To implement a stack using the singly linked list concept, all the singly linked list operations should be performed based on Stack operations LIFO(last in first out) and with the help of that knowledge, we are going to implement a stack using a singly linked list.
So we need to follow a simple rule in the implementation of a stack which is last in first out and all the operations can be performed with the help of a top variable. Let us learn how to perform Pop, Push, Peek, and Display operations in the following article:
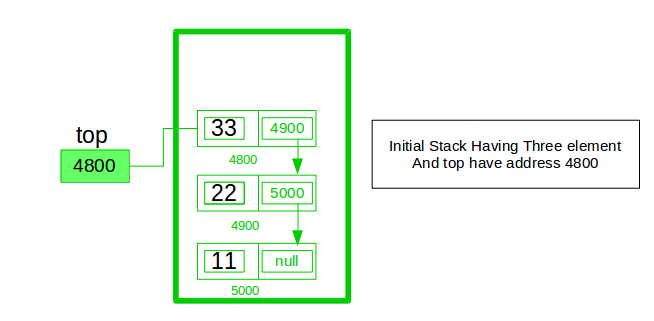
In the stack Implementation, a stack contains a top pointer. which is the “head” of the stack where pushing and popping items happens at the head of the list. The first node has a null in the link field and second node-link has the first node address in the link field and so on and the last node address is in the “top” pointer.
The main advantage of using a linked list over arrays is that it is possible to implement a stack that can shrink or grow as much as needed. Using an array will put a restriction on the maximum capacity of the array which can lead to stack overflow. Here each new node will be dynamically allocated. so overflow is not possible.
Stack Operations:
- push(): Insert a new element into the stack i.e just insert a new element at the beginning of the linked list.
- pop(): Return the top element of the Stack i.e simply delete the first element from the linked list.
- peek(): Return the top element.
- display(): Print all elements in Stack.
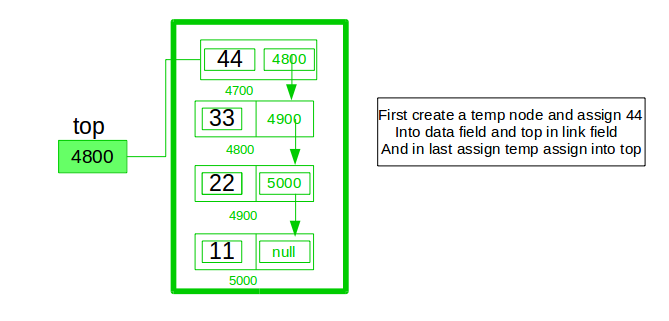
Push Operation:
- Initialise a node
- Update the value of that node by data i.e. node->data = data
- Now link this node to the top of the linked list
- And update top pointer to the current node
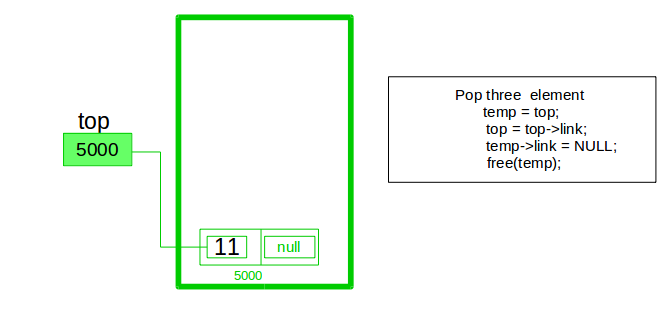
Pop Operation:
- First Check whether there is any node present in the linked list or not, if not then return
- Otherwise make pointer let say temp to the top node and move forward the top node by 1 step
- Now free this temp node
Peek Operation:
- Check if there is any node present or not, if not then return.
- Otherwise return the value of top node of the linked list
Display Operation:
- Take a temp node and initialize it with top pointer
- Now start traversing temp till it encounters NULL
- Simultaneously print the value of the temp node
Below is the implementation of the above operations
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* link;
Node(int n)
{
this->data = n;
this->link = NULL;
}
};
class Stack {
Node* top;
public:
Stack() { top = NULL; }
void push(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node(data);
if (!temp) {
cout << "\nStack Overflow";
exit(1);
}
temp->data = data;
temp->link = top;
top = temp;
}
bool isEmpty()
{
return top == NULL;
}
int peek()
{
if (!isEmpty())
return top->data;
else
exit(1);
}
void pop()
{
Node* temp;
if (top == NULL) {
cout << "\nStack Underflow" << endl;
exit(1);
}
else {
temp = top;
top = top->link;
free(temp);
}
}
void display()
{
Node* temp;
if (top == NULL) {
cout << "\nStack Underflow";
exit(1);
}
else {
temp = top;
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data;
temp = temp->link;
if (temp != NULL)
cout << " -> ";
}
}
}
};
int main()
{
Stack s;
s.push(11);
s.push(22);
s.push(33);
s.push(44);
s.display();
cout << "\nTop element is " << s.peek() << endl;
s.pop();
s.pop();
s.display();
cout << "\nTop element is " << s.peek() << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import static java.lang.System.exit;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StackUsingLinkedlist obj
= new StackUsingLinkedlist();
obj.push(11);
obj.push(22);
obj.push(33);
obj.push(44);
obj.display();
System.out.printf("\nTop element is %d\n",
obj.peek());
obj.pop();
obj.pop();
obj.display();
System.out.printf("\nTop element is %d\n",
obj.peek());
}
}
class StackUsingLinkedlist {
private class Node {
int data;
Node link;
}
Node top;
StackUsingLinkedlist() { this.top = null; }
public void push(int x)
{
Node temp = new Node();
if (temp == null) {
System.out.print("\nHeap Overflow");
return;
}
temp.data = x;
temp.link = top;
top = temp;
}
public boolean isEmpty() { return top == null; }
public int peek()
{
if (!isEmpty()) {
return top.data;
}
else {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
}
public void pop()
{
if (top == null) {
System.out.print("\nStack Underflow");
return;
}
top = (top).link;
}
public void display()
{
if (top == null) {
System.out.printf("\nStack Underflow");
exit(1);
}
else {
Node temp = top;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data);
temp = temp.link;
if(temp != null)
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def isempty(self):
if self.head == None:
return True
else:
return False
def push(self, data):
if self.head == None:
self.head = Node(data)
else:
newnode = Node(data)
newnode.next = self.head
self.head = newnode
def pop(self):
if self.isempty():
return None
else:
poppednode = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
poppednode.next = None
return poppednode.data
def peek(self):
if self.isempty():
return None
else:
return self.head.data
def display(self):
iternode = self.head
if self.isempty():
print("Stack Underflow")
else:
while(iternode != None):
print(iternode.data, end = "")
iternode = iternode.next
if(iternode != None):
print(" -> ", end = "")
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
MyStack = Stack()
MyStack.push(11)
MyStack.push(22)
MyStack.push(33)
MyStack.push(44)
MyStack.display()
print("\nTop element is ", MyStack.peek())
MyStack.pop()
MyStack.pop()
MyStack.display()
print("\nTop element is ", MyStack.peek())
|
C#
using System;
public class StackUsingLinkedlist {
private class Node {
public int data;
public Node link;
}
Node top;
public StackUsingLinkedlist() { this.top = null; }
public void push(int x)
{
Node temp = new Node();
if (temp == null) {
Console.Write("\nHeap Overflow");
return;
}
temp.data = x;
temp.link = top;
top = temp;
}
public bool isEmpty() { return top == null; }
public int peek()
{
if (!isEmpty()) {
return top.data;
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
}
public void pop()
{
if (top == null) {
Console.Write("\nStack Underflow");
return;
}
top = (top).link;
}
public void display()
{
if (top == null) {
Console.Write("\nStack Underflow");
return;
}
else {
Node temp = top;
while (temp != null) {
Console.Write(temp.data);
temp = temp.link;
if(temp != null)
Console.Write(" -> ");
}
}
}
}
public class GFG {
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
StackUsingLinkedlist obj
= new StackUsingLinkedlist();
obj.push(11);
obj.push(22);
obj.push(33);
obj.push(44);
obj.display();
Console.Write("\nTop element is {0}\n", obj.peek());
obj.pop();
obj.pop();
obj.display();
Console.Write("\nTop element is {0}\n", obj.peek());
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node
{
constructor()
{
this.data=0;
this.link=null;
}
}
class StackUsingLinkedlist
{
constructor()
{
this.top=null;
}
push(x)
{
let temp = new Node();
if (temp == null) {
document.write("<br>Heap Overflow");
return;
}
temp.data = x;
temp.link = this.top;
this.top = temp;
}
isEmpty()
{
return this.top == null;
}
peek()
{
if (!this.isEmpty()) {
return this.top.data;
}
else {
document.write("Stack is empty<br>");
return -1;
}
}
pop()
{
if (this.top == null) {
document.write("<br>Stack Underflow");
return;
}
this.top = this.top.link;
}
display()
{
if (this.top == null) {
document.write("<br>Stack Underflow");
}
else {
let temp = this.top;
while (temp != null) {
document.write(temp.data+"->");
temp = temp.link;
}
}
}
}
let obj = new StackUsingLinkedlist();
obj.push(11);
obj.push(22);
obj.push(33);
obj.push(44);
obj.display();
document.write("<br>Top element is ", obj.peek()+"<br>");
obj.pop();
obj.pop();
obj.display();
document.write("<br>Top element is ", obj.peek()+"<br>");
|
Output
44 -> 33 -> 22 -> 11
Top element is 44
22 -> 11
Top element is 22
Time Complexity: O(1), for all push(), pop(), and peek(), as we are not performing any kind of traversal over the list. We perform all the operations through the current pointer only.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), where N is the size of the stack
In this implementation, we define a Node class that represents a node in the linked list, and a Stack class that uses this node class to implement the stack. The head attribute of the Stack class points to the top of the stack (i.e., the first node in the linked list).
To push an item onto the stack, we create a new node with the given item and set its next pointer to the current head of the stack. We then set the head of the stack to the new node, effectively making it the new top of the stack.
To pop an item from the stack, we simply remove the first node from the linked list by setting the head of the stack to the next node in the list (i.e., the node pointed to by the next pointer of the current head). We return the data stored in the original head node, which is the item that was removed from the top of the stack.
Benefits of implementing a stack using a singly linked list include:
Dynamic memory allocation: The size of the stack can be increased or decreased dynamically by adding or removing nodes from the linked list, without the need to allocate a fixed amount of memory for the stack upfront.
Efficient memory usage: Since nodes in a singly linked list only have a next pointer and not a prev pointer, they use less memory than nodes in a doubly linked list.
Easy implementation: Implementing a stack using a singly linked list is straightforward and can be done using just a few lines of code.
Versatile: Singly linked lists can be used to implement other data structures such as queues, linked lists, and trees.
In summary, implementing a stack using a singly linked list is a simple and efficient way to create a dynamic stack data structure in Python.
Real time examples of stack:
Stacks are used in various real-world scenarios where a last-in, first-out (LIFO) data structure is required. Here are some examples of real-time applications of stacks:
Function call stack: When a function is called in a program, the return address and all the function parameters are pushed onto the function call stack. The stack allows the function to execute and return to the caller function in the reverse order in which they were called.
Undo/Redo operations: In many applications, such as text editors, image editors, or web browsers, the undo and redo functionalities are implemented using a stack. Every time an action is performed, it is pushed onto the stack. When the user wants to undo the last action, the top element of the stack is popped and the action is reversed.
Browser history: Web browsers use stacks to keep track of the pages visited by the user. Every time a new page is visited, its URL is pushed onto the stack. When the user clicks the “Back” button, the last visited URL is popped from the stack and the user is directed to the previous page.
Expression evaluation: Stacks are used in compilers and interpreters to evaluate expressions. When an expression is parsed, it is converted into postfix notation and pushed onto a stack. The postfix expression is then evaluated using the stack.
Call stack in recursion: When a recursive function is called, its call is pushed onto the stack. The function executes and calls itself, and each subsequent call is pushed onto the stack. When the recursion ends, the stack is popped, and the program returns to the previous function call.
In summary, stacks are widely used in many applications where LIFO functionality is required, such as function calls, undo/redo operations, browser history, expression evaluation, and recursive function calls.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...