Minimum number of swaps required to sort an array
Last Updated :
17 Apr, 2024
Given an array of N distinct elements, find the minimum number of swaps required to sort the array.
Examples:
Input: {4, 3, 2, 1}
Output: 2
Explanation: Swap index 0 with 3 and 1 with 2 to form the sorted array {1, 2, 3, 4}
Input: {1, 5, 4, 3, 2}
Output: 2
Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
This can be easily done by visualizing the problem as a graph. We will have N nodes and an edge directed from node i to node j if the element at the i’th index must be present at the j’th index in the sorted array.
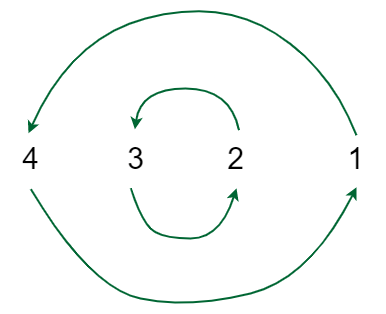
Graph for {4, 3, 2, 1}
The graph will now contain many non-intersecting cycles. Now a cycle with 2 nodes will only require 1 swap to reach the correct ordering, similarly, a cycle with 3 nodes will only require 2 swaps to do so.
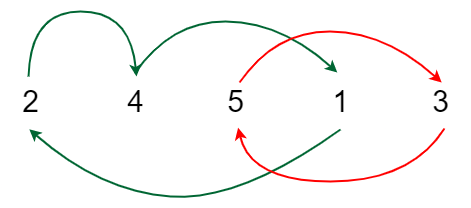
Graph for {2, 4, 5, 1, 3}
Hence, ans = ?i = 1k(cycle_size – 1), where k is the number of cycles
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Create an array of pairs arrPos to store the input array elements along with their index
- Sort arrPos and run a loop for i [0, N]
- If the current element is already visited or it is at its correct position then continue
- Else calculate the cycle size from the current element using a while loop
- Declare an integer j equal to i and in the while loop set j equal to the index of arrPos[j] and increase cycle size while the element at jth position is not visited
- Increase the answer by the size of the current cycle – 1
- Return answer
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
// C++ program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
int minSwaps(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create an array of
// pairs where first
// element is array element
// and second element
// is position of first element
pair<int, int> arrPos[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arrPos[i].first = arr[i];
arrPos[i].second = i;
}
// Sort the array by array
// element values to
// get right position of
// every element as second
// element of pair.
sort(arrPos, arrPos + n);
// To keep track of visited elements.
// Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
vector<bool> vis(n, false);
// Initialize result
int ans = 0;
// Traverse array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (vis[i] || arrPos[i].second == i)
continue;
// find out the number of node in
// this cycle and add in ans
int cycle_size = 0;
int j = i;
while (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = 1;
// move to next node
j = arrPos[j].second;
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
// Return result
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
int n = (sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
cout << minSwaps(arr, n);
return 0;
}
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// structure to store element and its position
struct ElementPosition {
int element;
int position;
};
// function to find minimum number of swaps required to sort
// the array
int minSwaps(int arr[], int n)
{
// create an array of ElementPosition structures
struct ElementPosition arrPos[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arrPos[i].element = arr[i];
arrPos[i].position = i;
}
// sort the array by element values to get right
// position of every element as second element of
// structure
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arrPos[i].element > arrPos[j].element) {
struct ElementPosition temp = arrPos[i];
arrPos[i] = arrPos[j];
arrPos[j] = temp;
}
}
}
// initialize a boolean array to keep track of visited
// elements
bool vis[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vis[i] = false;
}
// initialize result variable
int ans = 0;
// traverse array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or already present
// at correct pos
if (vis[i] || arrPos[i].position == i) {
continue;
}
// find out the number of elements in this cycle and
// add in ans
int cycle_size = 0;
int j = i;
while (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = arrPos[j].position;
cycle_size++;
}
// update answer by adding current cycle
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
// return result
return ans;
}
// driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("%d", minSwaps(arr, n));
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Pair {
int first, second;
Pair(int first, int second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
class GfG {
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
public static int minSwaps(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.length;
// Create two arrays and
// use as pairs where first
// array is element and second array
// is position of first element
ArrayList<Pair> arrpos
= new ArrayList<Pair>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arrpos.add(
new Pair(arr[i], i));
// Sort the array by array element values to
// get right position of every element as the
// elements of second array.
arrpos.sort(
new Comparator<Pair>() {
@Override
public int compare(
Pair o1,
Pair o2)
{
if (o1.first < o2.first)
return -1;
// We can change this to make
// it then look at the
// words alphabetical order
else if (o1.first == o2.first)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
});
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
Boolean[] vis = new Boolean[n];
Arrays.fill(vis, false);
// Initialize result
int ans = 0;
// Traverse array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (vis[i] || arrpos.get(i).second == i)
continue;
// find out the number of node in
// this cycle and add in ans
int cycle_size = 0;
int j = i;
while (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = arrpos.get(j).second;
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
// Return result
return ans;
}
}
class MinSwaps {
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
GfG g = new GfG();
System.out.println(g.minSwaps(a));
}
}
# Python3 program to find
# minimum number of swaps
# required to sort an array
# Function returns the minimum
# number of swaps required to
# sort the array
def minSwaps(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Create two arrays and use
# as pairs where first array
# is element and second array
# is position of first element
arrpos = [*enumerate(arr)]
# Sort the array by array element
# values to get right position of
# every element as the elements
# of second array.
arrpos.sort(key=lambda it: it[1])
# To keep track of visited elements.
# Initialize all elements as not
# visited or false.
vis = {k: False for k in range(n)}
# Initialize result
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
# already swapped or
# already present at
# correct position
if vis[i] or arrpos[i][0] == i:
continue
# find number of nodes
# in this cycle and
# add it to ans
cycle_size = 0
j = i
while not vis[j]:
# mark node as visited
vis[j] = True
# move to next node
j = arrpos[j][0]
cycle_size += 1
# update answer by adding
# current cycle
if cycle_size > 0:
ans += (cycle_size - 1)
# return answer
return ans
# Driver Code
arr = [1, 5, 4, 3, 2]
print(minSwaps(arr))
# This code is contributed
# by Dharan Aditya
// C# program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class GfG {
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
public int minSwaps(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
// Create two arrays and
// use as pairs where first
// array is element and second array
// is position of first element
List<KeyValuePair<int, int> > arrpos
= new List<KeyValuePair<int, int> >();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arrpos.Add(
new KeyValuePair<int, int>(arr[i], i));
// Sort the array by array element values to
// get right position of every element as the
// elements of second array.
arrpos.Sort((a, b) = > a.Key - b.Key);
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
Boolean[] vis = new Boolean[n];
// Initialize result
int ans = 0;
// Traverse array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (vis[i] || arrpos[i].Value == i)
continue;
// find out the number of node in
// this cycle and add in ans
int cycle_size = 0;
int j = i;
while (!vis[j]) {
vis[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = arrpos[j].Value;
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
// Return result
return ans;
}
}
// Driver class
public class MinSwaps {
// Driver program to test the above function
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
GfG g = new GfG();
Console.WriteLine(g.minSwaps(a));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
<script>
// JavaScript program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
function minSwaps(arr)
{
let n = arr.length;
// Create two arrays and
// use as pairs where first
// array is element and second array
// is position of first element
let arrpos = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
arrpos.push([arr[i], i]);
// Sort the array by array element values to
// get right position of every element as the
// elements of second array.
arrpos.sort(function(a,b){return a[0]-b[0];});
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
let vis = new Array(n);
for(let i=0;i<n;i++)
{
vis[i]=false;
}
// Initialize result
let ans = 0;
// Traverse array elements
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (vis[i] || arrpos[i][1] == i)
continue;
// find out the number of node in
// this cycle and add in ans
let cycle_size = 0;
let j = i;
while (!vis[j])
{
vis[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = arrpos[j][1];
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if(cycle_size > 0)
{
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
// Return result
return ans;
}
// Driver class
let a=[1, 5, 4, 3, 2];
document.write(minSwaps(a))
// This code is contributed by ab2127
</script>
Time Complexity: O(N * Log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Note: As the Pair class is available in java from java 8 so we can use hashmap in the older java version, so instead of using an ArrayList of pairs in java, we can use hashmap, rest of the steps remain the same.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
int minSwaps(int nums[], int n)
{
int len = n;
map<int, int> map;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
map[nums[i]] = i;
sort(nums, nums + n);
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
bool visited[len] = { 0 };
// Initialize result
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (visited[i] || map[nums[i]] == i)
continue;
int j = i, cycle_size = 0;
while (!visited[j]) {
visited[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = map[nums[j]];
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Driver program to test the above function
int a[] = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
int n = 5;
cout << minSwaps(a, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Harshal Khond
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Comparator function for qsort
int cmpfunc(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
int minSwaps(int nums[], int n)
{
int len = n;
int map[100001] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
map[nums[i]] = i;
qsort(nums, n, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
int visited[len];
memset(visited, 0, len * sizeof(int));
// Initialize result
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (visited[i] || map[nums[i]] == i)
continue;
int j = i, cycle_size = 0;
while (!visited[j]) {
visited[j] = 1;
// move to next node
j = map[nums[j]];
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Driver program to test the above function
int a[] = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
int n = 5;
printf("%d", minSwaps(a, n));
return 0;
}
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
public static int minSwaps(int[] nums)
{
int len = nums.length;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
map.put(nums[i], i);
Arrays.sort(nums);
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
boolean[] visited = new boolean[len];
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
// Initialize result
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (visited[i] || map.get(nums[i]) == i)
continue;
int j = i, cycle_size = 0;
while (!visited[j]) {
visited[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = map.get(nums[j]);
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
// Driver class
class MinSwaps {
// Driver program to test the above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
GfG g = new GfG();
System.out.println(g.minSwaps(a));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Saurabh Johari
# Function returns the
# minimum number of swaps
# required to sort the array
from functools import cmp_to_key
def cmp(a, b):
return a - b
def minSwaps(nums):
Len = len(nums)
map = {}
for i in range(Len):
map[nums[i]] = i
nums = sorted(nums, key=cmp_to_key(cmp))
# To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
# all elements as not visited or false.
visited = [False for col in range(Len)]
# Initialize result
ans = 0
for i in range(Len):
# already swapped and corrected or
# already present at correct pos
if (visited[i] or map[nums[i]] == i):
continue
j, cycle_size = i, 0
while (visited[j] == False):
visited[j] = True
# move to next node
j = map[nums[j]]
cycle_size += 1
# Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0):
ans += (cycle_size - 1)
return ans
# Driver program to test the above function
a = [1, 5, 4, 3, 2]
print(minSwaps(a))
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
public int minSwaps(int[] nums)
{
int len = nums.Length;
Dictionary<int, int> map
= new Dictionary<int, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
map.Add(nums[i], i);
Array.Sort(nums);
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
bool[] visited = new bool[len];
// Initialize result
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (visited[i] || map[nums[i]] == i)
continue;
int j = i, cycle_size = 0;
while (!visited[j]) {
visited[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = map[nums[j]];
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
// Driver class
public class MinSwaps {
// Driver program to test the above function
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = { 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 };
GfG g = new GfG();
Console.WriteLine(g.minSwaps(a));
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
<script>
// Function returns the
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort the array
function minSwaps(nums) {
var len = nums.length;
var map = new Map();
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
map.set(nums[i], i);
nums.sort((a,b)=>a-b);
// To keep track of visited elements. Initialize
// all elements as not visited or false.
var visited = Array(len).fill(false);
// Initialize result
var ans = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// already swapped and corrected or
// already present at correct pos
if (visited[i] || map.get(nums[i]) == i)
continue;
var j = i, cycle_size = 0;
while (!visited[j]) {
visited[j] = true;
// move to next node
j = map.get(nums[j]);
cycle_size++;
}
// Update answer by adding current cycle.
if (cycle_size > 0) {
ans += (cycle_size - 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver program to test the above function
var a = [ 1, 5, 4, 3, 2 ];
document.write(minSwaps(a));
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
Time Complexity: O(N Log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
The minimum number of swaps required to sort an array using a greedy algorithm:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
While iterating over the array, check the current element, and if not in the correct place, replace that element with the index of the element which should have come to this place greedily which will give the optimal answer
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Create a new array and copy the elements of the input array
- Sort the new array and declare a variable ans equal to 0
- Run a for loop to traverse the elements
- If the current element in the sorted array is not equal to the one in the input array then increase the ans by 1
- And swap the current element, with the required element at this index
- Return ans
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find minimum number
// of swaps required to sort an array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void swap(vector<int>& arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
int indexOf(vector<int>& arr, int ele)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr[i] == ele) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort the array
int minSwaps(vector<int> arr, int N)
{
int ans = 0;
vector<int> temp(arr.begin(), arr.end());
sort(temp.begin(), temp.end());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
// Swap the current element
// with the right index
// so that arr[0] to arr[i] is sorted
swap(arr, i, indexOf(arr, temp[i]));
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector<int> a
= { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = a.size();
// Output will be 5
cout << minSwaps(a, n);
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void swap(int* arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
int indexOf(int* arr, int size, int ele)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] == ele) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int cmpfunc(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort the array
int minSwaps(int* arr, int N)
{
int ans = 0;
int* temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
temp[i] = arr[i];
}
qsort(temp, N, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
// Swap the current element
// with the right index
// so that arr[0] to arr[i] is sorted
swap(arr, i, indexOf(arr, N, temp[i]));
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int a[] = { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
// Output will be 5
printf("%d", minSwaps(a, n));
return 0;
}
// Java program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort the array
public int minSwaps(int[] arr, int N)
{
int ans = 0;
int[] temp = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 0, N);
Arrays.sort(temp);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
// Swap the current element
// with the right index
// so that arr[0] to arr[i] is sorted
swap(arr, i, indexOf(arr, temp[i]));
}
}
return ans;
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
public int indexOf(int[] arr, int ele)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == ele) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
// Driver class
class Main {
// Driver program to test
// the above function
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
int[] a
= { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = a.length;
// Output will be 5
System.out.println(new GfG().minSwaps(a, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Satvik Nema
# Python3 program to find
# minimum number of swaps
# required to sort an array
# Return the minimum number
# of swaps required to sort
# the array
def minSwaps(arr, N):
ans = 0
temp = arr.copy()
temp.sort()
for i in range(N):
# This is checking whether
# the current element is
# at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]):
ans += 1
# Swap the current element
# with the right index
# so that arr[0] to arr[i]
# is sorted
swap(arr, i,
indexOf(arr, temp[i]))
return ans
def swap(arr, i, j):
temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
def indexOf(arr, ele):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if (arr[i] == ele):
return i
return -1
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
a = [101, 758, 315, 730,
472, 619, 460, 479]
n = len(a)
# Output will be 5
print(minSwaps(a, n))
# This code is contributed by Chitranayal
// C# program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
using System;
public class GFG {
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort the array
static int minSwaps(int[] arr, int N)
{
int ans = 0;
int[] temp = new int[N];
Array.Copy(arr, temp, N);
Array.Sort(temp);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
// Swap the current element
// with the right index
// so that arr[0] to arr[i] is sorted
swap(arr, i, indexOf(arr, temp[i]));
}
}
return ans;
}
static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
static int indexOf(int[] arr, int ele)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == ele) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Driver program to test
// the above function
static public void Main()
{
int[] a
= { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = a.Length;
// Output will be 5
Console.WriteLine(minSwaps(a, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
<script>
// Javascript program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort the array
function minSwaps(arr,N)
{
let ans = 0;
let temp = [...arr];
temp.sort(function(a,b){return a-b;});
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i])
{
ans++;
// Swap the current element
// with the right index
// so that arr[0] to arr[i] is sorted
swap(arr, i, indexOf(arr, temp[i]));
}
}
return ans;
}
function swap(arr,i,j)
{
let temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
function indexOf(arr,ele)
{
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == ele) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Driver class
let a=[101, 758, 315, 730, 472,
619, 460, 479 ];
let n = a.length;
document.write(minSwaps(a, n));
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Note: We can still improve the complexity by using a hashmap. The main operation here is the indexOf method inside the loop, which costs us n*n. We can improve this section to O(n), by using a hashmap to store the indexes. Still, we use the sort method, so the complexity cannot improve beyond O(n Log n)
The minimum number of swaps required to sort an array using Hash-Map:
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Make a new array (called temp), which is the sorted form of the input array. We know that we need to transform the input array to the new array (temp) in the minimum number of swaps.
- Make a map that stores the elements and their corresponding index, of the input array.
- So at each i starting from 0 to N in the given array, where N is the size of the array:
- If i is not in its correct position according to the sorted array, then
- We will fill this position with the correct element from the hashmap we built earlier. We know the correct element which should come here is temp[i], so we look up the index of this element from the hashmap.
- After swapping the required elements, we update the content of the hashmap accordingly, as temp[i] to the ith position, and arr[i] to where temp[i] was earlier
- Return answer
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void swap(vector<int>& arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort
// the array
int minSwaps(vector<int> arr, int N)
{
int ans = 0;
vector<int> temp = arr;
// Hashmap which stores the
// indexes of the input array
map<int, int> h;
sort(temp.begin(), temp.end());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
h[arr[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
int init = arr[i];
// If not, swap this element
// with the index of the
// element which should come here
swap(arr, i, h[temp[i]]);
// Update the indexes in
// the hashmap accordingly
h[init] = h[temp[i]];
h[temp[i]] = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector<int> a
= { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = a.size();
cout << minSwaps(a, n);
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void swap(int* arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
int cmpfunc(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort
// the array
int minSwaps(int arr[], int N)
{
int ans = 0;
int temp[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
temp[i] = arr[i];
}
// Hashmap which stores the
// indexes of the input array
int h[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
h[arr[i]] = i;
}
// Sort the temp array
qsort(temp, N, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
int init = arr[i];
// If not, swap this element
// with the index of the
// element which should come here
swap(arr, i, h[temp[i]]);
// Update the indexes in
// the hashmap accordingly
h[init] = h[temp[i]];
h[temp[i]] = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int a[] = { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(int);
printf("%d", minSwaps(a, n));
return 0;
}
// Java program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort the array
public int minSwaps(int[] arr, int N)
{
int ans = 0;
int[] temp = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 0, N);
// Hashmap which stores the
// indexes of the input array
HashMap<Integer, Integer> h
= new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
Arrays.sort(temp);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
h.put(arr[i], i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
int init = arr[i];
// If not, swap this element
// with the index of the
// element which should come here
swap(arr, i, h.get(temp[i]));
// Update the indexes in
// the hashmap accordingly
h.put(init, h.get(temp[i]));
h.put(temp[i], i);
}
}
return ans;
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Driver code
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
int[] a
= { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = a.length;
System.out.println(new GfG().minSwaps(a, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Satvik Nema
# Python3 program to find
# minimum number of swaps
# required to sort an array
# Return the minimum number
# of swaps required to sort
# the array
def minSwap(arr, n):
ans = 0
temp = arr.copy()
# Dictionary which stores the
# indexes of the input array
h = {}
temp.sort()
for i in range(n):
# h.[arr[i]
h[arr[i]] = i
init = 0
for i in range(n):
# This is checking whether
# the current element is
# at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]):
ans += 1
init = arr[i]
# If not, swap this element
# with the index of the
# element which should come here
arr[i], arr[h[temp[i]]] = arr[h[temp[i]]], arr[i]
# Update the indexes in
# the hashmap accordingly
h[init] = h[temp[i]]
h[temp[i]] = i
return ans
# Driver code
a = [101, 758, 315, 730,
472, 619, 460, 479]
n = len(a)
print(minSwap(a, n))
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
// C# program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class GfG {
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort the array
public int minSwaps(int[] arr, int N)
{
int ans = 0;
int[] temp = new int[N];
arr.CopyTo(temp, 0);
// Hashmap which stores the
// indexes of the input array
Dictionary<int, int> h = new Dictionary<int, int>();
Array.Sort(temp);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
h.Add(arr[i], i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i]) {
ans++;
int init = arr[i];
// If not, swap this element
// with the index of the
// element which should come here
swap(arr, i, h[temp[i]]);
// Update the indexes in
// the hashmap accordingly
h[init] = h[temp[i]];
h[temp[i]] = i;
}
}
return ans;
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Driver code
public class GFG {
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] a
= { 101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479 };
int n = a.Length;
Console.WriteLine(new GfG().minSwaps(a, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
<script>
// JavaScript program to find
// minimum number of swaps
// required to sort an array
function swap(arr, i, j)
{
let temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Return the minimum number
// of swaps required to sort
// the array
function minSwaps(arr,N)
{
let ans = 0;
let temp = arr.slice();
// Hashmap which stores the
// indexes of the input array
let h = new Map();
temp.sort();
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
h.set(arr[i], i);
}
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// This is checking whether
// the current element is
// at the right place or not
if (arr[i] != temp[i])
{
ans++;
let init = arr[i];
// If not, swap this element
// with the index of the
// element which should come here
swap(arr, i, h.get(temp[i]));
// Update the indexes in
// the hashmap accordingly
h.set(init,h.get(temp[i]));
h.set(temp[i],i);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver class
// Driver program to
// test the above function
let a = [101, 758, 315, 730, 472, 619, 460, 479];
let n = a.length;
// Output will be 5
document.write(minSwaps(a, n));
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
Time Complexity: O(N * Log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Related Article:
Number of swaps to sort when only adjacent swapping allowed
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...