Check for Balanced Brackets in an expression (well-formedness)
Last Updated :
04 May, 2023
Given an expression string exp, write a program to examine whether the pairs and the orders of “{“, “}”, “(“, “)”, “[“, “]” are correct in the given expression.
Example:
Input: exp = “[()]{}{[()()]()}”
Output: Balanced
Explanation: all the brackets are well-formed
Input: exp = “[(])”
Output: Not Balanced
Explanation: 1 and 4 brackets are not balanced because
there is a closing ‘]’ before the closing ‘(‘
Check for Balanced Bracket expression using Stack:
The idea is to put all the opening brackets in the stack. Whenever you hit a closing bracket, search if the top of the stack is the opening bracket of the same nature. If this holds then pop the stack and continue the iteration. In the end if the stack is empty, it means all brackets are balanced or well-formed. Otherwise, they are not balanced.
Illustration:
Below is the illustration of the above approach.
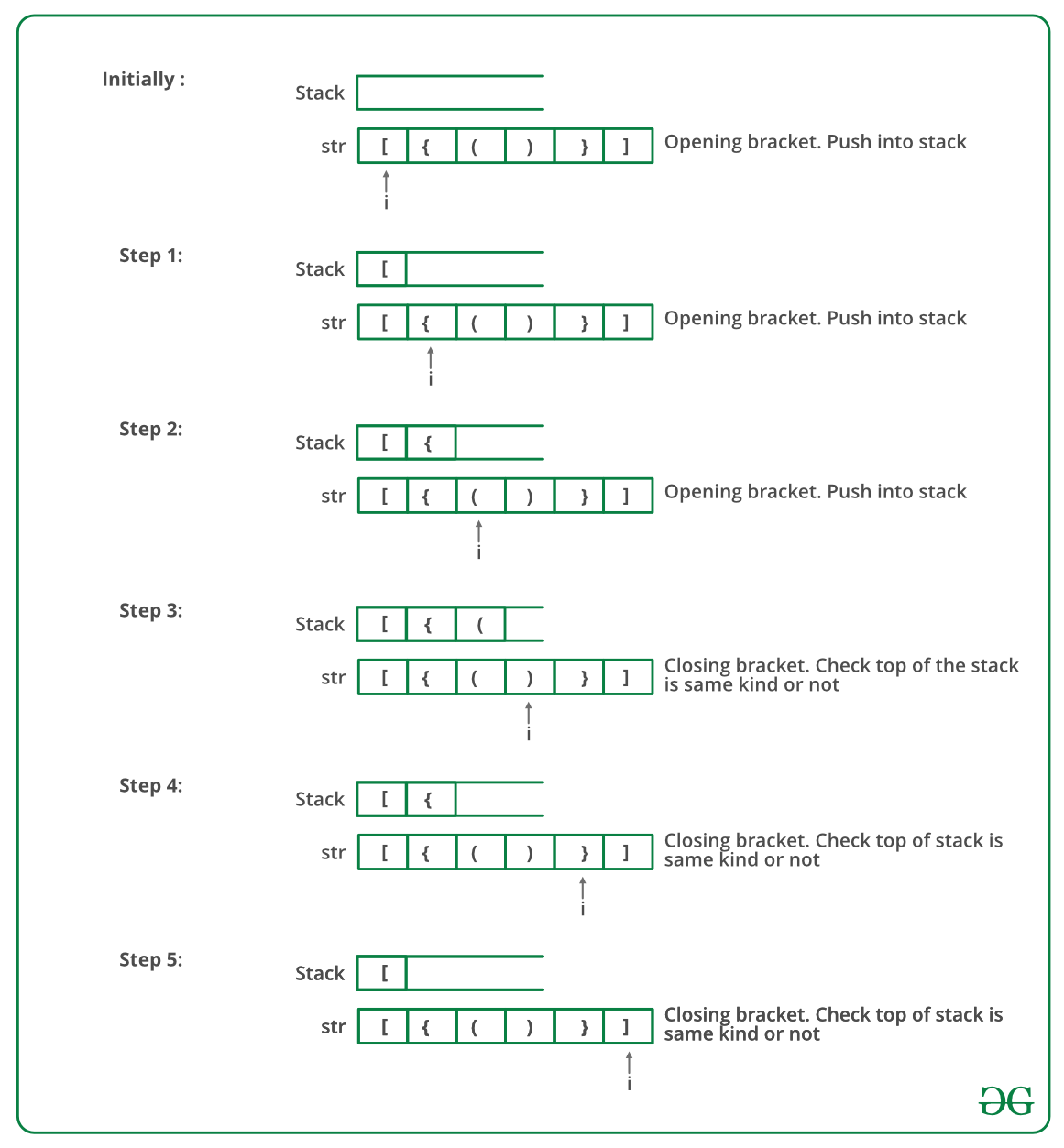
Follow the steps mentioned below to implement the idea:
- Declare a character stack (say temp).
- Now traverse the string exp.
- If the current character is a starting bracket ( ‘(‘ or ‘{‘ or ‘[‘ ) then push it to stack.
- If the current character is a closing bracket ( ‘)’ or ‘}’ or ‘]’ ) then pop from the stack and if the popped character is the matching starting bracket then fine.
- Else brackets are Not Balanced.
- After complete traversal, if some starting brackets are left in the stack then the expression is Not balanced, else Balanced.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool areBracketsBalanced(string expr)
{
stack<char> temp;
for (int i = 0; i < expr.length(); i++) {
if (temp.empty()) {
temp.push(expr[i]);
}
else if ((temp.top() == '(' && expr[i] == ')')
|| (temp.top() == '{' && expr[i] == '}')
|| (temp.top() == '[' && expr[i] == ']')) {
temp.pop();
}
else {
temp.push(expr[i]);
}
}
if (temp.empty()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
string expr = "{()}[]";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
cout << "Balanced";
else
cout << "Not Balanced";
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define bool int
struct sNode {
char data;
struct sNode* next;
};
void push(struct sNode** top_ref, int new_data);
int pop(struct sNode** top_ref);
bool isMatchingPair(char character1, char character2)
{
if (character1 == '(' && character2 == ')')
return 1;
else if (character1 == '{' && character2 == '}')
return 1;
else if (character1 == '[' && character2 == ']')
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
bool areBracketsBalanced(char exp[])
{
int i = 0;
struct sNode* stack = NULL;
while (exp[i]) {
if (exp[i] == '{' || exp[i] == '(' || exp[i] == '[')
push(&stack, exp[i]);
if (exp[i] == '}' || exp[i] == ')'
|| exp[i] == ']') {
if (stack == NULL)
return 0;
else if (!isMatchingPair(pop(&stack), exp[i]))
return 0;
}
i++;
}
if (stack == NULL)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char exp[100] = "{()}[]";
if (areBracketsBalanced(exp))
printf("Balanced \n");
else
printf("Not Balanced \n");
return 0;
}
void push(struct sNode** top_ref, int new_data)
{
struct sNode* new_node
= (struct sNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct sNode));
if (new_node == NULL) {
printf("Stack overflow n");
getchar();
exit(0);
}
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*top_ref);
(*top_ref) = new_node;
}
int pop(struct sNode** top_ref)
{
char res;
struct sNode* top;
if (*top_ref == NULL) {
printf("Stack overflow n");
getchar();
exit(0);
}
else {
top = *top_ref;
res = top->data;
*top_ref = top->next;
free(top);
return res;
}
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class BalancedBrackets {
static boolean areBracketsBalanced(String expr)
{
Deque<Character> stack
= new ArrayDeque<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < expr.length(); i++) {
char x = expr.charAt(i);
if (x == '(' || x == '[' || x == '{') {
stack.push(x);
continue;
}
if (stack.isEmpty())
return false;
char check;
switch (x) {
case ')':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '{' || check == '[')
return false;
break;
case '}':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '(' || check == '[')
return false;
break;
case ']':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '(' || check == '{')
return false;
break;
}
}
return (stack.isEmpty());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String expr = "([{}])";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
System.out.println("Balanced ");
else
System.out.println("Not Balanced ");
}
}
|
Python3
def areBracketsBalanced(expr):
stack = []
for char in expr:
if char in ["(", "{", "["]:
stack.append(char)
else:
if not stack:
return False
current_char = stack.pop()
if current_char == '(':
if char != ")":
return False
if current_char == '{':
if char != "}":
return False
if current_char == '[':
if char != "]":
return False
if stack:
return False
return True
if __name__ == "__main__":
expr = "{()}[]"
if areBracketsBalanced(expr):
print("Balanced")
else:
print("Not Balanced")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class BalancedBrackets {
public class stack {
public int top = -1;
public char[] items = new char[100];
public void push(char x)
{
if (top == 99) {
Console.WriteLine("Stack full");
}
else {
items[++top] = x;
}
}
char pop()
{
if (top == -1) {
Console.WriteLine("Underflow error");
return '\0';
}
else {
char element = items[top];
top--;
return element;
}
}
Boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top == -1) ? true : false;
}
}
static Boolean isMatchingPair(char character1,
char character2)
{
if (character1 == '(' && character2 == ')')
return true;
else if (character1 == '{' && character2 == '}')
return true;
else if (character1 == '[' && character2 == ']')
return true;
else
return false;
}
static Boolean areBracketsBalanced(char[] exp)
{
Stack<char> st = new Stack<char>();
for (int i = 0; i < exp.Length; i++) {
if (exp[i] == '{' || exp[i] == '('
|| exp[i] == '[')
st.Push(exp[i]);
if (exp[i] == '}' || exp[i] == ')'
|| exp[i] == ']') {
if (st.Count == 0) {
return false;
}
else if (!isMatchingPair(st.Pop(),
exp[i])) {
return false;
}
}
}
if (st.Count == 0)
return true;
else {
return false;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
char[] exp = { '{', '(', ')', '}', '[', ']' };
if (areBracketsBalanced(exp))
Console.WriteLine("Balanced ");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not Balanced ");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function areBracketsBalanced(expr)
{
let stack = [];
for(let i = 0; i < expr.length; i++)
{
let x = expr[i];
if (x == '(' || x == '[' || x == '{')
{
stack.push(x);
continue;
}
if (stack.length == 0)
return false;
let check;
switch (x){
case ')':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '{' || check == '[')
return false;
break;
case '}':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '(' || check == '[')
return false;
break;
case ']':
check = stack.pop();
if (check == '(' || check == '{')
return false;
break;
}
}
return (stack.length == 0);
}
let expr = "([{}])";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
document.write("Balanced ");
else
document.write("Not Balanced ");
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N), Iteration over the string of size N one time.
Auxiliary Space: O(N) for the stack.
Check for Balanced Bracket expression without using stack :
Following are the steps to be followed:
- Initialize a variable i with -1.
- Iterate through the string and
- If it is an open bracket then increment the counter by 1 and replace ith character of the string with the opening bracket.
- Else if it is a closing bracket of the same corresponding opening bracket (opening bracket stored in exp[i]) then decrement i by 1.
- At last, if we get i = -1, then the string is balanced and we will return true. Otherwise, the function will return false.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool areBracketsBalanced(string s) {
int i=-1;
for(auto& ch:s){
if(ch=='(' || ch=='{' || ch=='[')
s[++i]=ch;
else{
if(i>=0 && ((s[i]=='(' && ch==')') || (s[i]=='{' && ch=='}') || (s[i]=='[' && ch==']')))
i--;
else
return false;
}
}
return i==-1;
}
int main()
{
string expr = "{()}[]";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
cout << "Balanced";
else
cout << "Not Balanced";
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class GFG {
public static boolean areBracketsBalanced(String s)
{
int i = -1;
char[] stack = new char[s.length()];
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
if (ch == '(' || ch == '{' || ch == '[')
stack[++i] = ch;
else {
if (i >= 0
&& ((stack[i] == '(' && ch == ')')
|| (stack[i] == '{' && ch == '}')
|| (stack[i] == '[' && ch == ']')))
i--;
else
return false;
}
}
return i == -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String expr = "{()}[]";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
System.out.println("Balanced");
else
System.out.println("Not Balanced");
}
}
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static bool areBracketsBalanced(string s) {
int i = -1;
char[] stack = new char[s.Length];
foreach (char ch in s) {
if (ch == '(' || ch == '{' || ch == '[')
stack[++i] = ch;
else {
if (i >= 0 && ((stack[i] == '(' && ch == ')') || (stack[i] == '{' && ch == '}') || (stack[i] == '[' && ch == ']')))
i--;
else
return false;
}
}
return i == -1;
}
static void Main() {
string expr = "{()}[]";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
Console.WriteLine("Balanced");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not Balanced");
}
}
|
Python3
def are_brackets_balanced(s):
stack = []
for ch in s:
if ch in ('(', '{', '['):
stack.append(ch)
else:
if stack and ((stack[-1] == '(' and ch == ')') or
(stack[-1] == '{' and ch == '}') or
(stack[-1] == '[' and ch == ']')):
stack.pop()
else:
return False
return not stack
expr = "{()}[]"
if are_brackets_balanced(expr):
print("Balanced")
else:
print("Not Balanced")
|
Javascript
function areBracketsBalanced(s) {
let i = -1;
let stack = [];
for (let ch of s) {
if (ch === '(' || ch === '{' || ch === '[') {
stack.push(ch);
i++;
} else {
if (i >= 0 && ((stack[i] === '(' && ch === ')') || (stack[i] === '{' && ch === '}') || (stack[i] === '[' && ch === ']'))) {
stack.pop();
i--;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
return i === -1;
}
let expr = "{()}[]";
if (areBracketsBalanced(expr))
console.log("Balanced");
else
console.log("Not Balanced");
|
Time Complexity: O(N), Iteration over the string of size N one time.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...