Difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE
Last Updated :
03 Oct, 2023
DELETE is a DML(Data Manipulation Language) command and is used when we specify the row (tuple) that we want to remove or delete from the table or relation. The DELETE command can contain a WHERE clause. If the WHERE clause is used with the DELETE command, then it removes or deletes only those rows (tuples) that satisfy the condition; otherwise, by default, it removes all the tuples (rows) from the table. Remember that DELETE logs the row deletions.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM TableName
WHERE condition;
TRUNCATE is a DDL(Data Definition Language) command and is used to delete all the rows or tuples from a table. Unlike the DELETE command, the TRUNCATE command does not contain a WHERE clause. In the TRUNCATE command, the transaction log for each deleted data page is not recorded. Unlike the DELETE command, the TRUNCATE command is fast. We cannot roll back the data after using the TRUNCATE command.
Syntax:
TRUNCATE TABLE TableName;
Let’s understand it with taking one simple example in which we will create one dummy table and then do the delete operation.
Query:
CREATE table Employee (
Emp_id int,
name VARCHAR(20),
country VARCHAR(20),
Salary INT);
--insert the data in the Employee Table
INSERT INTO Employee (Emp_id, name, country, Salary)
values (101, 'Mohit', 'India', 60000),
(103, 'Anish', 'England', 70000),
(104, 'Shubham', 'France', 100000),
(102, 'Danish', 'Sweden', 40000),
(105, 'Vivek', 'Wales', 50000),
(106, 'Rohan', 'Scotland', 30000);
Select * from Employee ;
Output
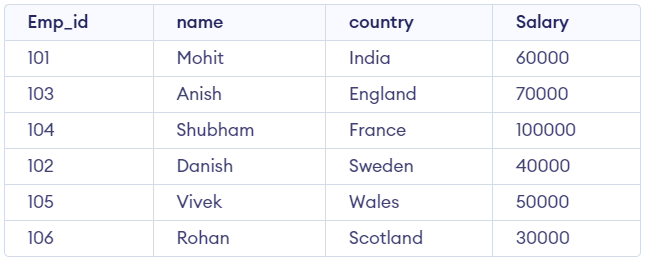
Employee Table
Example for Delete Command:
You must now create a query to remove the last entry with the value 106 for the Emp_id.
Query:
Delete from Employee where Emp_id = 106;
Output
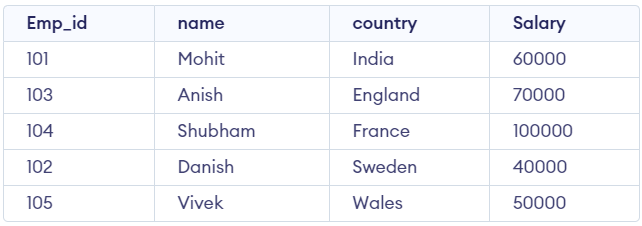
output
Example for TRUNCATE Command
To completely remove all records from the table players in this case, use the truncate command.
Query:
TRUNCATE TABLE Employee;
Differences between DELETE and TRUNCATE
| The DELETE command is used to delete specified rows(one or more). |
While this command is used to delete all the rows from a table. |
| It is a DML(Data Manipulation Language) command. |
While it is a DDL(Data Definition Language) command. |
| There may be a WHERE clause in the DELETE command in order to filter the records. |
While there may not be WHERE clause in the TRUNCATE command. |
| In the DELETE command, a tuple is locked before removing it. |
While in this command, the data page is locked before removing the table data. |
| The DELETE statement removes rows one at a time and records an entry in the transaction log for each deleted row. |
TRUNCATE TABLE removes the data by deallocating the data pages used to store the table data and records only the page deallocations in the transaction log. |
| DELETE command is slower than TRUNCATE command. |
While the TRUNCATE command is faster than the DELETE command. |
| To use Delete you need DELETE permission on the table. |
To use Truncate on a table we need at least ALTER permission on the table. |
| The identity of the fewer column retains the identity after using DELETE Statement on the table. |
Identity the column is reset to its seed value if the table contains an identity column. |
| The delete can be used with indexed views. |
Truncate cannot be used with indexed views. |
| This command can also active trigger. |
This command does not active trigger. |
| DELETE statement occupies more transaction spaces than Truncate. |
Truncate statement occupies less transaction spaces than DELETE. |
|
Delete operations can be ROLLED back.
|
TRUNCATE cannot be Rolled back as it causes an implicit commit.
|
|
Delete doesn’t DROP the whole table. It acquires a lock on table and starts deleting the rows.
|
TRUNCATE first drops the table & then re-create it, which is faster than deleting individual rows.
|
Conclusion
In this article, SQL developers can remove the rows appropriately by using the DELETE and TRUNCATE commands correctly. The TRUNCATE command must be used with caution because it deletes all of the table’s records. Beginners will also benefit from this tutorial’s explanation of the distinctions between the commands Delete and Truncate.
DELETE:
- You want to remove all Employees who haven’t purchased anything in the last six months from a table.
- You want to remove an Employee from a table.
TRUNCATE:
- You want to restore the table’s contents to their original state.
- You don’t need to be able to restore the data; you just want to remove it altogether from the table.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...