Nodal Analysis
Last Updated :
27 Feb, 2024
In this article, we will understand the nodal analysis with solved examples. We will discuss nodes and their types. We will discuss the procedure for nodal analysis along with some rules. We will also discuss the super node. Then we will see how nodal analysis is different from mesh analysis. Later in the article, we will discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
What is Nodal Analysis?
Nodal analysis is a type of circuit analysis in electrical networks. It analyses the circuit using the node voltages. A node is a point in a circuit where two or more branches or elements of a circuit network meet. The potential difference between nodes is used to find various parameters of the circuit. It applies to both the planar and non-planar networks, unlike mesh analysis. KCL is the main law that is used in the nodal analysis along with it KVL and Ohm’s law are also used.
Types of Nodes
There are two types of nodes used in nodal analysis.
Reference node
It is the node that is used as a reference point for all other nodes. It provides a Standard point from which measurements, comparisons and valuations are made. There are different types of reference node based on their function and Connection
Types of Reference Node
- Chassis Ground: When the node is common in more than one circuit then it is known as Chassis ground. This type of Reference node is connected in the chassis of the equipment which server as a common ground point for multiple circuits.
- Earth Ground: If the reference point is connected to the earth’s Potential or ground, then it is referred as earth ground. This type of reference forms connection between the electrical systems and earth which provides a safe path for electrical electric current to dissipate.
Non-Reference Node:
It is the node that has a definite voltage assigned to it. Unlike reference nodes, which serve as common points of reference for measurements and comparisons, non-reference nodes have predetermined voltages associated with them. These voltages may be established by power sources, voltage dividers, or other circuit components.

Nodal analysis Circuit Diagram
In the above diagram V1,V2,V3 are the non-reference nodes and the ground is taken as reference nodes. The current from nodes shown is how we write the KCL equations.
Procedure and Rules for applying Nodal Analysis
Given below are Procedure and Rules for applying Nodal Analysis
Procedure of applying Nodal Analysis
Following are the steps that need to be followed for applying nodal analysis to a circuit network.
- Identify the number of nodes in the circuit.
- Select one of the nodes as reference node and it is assigned ground potential. All other nodes are referred to as non-reference nodes and are assigned unknown voltages.
- Develop KCL equations at each non-refence nodes
- Solve the equations to find node voltages.
Rules for applying Nodal Analysis
- The total number of equation is equal to the total number of non-reference nodes (e=N-1) where n is the total number of nodes.
- Reference node is the node which has the maximum number of branches connected.
- Reference node is taken mostly at the bottom of the circuit and its value is taken as 0V for making calculation easy.
Basic steps for developing equations in Nodal Analysis
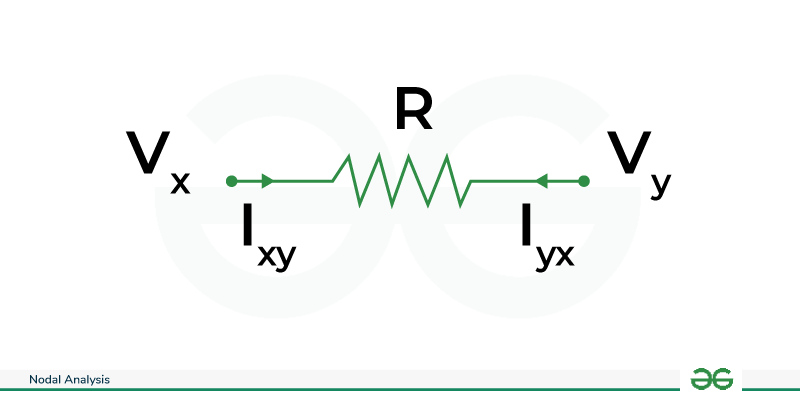
Steps

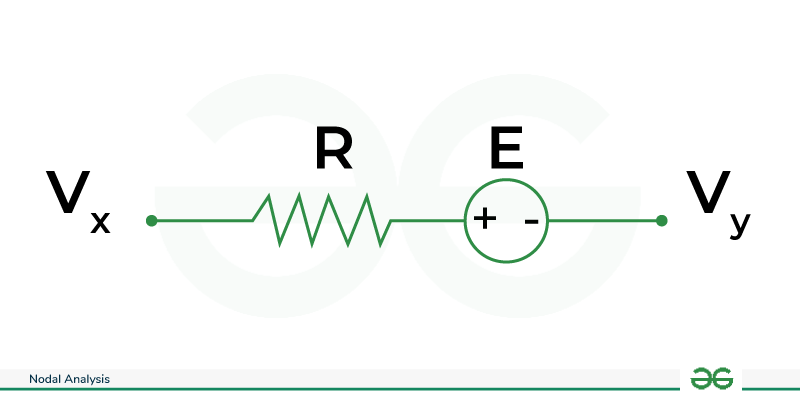
Steps
using KVL,


Steps
 , depending on the direction of current
, depending on the direction of current
Nodal Analysis Solved Example
Q. Using nodal analysis find the value of K which will cause Vy to be zero

Question
Using KCL at node x,

KCL at node y,

Q. Using nodal analysis find I(With Voltage source)
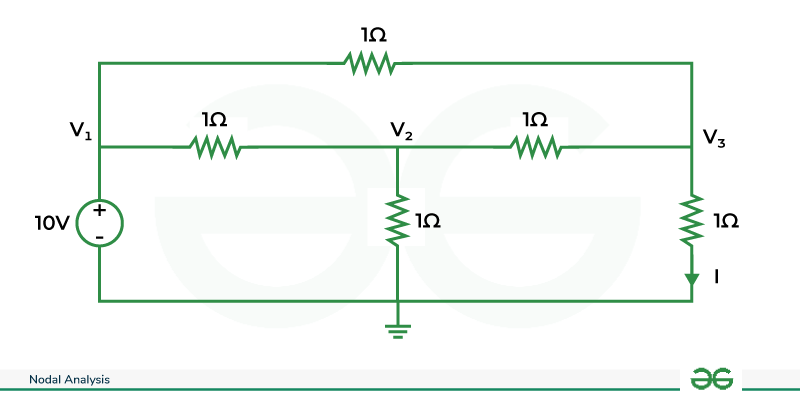
Question
We find the voltage of V1 ,
KCL at node 2:-

KCL at node 3:-

Solving the equations we get,

Q.Find V1 and V2 using nodal analysis(With current Source)
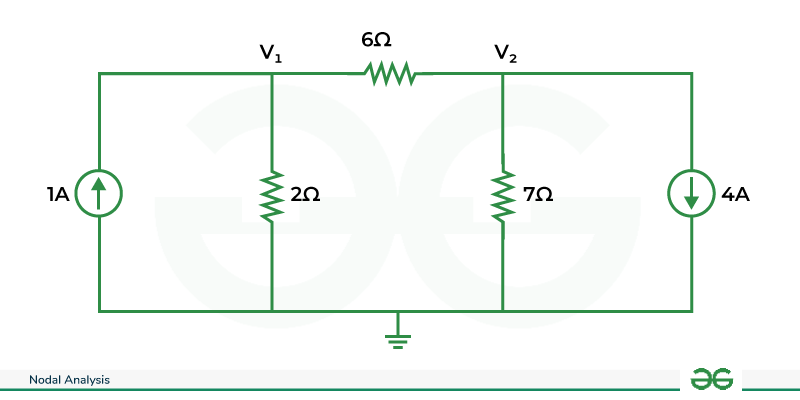
Question
Applying KCL at node 1,

Applying KCL at node 2,

Solving two equations we get,

Super Node Analysis
Super node is special condition of nodes. When a voltage source is present between two non-reference node then it is called as super node. KVL and KCL are both applied to the super node to solve the equations. The procedure remains same as normal nodal analysis but after writing the current equations of different nodes they are added together to define the super node equation and KVL for the super node is applied for solving the equations and finding the node voltages.
Properties of Super node
- It does not have well defined voltage
- Both KCL and KVL are required to solve the equations
- The voltage difference is zero between any two nodes in super node
Nodal Analysis Solved Examples
Q. Using nodal analysis find V1 and V2
.png)
Question
As the Voltage source is between two non-reference nodes then this a super node.
KCL at node 1,
KCL at node 2,
Adding equation 1 and 2 for writing the super node equation

By KVL on super node we get,
Solving equation 3 and 4 we get, 
Nodal Analysis Vs Mesh Analysis
Mesh Analysis
| Nodal Analysis
|
|---|
It is done through meshes
| Nodes are used for analyzing
|
KVL was the main law being used
| KCL was the main law being used
|
Mesh currents were found to find other variables
| No voltages were found to find other variables
|
Applicable to only planar network
| Applicable to both planar and non-planar network.
|
Used for circuit with more current sources
| Used for circuit with more voltage sources.
|
Applications
- Its most common application is in circuital analysis for complex circuits with multiple nodes.
- It is used for designing of circuits and also help in optimizing the circuits.
- It is used to analyze the power distribution in power systems and control systems. Also used for optimization of these systems.
Advantages
- Nodal analysis is simple to apply and makes complex circuit easy to solve.
- It has a systematic approach which helps the application easy by following steps.
- It can be applied to both planar network and non planar network.
- It can be used in both AC and DC circuit.
Disadvantages
- It becomes more complex to solve in case non-linear circuit as it is limited to linear relationships.
- Identification of nodes is very important as choosing wrong nodes may lead to errors.
- It is not able to provide proper results in case of voltage and current dependent sources.
Conclusions
In conclusion, nodal analysis is a systematic approach of solving complex circuits using node voltages. It uses KCL, KVL and ohm’s law for forming the equations. When a voltage source is present between two non-reference nodes then the node is known as super node. It is used for designing and optimizing circuits and also for power and control systems. It is versatile to use as it is applicable to AC, DC, Planar and non-planar circuits. It also have some limitations like for non-linear networks it becomes difficult to solve the circuits. Although having limitation it is still widely used for solving circuit networks.
FAQs on Nodal Analysis
How is reference node is selected?
The node where most of the of branches meet is selected as reference node. The reference node is mostly selected at the bottom of the circuit for easier calculation.
What are the main differences of nodal and analysis?
Nodal analysis can be used for both planar and non-planar networks whereas mesh can be used only for planar circuits. Mesh analysis is done using mesh currents and nodal analysis uses nodal voltages.
Where is KVL used in nodal analysis ?
KVL is used in case the case of super node where a voltage is connected between two non-reference nodes. IT is used to derive a equation between these non-reference nodes and further help in solving equations .
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...