Mesh Analysis
Last Updated :
08 Apr, 2024
In this article, We will discuss mesh current method. We will discuss the definition of mesh and the Steps for applying mesh analysis. We will discuss some rules that should be kept in mind while solving the circuits using Mesh analysis. We will also discuss the super mesh analysis and the steps for implementing it. Later in the article, we will differentiate between nodal and mesh analysis. At the end, we will discuss the applications, advantages, and disadvantages of the mesh analysis.
What is Mesh Analysis?
In circuit analysis, loop is an important term. Any closed path in a circuit is known as a loop. In mesh analysis, we solve the circuit by defining meshes in the circuit. A mesh is a loop that does not have any inner loop or it is the smallest possible loop in the circuit. Mesh analysis is only applicable to the planar network. A planar network is a network that can be drawn in a plane where none of its branches are crossing one another. A circuit network can be rearranged to make it planar but it can’t be simplified to make the network a planar network.
Mesh Current Diagram

Circuit Diagram of Mesh Analysis
In the above diagram, we can see that L1 and L2 are meshes whereas L3 is not as it has inner loops L1 andL2. It shows the circuit diagram for mesh analysis.
Steps to Conduct Mesh Analysis
To apply mesh analysis to a particular circuit network the following steps need to be followed :-
- Check if the network is planar or not. If rearrangement possible rearrange to make the network planar.
- Identify the total number of meshes in the circuit network.
- Assign mesh currents to each mesh.
- Develop the KVL equation in each mesh.
- Solve the KVL equations to find the mesh currents.
Rules of Mesh Analysis
- Direction of the flow of current inside the mesh can be in any direction either clockwise or anticlockwise. In most cases , it is taken to be clockwise as it is simpler.
- Direction should remain same for all the meshes.
- The number of equation required to sole an electrical network with the help of Mesh formula is:-
- e=M=b-(N-1)
- Where,
- e is the number of equations
- M is the number of meshes
- b is the number of branches
- N is the number of nodes
- We can say, number of equations = number of meshes
- When a resistor is common to two meshes then the current of the mesh for which we are writing the equation that current is given high value and the current of the other mesh is subtracted from it.
Solved Examples on Mesh Analysis
Solved Examples on Mesh Analysis are given below for better understanding :
Find the current I(current through 10 ohm resistor) using Mesh Analysis.

Solved Example Circuit Diagram 1
We first analyze the circuit and as it is planar we move forward with the mesh analysis. Next, we observe that the network has two meshes and then assign current I1 and I2 to the meshes respectively.

Circuit Diagram with Meshes 1
Developing the KVL equation for the Mesh-1,
[Tex]10-5I_1-5(I_1-I_2)=0 \newline \Rightarrow2I_1-I_2 =2 -(1)
[/Tex]
Developing the KVL equation for the Mesh-2,
[Tex]-5(I_2-I_1)-10I_2=0 \newline \Rightarrow3I_2-I_1 =0 -(2)
[/Tex]
Solving equation (1) and (2) ,
[Tex]3I_2 = I_1 \:from\: (2) \newline Putting\:values\: in\:(1)
\newline \Rightarrow 6I_2 – I_2 =2 \newline \Rightarrow I_2=\frac{2}{5}=0.4A
\newline \Rightarrow \because I_2=I \newline\therefore I=0.4A
[/Tex]
Find the current I using Mesh Analysis.

Solved Example Circuit Diagram 2
We first analyze the circuit and as it is planar we move forward with the mesh analysis. Next, we observe that the network has three meshes and then assign current I1, I2 and I3 to the meshes respectively.

Solved Example Circuit Diagram 3
KVL in Mesh -1
[Tex]5-I_1 -(I_1-I_2)=0 \newline \Rightarrow 2I_1-I_2=5 -(1)
[/Tex]
KVL in Mesh – 2
[Tex]-I_2 -(I_2-I_3)-2i -(I_2-I_1)=0 \newline\because i=I_1-I_2 \newline\Rightarrow -I_1-I_2+I_3=0 -(2)
[/Tex]
KVL in Mesh – 3
[Tex]-I_3+2i-(I_3-I_2)=0\newline\because i=I_1-I_2 \newline\Rightarrow 2I_1-I_2-2I_3=0 -(3)
[/Tex]
Solving equations (1)-(3) ,
[Tex]2I_3=5 \newline \Rightarrow I_3=2.5A \newline As,\:I=I_3 \therefore I=2.5A
[/Tex]
What is a Supermesh?
It is special method of mesh analysis where the current source is common between two meshes. When two meshes shares a current source the number of equations and variables don’t match so we consider the supermesh. thus, with the help of KCL at one node we will be able to get another equation
Steps for Supermesh Analysis
- Identify the current source that is common to meshes.
- Remove that source and the loop that you will get is supermesh.
- Assign mesh current in meshes like mesh analysis.
- Apply KVL in supermesh and develop the equation.
- Apply KCL to either node of the current source.
- Solve the KCL and KVL equation.
Solved Example of Supermesh Analysis
Find ix in the given circuit

Solved Example Circuit Diagram 3
In the given circuit we can see that the 3A current source is common so supermesh analysis will be used here.
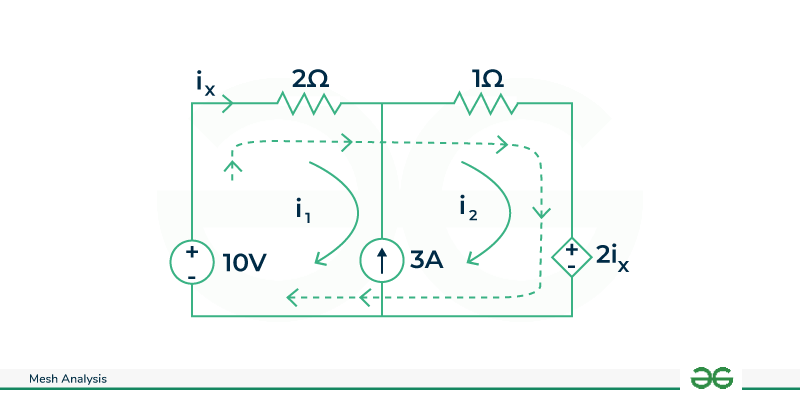
Circuit Diagram with Supermesh
Applying KVL in the supermesh
[Tex]10-2i_1-i_2-2i_x=0 \newline As,i_x=i_1
\newline \therefore 2i_1+i_2+2i_1=10
\newline \Rightarrow 4i_1+i_2=10-(1)
\newline applying\:KCL,\newline i_2-i_1=3-(2)
\newline Solving\: (1) and (2)
\newline \Rightarrow 5i_1=7
\newline \Rightarrow i_1=\frac{7}{5}A
\newline As, i_x=i_1\newline \therefore i_x=\frac{7}{5}A
[/Tex]
Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis
Mesh analysis is used for determining the current in meshes of planar circuit using KVL. Nodal analysis is used for determining voltages at nodes of the planar or non-planar circuits using KCL.
Difference between Mesh Analysis and Nodal Analysis
Mesh Analysis and Nodal Analysis are differentiated in detail below:
Mesh Analysis
| Nodal Analysis
|
|---|
In mesh analysis we divide the circuit into meshes for solving it.
| In nodal analysis we use different nodes in the circuit for solving the circuit
|
We assign currents to the meshes and find them.
| We find the voltage at different nodes.
|
Mesh analysis uses KVL for developing equations and the number of equal to the number of meshes.
| Nodal Analysis uses KCL for developing equations and the number of equations will depend on the number of nodes.
|
It is applicable for planar networks only.
| It is applicable for both planar and non-planar networks.
|
Useful for networks with current sources.
| Useful for networks with voltage sources.
|
Applications of Mesh Analysis
- It used for solving complex electrical networks and to determine current, voltage drop at any point of the circuit.
- In power systems, it is used to understand the flow of current and voltage in complex power networks.
- In control systems it is used in the analysis of feedback systems.
- It is used in finding faults and correcting them.
Advantages of Mesh Analysis
- It simplifies the circuit calculation and finding voltage and current at different points of the circuits.
- It has systematic and easy to implement approach.
- It reduces the number of equations in circuit solutions.
- It can be used in implementation of other network theorems like Thevenin, Norton, etc.
Disadvantages of Mesh Analysis
- It is only applicable to planar circuits.
- In case of presence of dependent sources the number of equation increases.
- It is limited to use in linear circuits
- If mesh and mesh current is not correctly assigned then the solution becomes complex and sometimes wrong.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mesh analysis is a useful method for solving complex circuits with the help of KVL, KCL and Ohm’s law. It reduces the number of equations for solving electrical circuit networks. Supermesh is another method that is used when there is a common current source between two meshes. While is useful in many areas like control systems, power systems, electrical networks but it has some limitations as well. It is only applicable for planar and linear circuits and also if dependent sources are present then the number of equation increases and it becomes difficult to solve. Although it has these limitations but still it is used in many network theorems for calculations.
Mesh Analysis – FAQs
Which laws are used in Mesh Analysis?
In mesh analysis, KVL and ohm’s law is used and in supermesh analysis KCL, KVL, and Ohm’s law is used.
What are the conditions that needs to be satisfied for implementing mesh analysis?
The electrical network should be planar and linear for mesh analysis to be applicable.
What is the difference between dependent and independent source?
In independent source is a source who is not dependent on any other voltage or current in the circuit whereas a dependent source is dependent on any other current or voltage source.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...