The chain of superior-subordinate relationships is known as the Levels of Management. The three levels of management are Top Level Management, Middle-Level Management, and Operational Level Management.
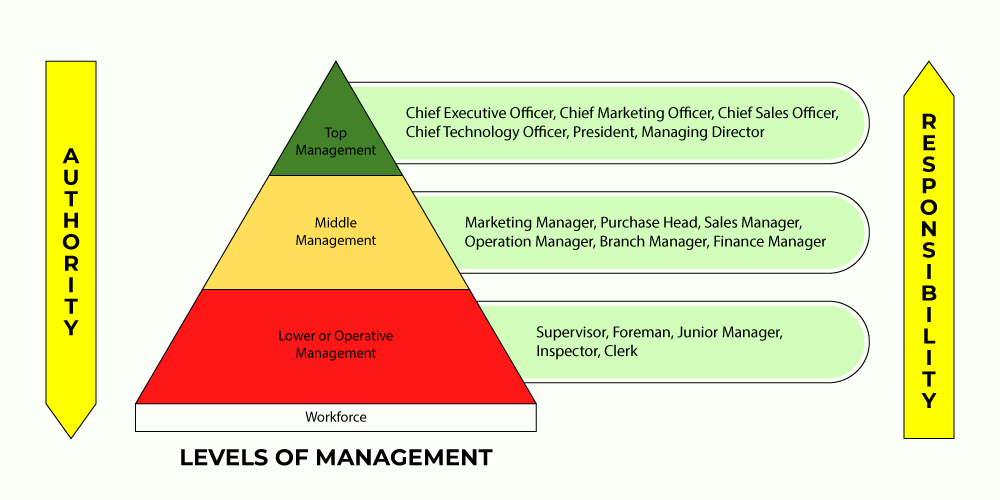
Management is a group activity, which means that every organization has a number of individuals placed at different positions and are provided with different responsibilities according to their skills, education, etc. For the fulfillment of the responsibilities given to the members of an organization, they are also provided with the required authority. Based on the amount and extent of responsibility and authority given to these members, a chain of superior-subordinate relationships is formed. This chain of superior-subordinate relationships is known as the Levels of Management. There are three levels of management; viz., Top Level Management, Middle Level Management, and Operational Level Management.
Three Levels of Management
1. Top Level Management
The senior most executives of the organization are found at the top level of management. The top level of an organization’s management consists of the Board of Directors, Managing Director, Chairman, Chief Executive Officer, Chief Operating Officer, Vice-President, President, General Manager, and other Senior Executives. The managers at the top level of management of an organization are responsible for its survival and welfare. These managers perform stressful and complex work that demands long hours and commitment towards the company.
Functions of the Top Level Management
i) Determination of the objectives for the organization: The managers at the top level management formulates the goals or objectives for an organization along with the strategies to achieve those goals.
ii) Framing of plans and policies: For the achievement of the pre-determined goals or objectives of an organization, it is essential to formulate proper strategies, plans and policies within the organization. The top level managers are responsible for the formulation of these plans and policies.
iii) Coordination and control of the performance: Based on the overall pre-determined objectives of the organization, the top level managers coordinate and control different activities of different departments of the organization.
iv) Analysis of the business environment: Business environment of an organization plays a crucial role in its success and survival. The managers at the top level of management of an organization carefully analyze the business environment and its implication and make necessary decisions for better results.
v) Setting up an organizational framework: For the success and survival of an organization, it is essential to form a proper framework or structure within the company. The top level managers are responsible for the determination of the organizational framework for the proper and successful execution of its plans and policies.
vi) Assembling of the resources: Achievement of the organizational goals requires different resources of materials, machines, men, money and materials. It is the duty of the managers at the top level management to arrange these resources.
2. Middle Level Management
The next level of management is the Middle Level, which serves as a link between the Top Level Management and the Lower Level Management. The middle level management is superior to the lower or operational level management and subordinate to the top level management. The middle level of an organization’s management consists of different functional department heads, such as Departmental Managers including Production, Purchase, Finance, Personnel, Marketing Managers, and other executive officers for different departments such as plant superintendent, etc. The employees or members of the middle level management are responsible to the top level management for their performance.
Functions of the Middle Level Management
i) Interpretation of the policies framed by the Top Level Management: As the middle level management acts as a subordinate to the top level management, the managers at this level have to clearly interpret the plans and policies framed by the managers at the top level management to the managers at the lower or operational level management.
ii) Selection of suitable operative and supervisory personnel: To perform any function properly, an organization needs the required personnel. It is the duty of the Middle Level Managers to make sure that the organization has sufficient personnel with them to perform the functions and duties better. For the fulfillment of this duty, the middle level managers recruit and select suitable employees for different departments based on the applicant’s skills, etc., and the firm’s requirements.
iii) Assigning of duties and responsibilities to the Lower Level Management: The middle level managers acts as superior to the operational level managers. These managers have to assign respective duties and responsibilities to the lower level managers and coordinate with them regarding the activities of different work units.
iv) Motivating employees to get desired objectives: An organization can effectively and efficiently achieve its desired goals only when its employees are motivated enough to work towards the betterment of the organization. Therefore, the managers at the middle level management motivate the employees towards the achievement of the organizational goals and improvement of their performance.
v) Cooperating with the entire organization: As middle level management serves as a link between the top level management and the lower level management, the managers at this level have to cooperate with every other department for the smooth functioning of the organization.
3. Lower Level Management
The last level of management is the lower level management and is also known as the Supervisory or Operational Level Management. The managers at the lower level of management play a crucial role in the proper management of an organization, as they directly interact with the actual work force and interpret the instructions of the middle level managers to them. The responsibility and authority of the lower level managers depend upon the plans and policies formed by the top level management. The lower level management consists of foremen, supervisors, section officers, superintendents, and other managers who have direct control over the operative employees of the organization.
Functions of the Lower Level Management
i) Issuing of orders and instructions: The managers at the operational level management issue orders to the workers and supervisors and instructs them on their roles, responsibilities, and authority. Besides, these managers also control the functioning of the workers.
ii) Preparation of plan for activities: The lower level managers plan the day-to-day activities of the organization. Besides, these managers also assign work to the subordinates, guide them for the same, and take corrective measures wherever and whenever necessary.
iii) Assigning and assisting in work: The job or responsibility of the lower level managers includes assigning work to the subordinates and assisting them with the work. They do so by explaining the work procedure to the employees and solving their problems for better performance.
iv) Representing workers’ grievances: As the managers at the lower level management are in direct contact with the managers at the middle level management, they listen to the grievances of the workers and report those issues to the middle level managers.
v) Ensuring a safe and proper work environment: The lower level managers are responsible for providing the work force with a safe and proper work environment. They also have to maintain proper discipline and a good atmosphere within the organization, as it motivates the employees to work towards the accomplishment of the organizational goals.
vi) Helping the middle level management: The managers at the operational level management helps the middle level managers in selecting, training, placing, and promoting the workers of an organization as they can give a direct insight as to what is required for the achievement of the organizational goals and about the performance of the workers.
vii) Encourage initiative of employees: The best way to motivate employees and make them feel an important part of the organization is by encouraging them to take initiative. The lower level managers do so by welcoming their suggestions and ideas and by rewarding them for the good ones.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...