Difference Between Cell and Tissue
Last Updated :
16 Apr, 2024
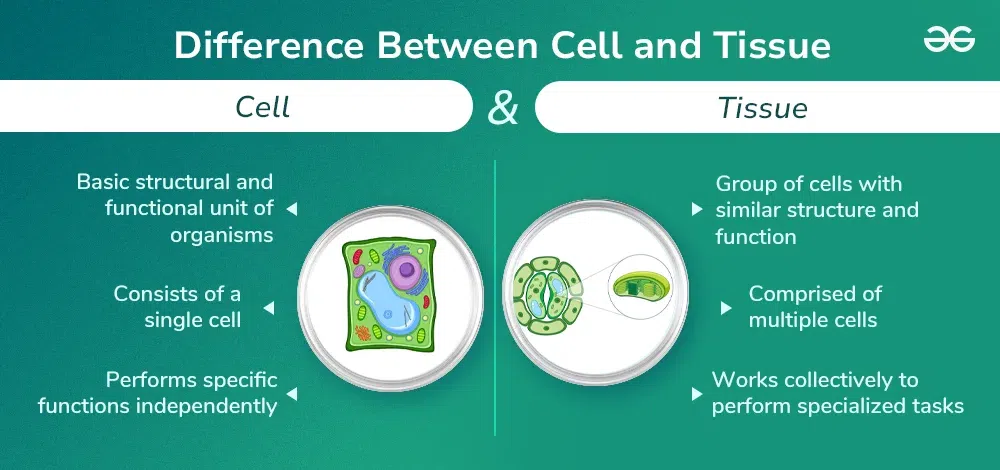
The major difference between cells and tissue lies in their organizational level. Cells and tissues are fundamental components of living organisms. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms, while tissue is a group of cells with similar structures and functions that work together to perform specific tasks. This article will cover the key differences between cells and tissue along with some similarities in detail.
What is a Cell?
A cell is the smallest unit of life and the fundamental component of all living beings. Each living organism is made up of one or more cells that perform different functions important for the organism’s survival. Cells vary in structure, size, and function, but they all have some components, such as a nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material, whereas the cytoplasm contains the organelles, which are specialized structures that perform certain functions.
Types of Cells
There are two types of cells based on the presence or absence of the nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotic cells are characterized by having a true nucleus enclosed within a membrane, along with other membrane-bound organelles, and are found in organisms ranging from protists to plants and animals.
- Prokaryotic (primitive) cells: Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, typically found in bacteria and archae.
Also Read: Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
What is a Tissue?
Tissues are groups of cells with similar structures and functions that collaborate to complete specified activities. Tissues are divided into four types: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nerve tissue. Epithelial tissue covers the body’s surfaces and lines organ cavities. Muscle tissue provides mobility whereas connective tissue supports and links different parts of the body. Nervous tissue transmits signals throughout the body and coordinates the body’s reaction to environmental stimuli.
Types of Tissue
In plants, tissues are of two types
- Meristematic tissue: Meristematic tissue is responsible for plant growth and consists of actively dividing cells.
- Permanent tissue: Permanent tissue comprises cells that have stopped division and perform specialized functions in plants, providing structural support, storage, and transportation of nutrients.
In animals, there are four types of tissues
- Epithelial tissue: Epithelial tissue forms the linings and coverings of body surfaces and organs, serving protective, absorptive, and secretory functions.
- Muscle tissue: Muscles of the skeleton, voluntary muscles, and involuntary muscles are formed by them. They cause the inside and outside movement of the body.
- Connective tissues: Blood, bone, ligaments, tendons, and adipose tissues are connective tissues that connect other tissues.
- Nervous tissues: The tissues in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system that transfer neural information for control and coordination are known as nervous tissues.
Difference Between Cell and Tissue
The major differences between cell and tissue in tabular form is given below:
Characteristics
|
Cell
|
Tissue
|
| Definition |
The basic unit of life, capable of performing all the necessary functions of an organism. |
A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. |
| Size |
Usually microscopic, although some cells can be seen with the naked eye. |
Can range in size from a few cells to thousands of cells. |
| Composition |
Single unit with specific characteristics and functions. |
Consists of multiple cells working together. |
| Structure |
Typically have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus containing genetic material. |
Can have specialized structures such as blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. |
| Function |
Can perform a wide variety of functions, such as metabolism, reproduction, and communication. |
Typically perform a specific function related to the tissue they belong to, such as contracting in muscle tissue or secreting hormones in glandular tissue. |
| Characterization |
Cells can be characterized based on their structure, function, and genetic information, and can be classified into different types such as muscle cells, nerve cells, and blood cells. |
Tissues can be characterized based on their structure, function, and location, and can be classified into different types such as epithelial tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue. |
| Reproduction |
Can undergo cell division to reproduce and replace damaged or old cells |
Tissues generally do not replicate themselves but can regenerate or repair through cell proliferation |
| Examples |
Red blood cell, neuron, muscle cell |
Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue |
What are the Similarities Between Cells and Tissues?
Similarities between cell and tissues are:
- Both cells and tissues are essential components of living organisms, which playan important roles in the functioning of organs and systems.
- They are both biological entities, composed of organic molecules and participating in metabolic processes necessary for life.
- Cells make up tissues, and tissues, in turn, form the higher-order structures of organs and systems, reflecting a hierarchical organization in biological systems.
- Both cells and tissues can exhibit specialization, with specific cells or groups of cells adapted to perform specialized functions within an organism.
- Cells within tissues depend on each other for support, communication, and coordination to carry out collective functions, emphasizing their interdependence in physiological processe.
Conclusion – Difference Between Cell and Tissue
In summary, cells, and tissues are both essential components of living organisms. While cells are the basic unit of life, tissues are groups of cells that have similar structures and functions. Cells are capable of performing all functions necessary for life, while tissues perform specific functions such as support, protection, and movement. Understanding the differences between cells and tissues is important in biology and medical sciences.
Also Read:
FAQs on Difference Between Cell and Tissue
What is the Main Difference Between Cells and Tissues?
The main difference between cells and tissues is that cells are the basic building blocks of life, while tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform specific tasks.
What is the Function of a Cell?
The function of a cell depends on its type, but all cells carry out basic functions such as producing energy, synthesizing proteins, and replicating genetic material.
What are the Four Types of Tissues?
The four types of tissues are Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, a and nervous tissue.
What is Nervous Tissue?
Nervous tissue carries messages between different parts of the body and coordinates the body’s response to external stimuli. It is responsible for sensation, perception, and control of body functions.
What is the Relationship Between Tissue and Cells?
Tissues are composed of organized groups of cells with similar structures and functions, forming the building blocks of organs and systems within an organism.
How Do Cells Specialize in Functions to Form a Tissue?
Cells specialize through differential gene expression and interactions with neighboring cells to perform specific functions within a tissue.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...