Depth First Search or DFS for disconnected Graph
Last Updated :
13 Jun, 2023
Given a Disconnected Graph, the task is to implement DFS or Depth First Search Algorithm for this Disconnected Graph.
Example:
Input:
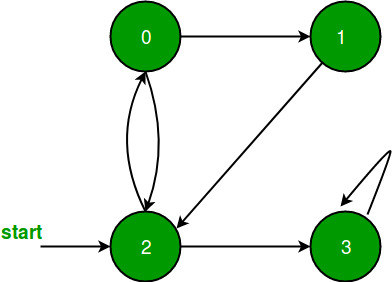
Disconnected Graph
Output: 0 1 2 3
Algorithm for DFS on Disconnected Graph:
In the post for Depth First Search for Graph, only the vertices reachable from a given source vertex can be visited. All the vertices may not be reachable from a given vertex, as in a Disconnected graph. This issue can be resolved by following the below idea:
Iterate over all the vertices of the graph and for any unvisited vertex, run a DFS from that vertex. The recursive function in this case remains the same as in the previous post.
Code Implementation of DFS for Disconnected Graph:
C++
// C++ program to print DFS
// traversal for a given graph
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v);
public:
map<int, bool> visited;
map<int, list<int> > adj;
// Function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Prints DFS traversal of the complete graph
void DFS();
};
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v’s list.
adj[v].push_back(w);
}
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
cout << v << " ";
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i);
}
// The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void Graph::DFS()
{
// Call the recursive helper function to print DFS
// traversal starting from all vertices one by one
for (auto i : adj)
if (visited[i.first] == false)
DFSUtil(i.first);
}
// Driver's Code
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g;
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
cout << "Following is Depth First Traversal \n";
// Function call
g.DFS();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print DFS
// traversal from a given graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph {
private int V;
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[];
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v's list.
adj[v].add(w);
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
System.out.print(v + " ");
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this
// vertex
Iterator<Integer> i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do DFS traversal. It uses recursive
// DFSUtil()
void DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(set as
// false by default in java)
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
// Call the recursive helper function to print DFS
// traversal starting from all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
if (visited[i] == false)
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver's Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
System.out.println(
"Following is Depth First Traversal");
// Function call
g.DFS();
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program to print DFS traversal
# for complete graph
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self):
# Default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# Function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# A function used by DFS
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited.add(v)
print(v, end=" ")
# Recur for all the vertices
# adjacent to this vertex
for neighbour in self.graph[v]:
if neighbour not in visited:
self.DFSUtil(neighbour, visited)
# The function to do DFS traversal.
# It uses recursive DFSUtil
def DFS(self):
# Create a set to store all visited vertices
visited = set()
# Call the recursive helper function
# to print DFS traversal starting from all
# vertices one by one
for vertex in self.graph:
if vertex not in visited:
self.DFSUtil(vertex, visited)
# Driver's code
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Following is Depth First Traversal")
g = Graph()
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 3)
# Function call
g.DFS()
C#
// C# program to print DFS
// traversal from a given graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
public class Graph {
private int V;
// Array of lists for
// Adjacency List Representation
private List<int>[] adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List<int>[ v ];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v's list.
adj[v].Add(w);
}
// A function used by DFS
void DFSUtil(int v, bool[] visited)
{
// Mark the current
// node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
Console.Write(v + " ");
// Recur for all the
// vertices adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int i in adj[v])
{
int n = i;
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do
// DFS traversal. It uses recursive DFSUtil()
void DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(set as
// false by default in java)
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
// Call the recursive helper
// function to print DFS
// traversal starting from
// all vertices one by one
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
if (visited[i] == false)
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
// Driver's code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(
"Following is Depth First Traversal");
// Function call
g.DFS();
}
}
Javascript
// JavaScript program to print DFS
// traversal from a given graph
// This class represents a
// directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph
{
// Constructor
constructor(v) {
this.V = v;
this.adj = new Array(v).fill([]);
}
// Function to Add an edge into the graph
AddEdge(v, w) {
// Add w to v's list.
this.adj[v].push(w);
}
// A function used by DFS
DFSUtil(v, visited)
{
// Mark the current
// node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
console.log(v + " ");
// Recur for all the
// vertices adjacent to this vertex
for (const n of this.adj[v]) {
if (!visited[n]) this.DFSUtil(n, visited);
}
}
// The function to do
// DFS traversal. It uses recursive DFSUtil()
DFS()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited(set as
var visited = new Array(this.V).fill(false);
// Call the recursive helper
// function to print DFS
// traversal starting from
// all vertices one by one
for (var i = 0; i < this.V; ++i)
if (visited[i] == false) this.DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Driver Code
var g = new Graph(4);
g.AddEdge(0, 1);
g.AddEdge(0, 2);
g.AddEdge(1, 2);
g.AddEdge(2, 0);
g.AddEdge(2, 3);
g.AddEdge(3, 3);
console.log("Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS();
Output
Following is Depth First Traversal
0 1 2 3
Time complexity: O(V + E), where V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges in the graph.
Auxiliary Space: O(V), since an extra visited array of size V is required.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...