Financial Statement with Adjustment with Examples-V
Last Updated :
23 Jun, 2023
Through adjustments in the financial statement, we consider all the accounting items which are relevant to the current financial year, but not recorded in the books due to any reason or wrongly recorded. This helps us in getting the actual profit or loss for the year and the accurate financial position of the company. Six basic adjustments, like Use of Goods in Business, Manager’s Commission on Profit, Deferred Revenue Expenditure, Contingent Liability, Sale of Goods on Sale or Return Basis, Goods in Transit are discussed below.
The goods which have been purchased by the trader in order to run the business efficiently and brought into the firm for use by the business are known to be the goods for use in business.
Adjustment:
A. If Use of Goods in Business is given outside the trial balance:
In such a case, two effects will take place:
- Deducted from Purchases A/c in the Trading A/c.
- Shown as an Asset on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
B. If Use of Goods in Business is given inside the trial balance:
It will only be shown as an Asset on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
The manager may be paid a commission due to an increase in sales of the business. This commission is paid on the net profit of the company. There can be two instances i.e. it can be paid before or after charging a commission.
Adjustment:
A. If Manager’s Commission is given outside the trial balance
In such case, two effects will take place:
- Shown in the Dr. side of the Profit & Loss A/c.
- Shown as an Outstanding Liability on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
B. If Manager’s Commission is given inside the trial balance
It will only be shown in the Dr. side of the Profit & Loss A/c.
Deferred revenue expenditure means the expenditure, the benefit of which is accrued in more than one accounting period. In other words, it means that the expense that has been incurred at once, its benefit shall be received in the coming years as well. If the whole expense is debited in the current year, it may lead to an underestimation of the profit of the business and the balance sheet may not depict the correct financial position of the business. So, this expense is distributed over the different years in terms of the benefit that are estimated to be received every year.
Adjustment:
A. If Deferred Revenue Expenditure is given outside the trial balance:
- Will be shown in the Dr. side of the Profit & Loss A/c.
- The balance amount shall appear as an asset on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
B. If Deferred Revenue Expenditure is given inside the trial balance:
Only the balance amount shall appear as an asset on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
4. Contingent Liability:
Contingent Liability is the liability that may or may not arise in the future. It is not recorded on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet but is shown in Notes to Accounts. For example, order of the court.
5. Sale of Goods on Sale or Return Basis:
Sale of goods may be made on a sale or return basis. This sale should not be recorded as an actual sale until the customer gives his approval of acceptance. In case the goods sent to customers have been recorded as an actual sale, an adjusting entry has to be passed to nullify the effect that has taken place i.e. it will be recorded as an inventory lying with the customers at the end of the year.
Adjustment:
A. If Sale of Goods on Sale or Return Basis is given outside the trial balance
In such a case, the following effects will take place:
- Deducted from Sales A/c in the Cr. Side of the Trading A/c. [At Selling Price]
- Deducted from Debtors on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet. [At Selling Price]
- Added to Closing Stock in the Cr. side of the Trading A/c. [At Cost Price]
- Added to Closing Stock in the Assets side of the Balance Sheet. [At Cost Price]
6. Goods in Transit:
When the goods are sent or dispatched by the supplier but not received by the business till the end of the year, these goods are recorded as goods in transit.
Adjustment:
A. If Goods in Transit is given outside the trial balance
In such case, two effects will take place:
- Will be shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
- Added to the Creditors A/c on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.
B. If Goods in Transit is given inside the trial balance
In such a case, it will be shown only once on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
Illustration:
Following is the trial balance of Mr. Rajan.
The following adjustments were noted:
- Goods to be used in business amounting to ₹10,000.
- The manager is entitled to commission @10% on net profit before charging such commission.
- Out of the total Advertisement expenditure incurred, only ₹4,000 belongs to the current year.
- Goods are sent to customers on a sale or return basis at cost plus 25% profit, the cost is ₹10,000.
- Goods in transit costs ₹2,000.
- Closing stock ₹4,500 to be taken into account.
Prepare Trading A/c, P & L A/c, and Balance sheet.
Solution:
Note: Contingent Liability will not be taken into account in the Balance sheet. It will be shown in Notes to Account.
Working Notes:
1. Calculation of Manager’s Commission
Manager’s Commission = 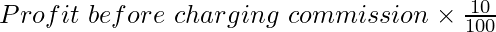
= 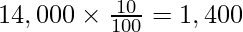
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...