sent from a known one and is legit, else it means that it’s not a legit one.
2. Confidentiality in PGP
Sometimes we see some packages labelled as ‘Confidential’, which means that those packages are not meant for all the people and only selected persons can see them. The same applies to the email confidentiality as well. Here, in the email service, only the sender and the receiver should be able to read the message, that means the contents have to be kept secret from every other person, except for those two.
PGP provides that Confidentiality service in the following manner:
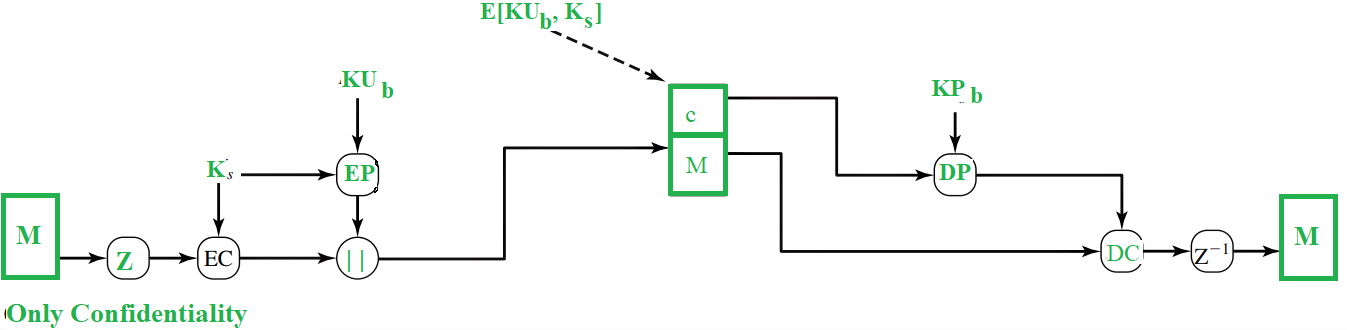
Then, the session key (Ks) itself gets encrypted through public key encryption (EP) using receiver’s public key(KUb) . Both the encrypted entities are now concatenated and sent to the receiver.
As you can see, the original message was compressed and then encrypted initially and hence even if any one could get hold of the traffic, he cannot read the contents as they are not in readable form and they can only read them if they had the session key (Ks). Even though session key is transmitted to the receiver and hence, is in the traffic, it is in encrypted form and only the receiver’s private key (KPb)can be used to decrypt that and thus our message would be completely safe.
At the receiver’s end, the encrypted key is decrypted using KPb and the message is decrypted with the obtained session key. Then, the message is decompressed to obtain the M.
RSA algorithm is used for the public-key encryption and for the symmetric key encryption, CAST-128(or IDEA or 3DES) is used.
Practically, both the Authentication and Confidentiality services are provided in parallel as follows :
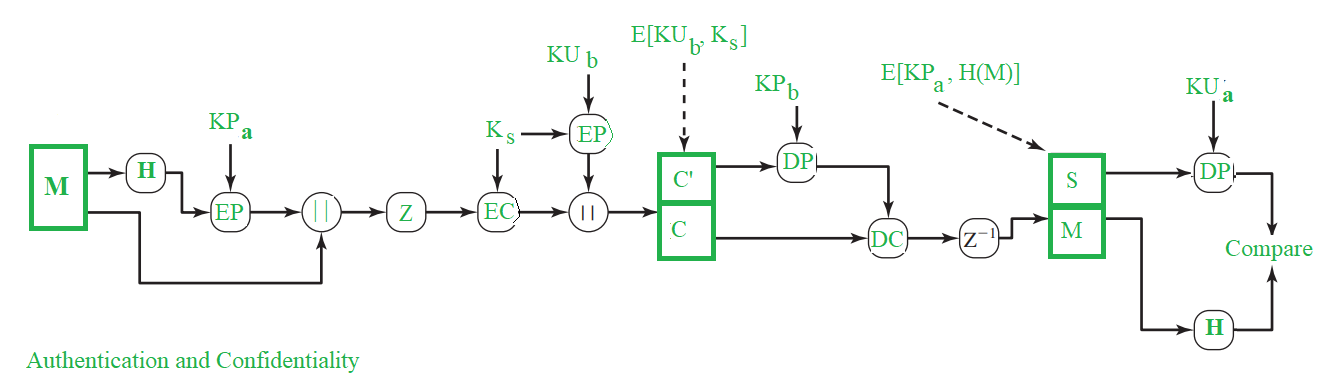
Note:
M – Message
H – Hash Function
Ks – A random Session Key created for Symmetric Encryption purpose
DP – Public-Key Decryption Algorithm
EP – Public-Key Encryption Algorithm
DC – Asymmetric Decryption Algorithm
EC – Symmetric Encryption Algorithm
KPb – A private key of user B used in Public-key encryption process
KPa – A private key of user A used in Public-key encryption process
PUa – A public key of user A used in Public-key encryption process
PUb – A public key of user B used in Public-key encryption process
|| – Concatenation
Z – Compression Function
Z-1 – Decompression Function
Why Authentication and Confidentiality are important in PGP?
Authentication and confidentiality play pivotal roles in Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), ensuring the security and integrity of virtual verbal exchange. Authentication, carried out thru virtual signatures, verifies the identity of the sender and safeguards towards spoofing and impersonation. By signing messages with their personal key, senders offer recipients with a means to verify the authenticity of the verbal exchange. This authentication mechanism not simplest fosters agree with among parties but additionally guarantees message integrity, as virtual signatures verify that the message has not been tampered with at some stage in transmission. On the opposite hand, confidentiality, facilitated via encryption, protects the content material of messages from unauthorized access. Through encryption algorithms, PGP scrambles the message, rendering it unreadable to everybody with out the decryption key. This ensures that touchy facts stays private and inaccessible to eavesdroppers and unauthorized parties. Together, authentication and confidentiality in PGP set up a stable framework for relied on conversation, allowing individuals and corporations to change information confidentially and securely while keeping privacy and integrity.
Advantages of PGP
- The primary benefit of PGP encryption lies in its unbreakable algorithm.
- It is regarded as a top technique for improving cloud security and is frequently utilised by users who need to encrypt their private conversations.
- This is due to PGP’s ability to prevent hackers, governments, and nation-states from accessing files or emails that are encrypted with PGP.
Disadvantage of PGP
- The main drawback of PGP encryption is that it is usually not intuitive to use. PGP requires time and effort to fully encrypt data and files, which might make messaging more difficult for users. If an organisation is thinking about deploying PGP, it has to train its employees.
- It is imperative that users comprehend the intricacies of the PGP system to prevent unintentionally weakening their security measures. This may occur from using PGP incorrectly or from losing or corrupting keys, endangering other users in situations where security is at an extreme.
- Absence of anonymity: PGP encrypts user messages but does not provide users with any anonymity. This makes it possible to identify the source and recipient of emails sent using a PGP solution.
Conclusion
Today, PGP continues to play a key role in protecting digital privacy and protecting sensitive information for individuals, businesses and organizations worldwide Through integration into a range of encryption tools, email clients and enterprise security solutions, -And a reliable and widely used tool for supporting authority, as technology continues to evolve, PGP will no doubt continue to evolve alongside it, cementing its position as a secure network and the cornerstone of digital privacy for years to come.
Frequently Asked Question on PGP- FAQs
Who developed PGP?
PGP was designed by Phil Zimmermann way back in 1991.
Can PGP be used for file encryption?
Yes PGP can be used for file encryption.
What is keyserver in PGP?
Keyserver is a server that store PGP public keys.
Drawbacks of PGP?
The main drawback of PGP encryption is that it is usually not intuitive to use. PGP requires time and effort to fully encrypt data and files, which might make messaging more difficult for users. If an organisation is thinking about deploying PGP, it has to train its employees.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...