File Transfer Protocol (FTP) in Application Layer
Last Updated :
23 Jan, 2024
File Transfer Protocol(FTP) is an application layer protocol that moves files between local and remote file systems. It runs on top of TCP, like HTTP. To transfer a file, 2 TCP connections are used by FTP in parallel: control connection and data connection.
What is File Transfer Protocol?
FTP is a standard communication protocol. There are various other protocols like HTTP which are used to transfer files between computers, but they lack clarity and focus as compared to FTP. Moreover, the systems involved in connection are heterogeneous, i.e. they differ in operating systems, directories, structures, character sets, etc the FTP shields the user from these differences and transfers data efficiently and reliably. FTP can transfer ASCII, EBCDIC, or image files. The ASCII is the default file share format, in this, each character is encoded by NVT ASCII. In ASCII or EBCDIC the destination must be ready to accept files in this mode. The image file format is the default format for transforming binary files.

File Transfer Protocol
Types of FTP
There are different ways through which a server and a client do a file transfer using FTP. Some of them are mentioned below:
- Anonymous FTP: Anonymous FTP is enabled on some sites whose files are available for public access. A user can access these files without having any username or password. Instead, the username is set to anonymous, and the password is to the guest by default. Here, user access is very limited. For example, the user can be allowed to copy the files but not to navigate through directories.
- Password Protected FTP: This type of FTP is similar to the previous one, but the change in it is the use of username and password.
- FTP Secure (FTPS): It is also called as FTP Secure Sockets Layer (FTP SSL). It is a more secure version of FTP data transfer. Whenever FTP connection is established, Transport Layer Security (TLS) is enabled.
- FTP over Explicit SSL/TLS (FTPES): FTPES helps by upgrading FTP Connection from port 21 to an encrypted connection.
- Secure FTP (SFTP): SFTP is not a FTP Protocol, but it is a subset of Secure Shell Protocol, as it works on port 22.
How Does FTP Work?
FTP is a client server protocol that has two communication channel, command channel for conversation control and data channel for file content.
Here are steps mentioned in which FTP works:
- A user has to log in to FTP Server first, there may be some servers where you can access to content without login, known as anonymous FTP.
- Client can start a conversation with server, upon requesting to download a file.
- The user can start different functions like upload, delete, rename, copy files, etc. on server.
FTP can work on different modes like Active and Passive modes. For more, you can refer to Difference between Active and Passive FTP.
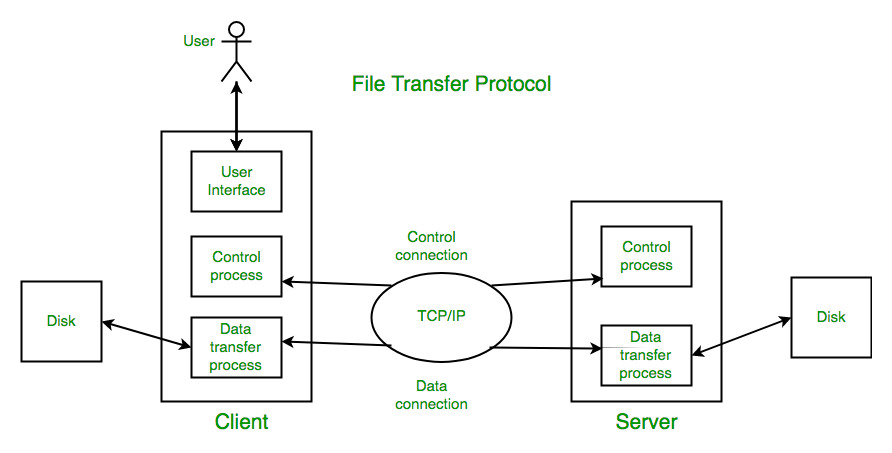
Types of Connection in FTP
- Control Connection
- Data Connection
Control Connection
For sending control information like user identification, password, commands to change the remote directory, commands to retrieve and store files, etc., FTP makes use of a control connection. The control connection is initiated on port number 21.
Data connection
For sending the actual file, FTP makes use of a data connection. A data connection is initiated on port number 20.
FTP sends the control information out-of-band as it uses a separate control connection. Some protocols send their request and response header lines and the data in the same TCP connection. For this reason, they are said to send their control information in-band. HTTP and SMTP are such examples.

FTP Session
When an FTP session is started between a client and a server, the client initiates a control TCP connection with the server side. The client sends control information over this. When the server receives this, it initiates a data connection to the client side. But the control connection remains active throughout the user session. As we know HTTP is stateless . But FTP needs to maintain a state about its user throughout the session.
FTP Clients
FTP works on a client-server model. The FTP client is a program that runs on the user’s computer to enable the user to talk to and get files from remote computers. It is a set of commands that establishes the connection between two hosts, helps to transfer the files, and then closes the connection.
Some of the commands are:
get the filename(retrieve the file from the server)
get the filename(retrieve multiple files from the server )
ls(list files available in the current directory of the server)
There are also built-in FTP programs, which makes it easier to transfer files and it does not require remembering the commands.
FTP Data Types
The data type of a file, which determines how the file is represented overall, is the first piece of information that can be provided about it. The FTP standard specifies the following four categories of data:
- ASCII: Describes an ASCII text file in which each line is indicated by the previously mentioned type of end-of-line marker.
- EBCDIC: For files that use IBM’s EBCDIC character set, this type is conceptually identical to ASCII.
- Image: This is the “black box” mode I described earlier; the file has no formal internal structure and is transferred one byte at a time without any processing.
- Local: Files containing data in logical bytes with a bit count other than eight can be handled by this data type.
FTP Replies
Some of the FTP replies are:
- 200 – Command okay.
- 530 – Not logged in.
- 331 – User name okay, need a password.
- 221 – Service closing control connection.
- 551 – Requested action aborted: page type unknown.
- 502 – Command not implemented.
- 503 – Bad sequence of commands.
- 504 – Command not implemented for that parameter.
Characteristics of FTP
- FTP uses TCP as a transport layer protocol.
- It is good for simple file transfers, such as during boot time.
- Errors in the transmission (lost packets, checksum errors) must be handled by the TFTP server.
- It uses only one connection through well-known port 69.
- TFTP uses a simple lock-step protocol (each data packet needs to be acknowledged). Thus the throughput is limited.
FTP’s Security Issues
- Information could not go across a secure tunnel since FTP was not intended to do so. Thus, encryption is not present. A hacker would not need to struggle with encryption to access or alter data that is usable if they could intercept an FTP transaction.
- Even with FTP cloud storage, data can still be intercepted and misused if the service provider’s system is attacked.
- As a result, data sent via FTP is a target for spoofing, sniffing, brute force, and other types of attacks that move somewhat slowly. A hacker might examine an FTP transmission and try to take advantage of any flaws by simply port scanning.
- The fact that FTP uses clear-text passwords—passwords that haven’t been encrypted—is one of its main security flaws. Put differently, “Jerry1992” appears exactly like “Jerry1992.” The real password is hidden via an algorithm in more secure protocols. As a result, “Jerry1992” might appear as “dj18387saksng8937d9d8d7s6a8d89.” Passwords like this are not secured by FTP, which makes them more easily cracked by malicious actors.
Advantages of FTP
- File sharing also comes in the category of advantages of FTP in this between two machines files can be shared on the network.
- Speed is one of the main benefits of FTP.
- Since we don’t have to finish every operation to obtain the entire file, it is more efficient.
- Using the username and password, we must log in to the FTP server. As a result, FTP might be considered more secure.
- We can move the files back and forth via FTP. Let’s say you are the firm manager and you provide information to every employee, and they all reply on the same server.
Disadvantages of FTP
- File size limit is the drawback of FTP only 2 GB size files can be transferred.
- More then one receivers are not supported by FTP.
- FTP does not encrypt the data this is one of the biggest drawbacks of FTP.
- FTP is unsecured we use login IDs and passwords making it secure but they can be attacked by hackers.
Difference Between FTP and SFTP
|
It stands for File Transfer Protocol.
|
It stands for Secure File Transfer Protocol.
|
|
In FTP, secure channel is not provided to transfer the files between the hosts.
|
In SFTP, a secure channel is provided to transfer the files between the hosts.
|
|
It usually runs on port no-21.
|
It usually runs on port no-22.
|
|
It does not encrypt the data before sending
|
It encrypted data before sending.
|
|
It makes uploading and downloading of files without any security.
|
It maintains full security of the data by using SSH keys.
|
Frequently Asked Questions on File Transfer Protocol – FAQs
Differentiate between FTP and SFTP?
FTP is a insecure method and transfers the data in plain text whereas SFTP is a secure method that transfers the data in encrypted text.
What is passive FTP Connection?
In passive FTP, the client initiates both the control and data connections to the server.
What is the default port for FTP?
The default port for FTP is 21. Default port is used for the control connection when the data transfer is occuring on other ports.
Name the two modes of FTP data transfer?
What is the difference between FTP and SFTP?
The conventional file transmission protocol is called FTP. It’s a simple method of sharing files via the Internet. An additional degree of security is added to file transfers with SFTP, or Secure File Transfer Protocol, an alternative to FTP.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...