ML | Raw and Central Moments
Last Updated :
25 May, 2022
Moments are a set of statistical parameters which are used to describe different characteristics and feature of a frequency distribution i.e. central tendency, dispersion, symmetry, and peakedness (hump) of the frequency curve. For Ungrouped data i.e. discrete data, observations on a variable X are obtained as 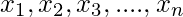 , For Grouped data i.e. continuous data, observations on a variable X are obtained and tabulated in K class intervals in a frequency table. The mid points of the intervals are denoted by
, For Grouped data i.e. continuous data, observations on a variable X are obtained and tabulated in K class intervals in a frequency table. The mid points of the intervals are denoted by 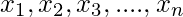 which occur with frequencies
which occur with frequencies 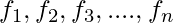 respectively and
respectively and 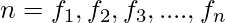 .
.
| Class Intervals | Mid Points (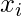 ) ) | Absolute Frequency (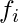 ) ) |
|---|
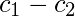 | 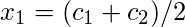 |  |
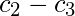 | 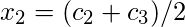 | 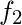 |
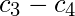 | 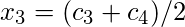 | 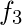 |
| … | … | … |
| … | … | … |
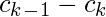 | 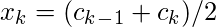 | 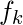 |
Moments about an arbitrary point A The 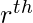 moment of a variable X about any arbitrary point A on the observations
moment of a variable X about any arbitrary point A on the observations 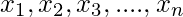 is defined as:
is defined as:
For ungrouped data 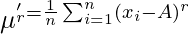 For grouped data
For grouped data 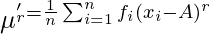 where
where 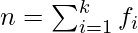
Moment about any arbitrary point in Python – Consider the given data points. Following are the time (in hours) spent by 20 different persons at GeeksforGeeks portal every week.
15, 25, 18, 36, 40, 28, 30, 32, 23, 22, 21, 27, 31, 20, 14, 10, 33, 11, 7, 13
Python3
time = [15, 25, 18, 36, 40, 28, 30, 32, 23, 22,
21, 27, 31, 20, 14, 10, 33, 11, 7, 13]
A = 22
moment = (sum([(item-A) for item in time]))/len(time)
|
Raw Moments –
The 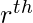 moment around origin A = 0 known as raw moment and is defined as:
moment around origin A = 0 known as raw moment and is defined as:
For ungrouped data, 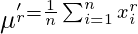 For grouped data,
For grouped data, 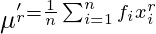 where,
where, 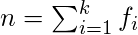
Notes:
-> We can find first raw moment (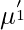 ) just by replacing r with 1 and second raw moment (
) just by replacing r with 1 and second raw moment (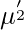 ) just by replacing r with 2 and so on. -> When r = 0 the moment
) just by replacing r with 2 and so on. -> When r = 0 the moment 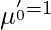 for both grouped and ungrouped data.
for both grouped and ungrouped data.
Raw moment in Python –
Python3
time = [15, 25, 18, 36, 40, 28, 30, 32, 23,
22, 21, 27, 31, 20, 14, 10, 33, 11, 7, 13]
moment = sum(time)/len(time)
|
Central Moments –
The moments of a variable X about the arithmetic mean (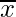 ) are known as central moments and defined as:
) are known as central moments and defined as:
For ungrouped data,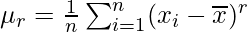 For grouped data,
For grouped data,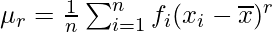 where
where 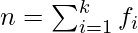 and
and 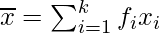
Notes:
-> We can find first raw moment (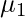 ) just by replacing r with 1 and second raw moment (
) just by replacing r with 1 and second raw moment (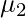 ) just by replacing r with 2 and so on. -> When r = 0 the moment
) just by replacing r with 2 and so on. -> When r = 0 the moment 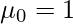 , and when r = 1 the moment
, and when r = 1 the moment 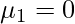 for both grouped and ungrouped data.
for both grouped and ungrouped data.
Python3
time = [15, 25, 18, 36, 40, 28, 30, 32, 23, 22,
21, 27, 31, 20, 14, 10, 33, 11, 7, 13]
A = sum(time)/len(time)
moment = (sum([(item-A) for item in time]))/len(time)
|
Relationship between Raw and Central moments – 
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...