HTML Canvas Basics
Last Updated :
06 Sep, 2023
In this article, we will know HTML Canvas Basics, and their implementation through the examples.
The HTML “canvas” element is used to draw graphics via JavaScript. The “canvas” element is only a container for graphics. One must use JavaScript to actually draw the graphics. Canvas has several methods for drawing paths, boxes, circles, text, and adding images. The canvas would be a rectangular area on an HTML page. By default, a canvas has no border and no content.
Syntax:
<canvas>
Content...
</canvas>
It is recommended to have an id attribute (to be referred to in a script), and a width and height attribute to define the size of the canvas. To add a border, use the style attribute.
Supported Properties: The properties like Colors, Styles, Shadows, Line Styles, Rectangles, Paths, Transformations, Text, Pixel Manipulation, Compositing & Image Drawing, are the global attributes that are supported by all the canvas tags. Please refer to the HTML Canvas Complete Reference article for the details.
Example 1: This example illustrates the use of canvas with a linear gradient & stroke-style text in HTML.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="gfg"
width="300px"
height="100px"
style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3;">
</canvas>
<script>
let g = document.getElementById("gfg");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
let gradient = geeks.createLinearGradient(1, 4, g.width, 2);
gradient.addColorStop("0", "green");
gradient.addColorStop("0.4", "yellow");
gradient.addColorStop("1.0", "aqua");
geeks.font = "40px sans-serif";
geeks.fillStyle = "red";
geeks.strokeStyle = gradient;
geeks.strokeText("GeeksforGeeks", 10, 60);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

HTML canvas with a linear gradient
Example 2: The following code demonstrates the empty canvas.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="myCanvas"
width="400"
height="200"
style="border:2px solid #000000;">
</canvas>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

HTML empty canvas
There are various shapes that can be possible to draw using Canvas, which are discussed below.
Example 1: This example shows the HTML Canvas to draw a circle.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Circle Drawing</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="GFG" width="400" height="200" style="border:2px solid #d3d3d3;"></canvas>
<script>
let g = document.getElementById("GFG");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
geeks.beginPath();
geeks.arc(200, 100, 50, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
geeks.stroke();
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
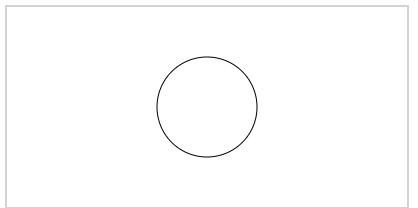
Drawing Circle with HTML Canvas
Example 2: In this example, we will write a text using HTML Canvas.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="GFG"
width="600"
height="200"
style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3;">
</canvas>
<script>
let g = document.getElementById("GFG");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
geeks.font = "30px Arial";
geeks.fillText("GeeksForGeeks", 170, 50);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

Writing text with HTML Canvas
Example 3: This example illustrates the use of linear-gradient property in HTML Canvas.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="GFG"
width="400"
height="200"
style="border:2px solid #d3d3d3;">
</canvas>
<script>
let G = document.getElementById("GFG");
let geeks = G.getContext("2d");
let grd = geeks.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 200, 0);
grd.addColorStop(0, "yellow");
grd.addColorStop(1, "grey");
geeks.fillStyle = grd;
geeks.fillRect(50, 50, 300, 80);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
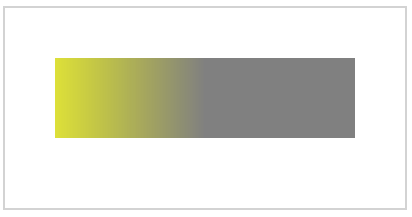
HTML Canvas with linear-gradient
Example 4: In this example, we will draw the image by using the <canvas> tag.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Image to use:</p>
<img id="image"
src=
alt="GeeksforGeeks logo"
width="250"
height="200">
<p>Canvas to fill:</p>
<canvas id="gfg"
width="300"
height="300"
style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3; ">
</canvas>
<p>
<button onclick="gfg()">
Click to Try
</button>
</p>
<script>
function gfg() {
let g = document.getElementById("gfg");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
let img = document.getElementById("image");
geeks.drawImage(img, 0, 0);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

Drawing image with tag
Example 5: This example demonstrates the use of the Shadow blur property in HTML Canvas.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="GFG"
width="500"
height="250" ;>
</canvas>
<script>
let g = document.getElementById("GFG");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
geeks.shadowBlur = 20;
geeks.shadowColor = "yellow";
geeks.fillStyle = "red";
geeks.fillRect(30, 20, 100, 80);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

HTML Canvas with Shadow blur property
Example 6: In this example, we will use rotate() method in the HTML Canvas.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="GFG"
width="300"
height="150;">
</canvas>
<script>
let g = document.getElementById("GFG");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
geeks.rotate(20 * Math.PI / 180);
geeks.fillRect(100, 20, 100, 50);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

HTML Canvas with rotate() method
Example 7: In this example, we have used the translate() method to remap the (0,0) position on the canvas.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="GFG"
width="300"
height="150;">
</canvas>
<script>
let g = document.getElementById("GFG");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
geeks.fillRect(10, 10, 100, 50);
geeks.translate(80, 90);
geeks.fillRect(10, 10, 100, 50);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
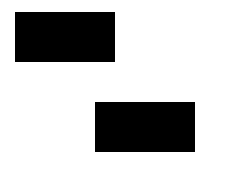
HTML Canvas with translate() method
Example 8: This example illustrates the use of the transform() method in HTML Canvas.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="GFG"
width="300"
height="150;">
</canvas>
<script>
let g = document.getElementById("GFG");
let geeks = g.getContext("2d");
geeks.fillStyle = "yellow";
geeks.fillRect(0, 0, 250, 100)
geeks.transform(1, 0.5, -0.5, 1, 30, 10);
geeks.fillStyle = "grey";
geeks.fillRect(0, 0, 250, 100);
geeks.transform(1, 0.5, -0.5, 1, 30, 10);
geeks.fillStyle = "black";
geeks.fillRect(0, 0, 250, 100);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

HTML Canvas with transform() method
Creating Animation in HTML Canvas: JavaScript helps to simulate good animation over an HTML5 canvas. Two important JavaScript methods which can be used to animate an image on a canvas:
- setInterval(callback, time): This method repeatedly executes the supplied code after a given time.
- setTimeout(callback, time): This method executes the supplied code only once after a given time.
Supported Browser:
- Google Chrome 93.0
- Microsoft Edge 93.0
- IE 11.0
- Firefox 92.0
- Opera 78.0
- Safari 14.1
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...