How to Enable Hibernate in Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
Last Updated :
02 Feb, 2024
Hibernate is a power-saving feature in Ubuntu that saves your open programs and files before completely shutting down. It allows restoring your previous session as it was when you powered on again. This means you don’t have to reopen your work after restarting Ubuntu. Enabling hibernate makes this useful feature available in the power options. It can improve workflow convenience on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS for desktops and laptops. The process involves installing a package and editing a configuration file to activate hibernate support. It improves resumes and preserves the work state on rebooting Ubuntu systems.
Importance of Hibernate Mode
Hibernate mode saves what you are working on so you can turn off your computer without losing your work. It stores your open documents, browser tabs, and programs even when powered down. When you turn your computer back on, everything reopens right where you left off. This allows you to temporarily shut down without rebooting from scratch and lose your progress. It’s a convenient way for beginners to take a break while ensuring nothing gets erased from memory. In short, hibernate lets you safely power off your computer without consequences to your open tasks.
Steps to Enable Hibernation in Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
Method 1 : Using Terminal
Step 1: Getting the UUID
The Following command is used to get the UUID ( Universal Unique Identifier ) of the Linux swap partition configured on your Ubuntu system.
sudo blkid | grep swap
The resulting line printed shows attributes of the active Linux swap partition, including the UUID unique identifier.
Copy these UUID Because , we’re gonna need it in the Next Step.
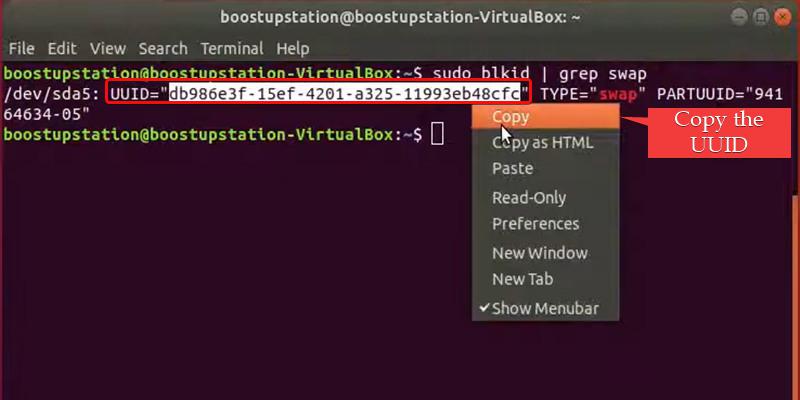
Use the Given Command to See UUID
Step 2 : Open the Grub folder with Gedit and Edit the file
First of all we need to Open and edit the Grub file to do that use the below Command and hit Enter.
sudo gedit /etc/default/grub
This command opens the main GRUB configuration file for editing using the gedit text editor.
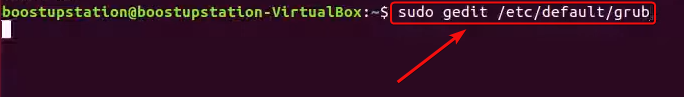
Open the GRUB File in Gedit text editor
We need to edit this file to add the resume device parameter for hibernation support. This tells GRUB which Linux swap partition to use when resuming from hibernation.
quiet splash resume=UUID=" Paste Your UUID here "
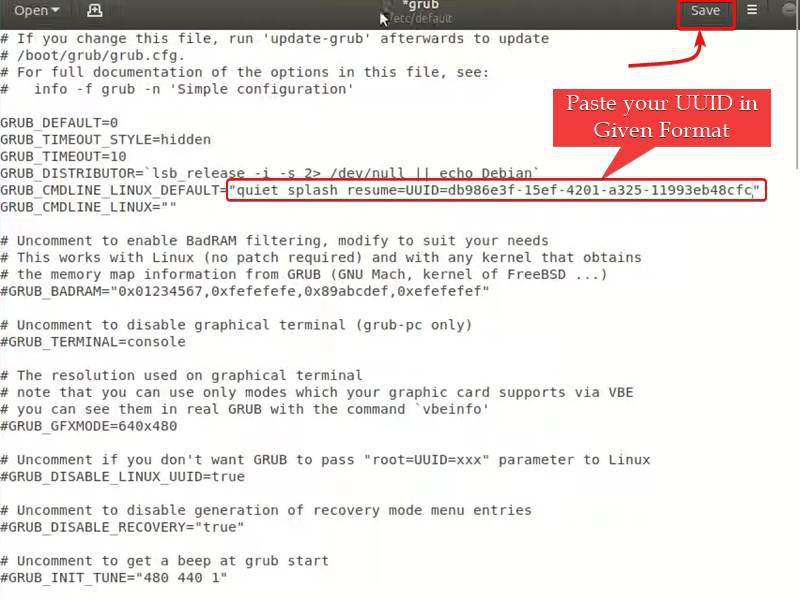
Paste your UUID
Step 3 : Update the GRUB File
The Following command is used to generate and update the GRUB boot menu after changes have been made to the GRUB configuration files.
sudo update-grub
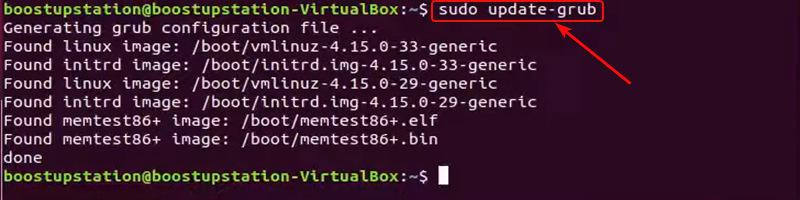
Updating the GRUB file
This Command applies edits made to GRUB files and creates an updated boot menu reflecting those changes.
Step 4 : Start the Hibernation
The Following command is used to immediately hibernate your Ubuntu system by Saving & suspending machine state to disk.
sudo systemctl hibernate
Hibernation saves the current system state including RAM contents to disk and powers down the machine.
When powered back on, the saved system state is restored and programs/sessions resume as they were before hibernation.
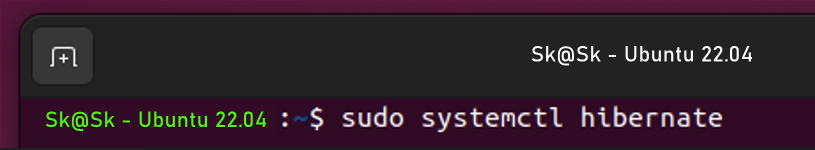
Start the Hibernation using this Command
Method 2 : Using GUI
Step 1 : Open the Terminal
Open the file with the help of the following command. It will open in Gedit or if Gedit is not installed, you can open the file in Nano text editor by replacing “gedit” with “nano” :
sudo gedit /var/lib/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/hibernate.pkla
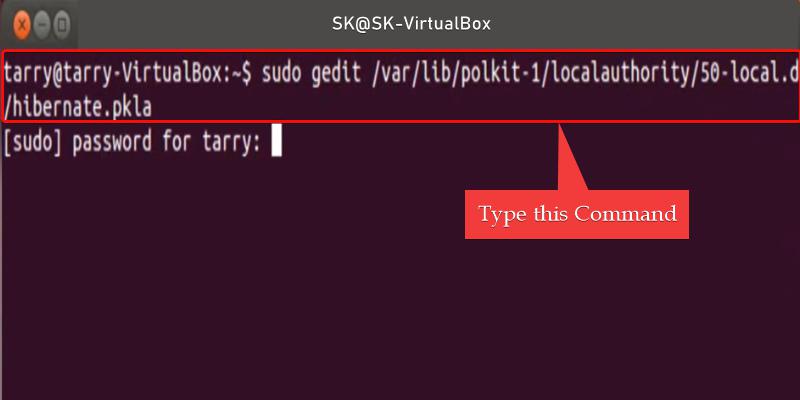
Type or Paste the Command
Step 2 : Paste the Command and Restart the Ubuntu System
Paste the following commands to enable the hibernate button in the power menu:
[Re-enable hibernate by default]
Identity=unix-user:*
Action=org.freedesktop.upower.hibernate
ResultActive=yes
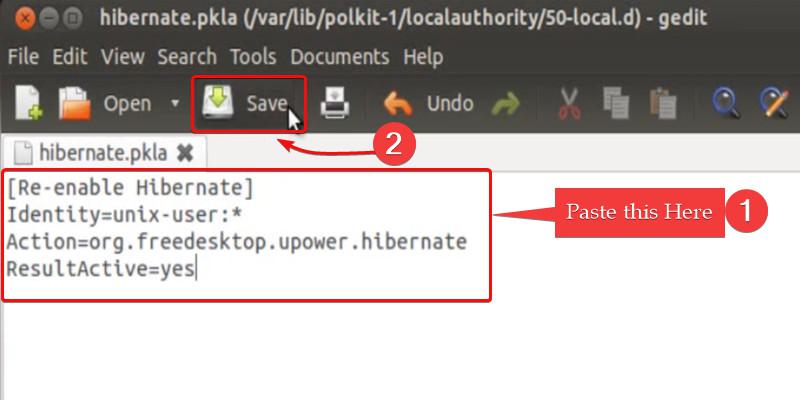
Enable Hibernate Button Command
After pasting the commands, save and close the file. Then restart your Ubuntu system for the changes to take effect.
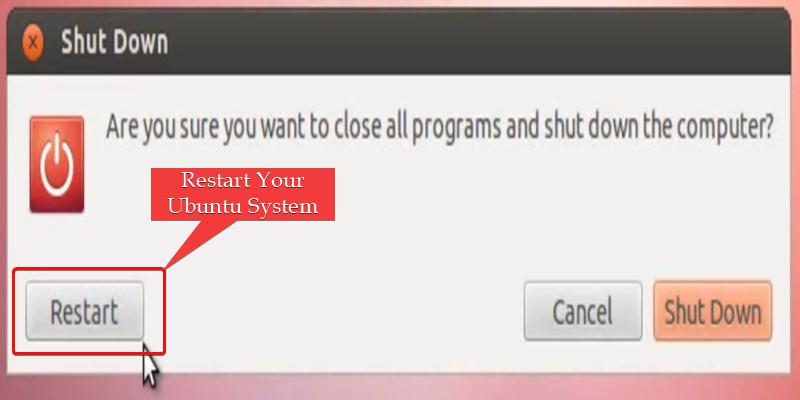
Restart the Ubuntu System
Step 3 : Enable the Hibernation
After , Restarting the System open the Power Menu The hibernate option should now be available in the power menu after rebooting.
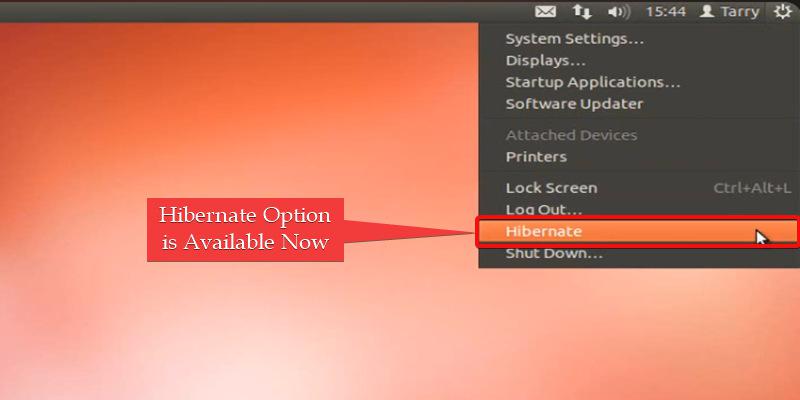
Hibernate Button Shortcut is Available
Conclusion
Hibernate lets you conveniently resume your Ubuntu system after powering off by restoring your open programs and files. Enabling it allows your work to continue where you left off. The process involves installing a package, editing boot configurations to activate hibernation, and updating the boot menu. A few precise terminal commands set up Ubuntu to hibernate when chosen from the UI power option or when entering the ‘systemctl hibernate’ command. In short, it enables preserving active sessions on power off to improve workflow for Ubuntu desktop users.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...