Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 2 The World Population: Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 2 The World Population talks about the key concepts of the World Population. The chapter discusses the interdisciplinary nature of human geography. It also covers the interplay between the physical and socio-cultural environment.
In this article, we will talk about the Patterns of Population Distribution in the World, Density of Population, Factors influencing the distribution of Population, Population Growth, Components of Population Change, Migration, Trends in Population Growth, Doubling time of World Population, Spatial Pattern of Population Change, Impact of Population Change, Demographic Transition and Population Control Measures.
Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 2 The World Population
In reality, it is the people of a country that are its major assets. It is the people who are the ones that make use of a country’s resources and decide its policies. It is the because of the people that a country is known for. Knowing the number of men and women, how many children are born each year, how many people die and how are some important matters.
Whether the people live in cities or villages , whether they can read or write and what work they do. In the beginning of the 21st century, the world’s population was about 6 billion. Now the world’s population is around 8.1 billion people and counting. Around the world, population is unevenly distributed.
Patterns of Population Distribution in the World
The demographic characteristics of any area are understood by the patterns of population distribution and density. Population Distribution means “the way the people are spaced over the earth’s surface.” Around, 90% of the world population lives in about 10% of its land area. In the world, 10 most populous countries contribute about 60% of the world’s population. Out of these 10 populous countries, 6 are in Asia which are: China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, India, Russia and Indonesia, and then Japan, Brazil and USA.
Density of Population
A land has limited capacity to support people living on it. It is essential to understand the ratio between the numbers of people to the land’s size. This ratio is known as the density of population. It is measured in persons per sq. km.
Density of Population= Number of People/Land Area
Let us have a look at a rough estimate of the number of people living per sq. km in various regions of the world.
- High density areas ( more than 200 persons/sq. km)- North- Eastern part of USA, North- Western part of Europe, South, South- East and East Asia
- Medium density areas (11-50 persons/sq. km)- Western China, Southern India in Asia, Norway, Sweden (Europe)
- Low density areas (less the 1 person / sq km)- North and South poles, Hot and Cold deserts and High Rainfall Zones near Equator.
Factors influencing the Distribution of Population
There are several factors which determine how the population is distributed across a region such as:
|
1. Geographical Factors
|
When it comes to the geography of a reason, the important factors are:
- Availability of Water– People prefer living in an area which has fresh water that is easily available. Water is used for several purposes like: drinking, bathing and cooking, for cattle, crops, industries and navigation. These river valleys are densely populated.
- Land forms– People prefer living on flat plains and gentle slopes as these areas are favourable for producing crops and to build roads and industries. Eg: Ganga Plains. Whereas mountainous and hilly regions are less populated due to lack of transport, agricultural and industrial development. Eg: Himalayan Region.
- Climate- Areas with very heavy rainfall or extreme and harsh climates have low population, Eg: Mediterranean Regions. People prefer living in areas with a comfortable climate, where there is not
much seasonal variation.
- Soils- Fertile soils are important for agricultural and allied activities. Therefore,
areas which have fertile loamy soils have dense population. Eg. Northern Plains of India
|
|
2. Economic Factors
|
- Minerals- Areas which have mineral deposits are suitable for setting up industries and generate employment. Skilled and semi-skilled workers move to these areas and make them densely populated. Eg: Katanga Zambia Copper Belt in Africa.
- Urbanization- People prefer living in cities which offer better employment opportunities, educational and medical facilities, better means of transport and communication and good civic amenities.
- Industrialization- Industrial belts provide job opportunities and attract large
numbers of people. Eg: The Kobe-Osaka region of Japan
|
|
3. Social & Cultural Factors
|
- Regions which have religious and cultural significance, attract more people.
- If there is a region which witnesses political and social unrest, people prefer to move away from such places.
- Many a times, it is seen that governments offer incentives to people to live in sparsely populated areas or move away from overcrowded places.
|
Population Growth
The Population Growth or population change means change in number of inhabitants of a territory during a specific period of time. This change may be both positive and negative. It is represented in terms of absolute numbers/percentage. Population change is an indicator of economic development, social upliftment and historical and cultural background of the region.
Growth Rate of Population is the change of population expressed in % .
Natural Growth of Population- When population increases by the difference between births and deaths in a particular region between two points of time.
Natural Growth= Births – Deaths
Actual Growth of Population= Births – Deaths + In Migration – Out Migration
Positive Growth of Population happens when the birth rate is more than the death rate between two points of time or when people from other countries migrate permanently to a region.
Negative Growth of Population happens when the population decreases between two points of time. It occurs when the birth rate falls below the death rate or people migrate to other countries.
Components of Population Change
Several components of Population Change are as follows:
- Birth Rate: Number of live births in a year per thousand of women
- Death Rate: No. of death in a particular year per 1000 of population.
|
Birth Rate
|
Crude Birth Rate (CBR): Number of live births in a year per thousand of women
CBR 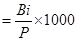
Bi= Live births
P= Mid-year population
|
|
Death Rate
|
Crude Death Rate (CDR): No. of death in a particular year per 1000 of population.
CDR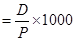
CDR= Crude Death Rate
D= No. of Deaths
P= Estimated Mid-Year Population
By and large mortality rates are affected by demographic structure, social advancement and economic development.
|
Migration
When people move from one place to another, it is known as migration. The place from which people move, is known as the Place of origin. The Place of destination is the place people move in.
Migration can be permanent, temporary and seasonal. There are various types of migration such as:
At times, the same person can both be an immigrant as well as a emigrant. While Immigration means when migrants move into a new place. Emigration means when migrants move out of a place.
There are several factors which influence migration such as:
- Push factors are reasons due to which people move out of a region. Such reasons are: unemployment, poor living conditions, political turmoil, unpleasant climate, natural disasters, epidemics and socio-economic backwardness
- Pull factors are reasons due to which people want to move into a place. Such reasons are: better job opportunities and living conditions, peace and stability, security of life and property and pleasant climate.
Trends in Population Growth
Earth’s population is more than 6 billion. Over the centuries, the population size has increased manifold. After the evolution and introduction of agriculture which was about 8,000 to 12,000 years ago, the size of population was 8 million. In the first century A.D., it was below 300 million.
In the 16th and 17th century the population growth rate increased due to expanding world trade. Around 1750, at the dawn of the Industrial Revolution, the world population stood at 550 million. The 18th century witnessed a surge in the world population due to the industrial revolution.
Doubling Time of World Population
It took more than a million years for the human population to attain the one billion mark. But it took only. 12 years for it to rise from 5 billion to 6 billion. Developed countries take more time to double their population as compared to developing countries. Most of the Population is growing in developing countries.
Eg: Yemen, Liberia, Somalia, Saudi Arabia and Oman.
|
Period
|
Population
|
Time in which Population Doubles
|
|
10,000 B.C.
|
5 million
|
|
|
1650 A.D.
|
500 million
|
1500 years
|
|
1804 A.D.
|
1000 million
|
154 years
|
|
1927 A.D.
|
2000 million
|
123 years
|
|
1974 A.D.
|
4000 million
|
47 years
|
|
2025 A.D.
|
8000 million protected figure
|
51 years
|
Population Growth Rates (%) 1995-2000
|
High
|
|
Low
|
|
|
Liberia
|
8.2
|
Latvia
|
-1.5
|
|
Somalia
|
4.2
|
Estonia
|
-1.2
|
|
Yemen
|
3.7
|
Russia, Ukraine
|
-0.6
|
|
Saudi Arabia
|
3.4
|
Albania, Bulgaria
|
|
|
Oman
|
3.3
|
Croatia
|
|
|
|
|
Slovania, Czech Republic
|
|
|
|
|
Germany, Portugal
|
-0.1
|
|
|
|
Spain, Italy
|
|
|
|
|
Denmark
|
0
|
Spatial Pattern of Population Change
One can compare the growth of population in different parts of the world. The growth of population is low in developed countries as compared to developing countries. There is negative correlation between economic development and population growth.
Annual population rate change i.e. 1.6% in 1990-95 to 1.4% in 2004-05. This is because when a small annual rate is applied to a very large population, it will lead to a large population change. The total population grows each year, even if there is a decline in the growth rates. Another main reason is due to increase in infant mortality rate and increase in death rate during childbirth.
Growth of Population 2004-05 over 1990-95
|
Region
|
Growth Rate
1990- 1995
|
2004-05 (Estimated)
|
|
World
|
1.6
|
1.4
|
|
Africa
|
2.4
|
2.6
|
|
Europe
|
0.2
|
0.0
|
|
North & Central America
|
1.4
|
1.1
|
|
South America
|
1.7
|
1.4
|
|
Asia
|
1.6
|
1.4
|
|
Oceania (Australia, New Zealand & Fiji)
|
1.5
|
1.3
|
Impact of Population Change
In a growing economy, a small increase in population, is considered to be desirable. However, if the population growth is more than a particular level, then there might be problems. The most severe being the depletion of resources. Decline in population is also an issue. It indicates that resources that had supported a population earlier are now insufficient to maintain the population.
The Death rate increase in areas like Africa and some parts of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and Asia is due to the deadly HIV/AIDS epidemics. This has slowed down the population growth.
Demographic Transition
Demographic Transition is the theory used to describe and predict the future population of any area. The Population of any region changes from high births and high deaths to low births and low deaths as society progresses from rural agrarian and illiterate to urban industrial and literate society.
These changes occur in stages which are a part of the demographic transition theory, which has 3 stages:
- High fertility and high mortality; high fertility because people reproduce more to compensate for the deaths due to epidemics and variable food supply.
- Fertility remains high but declines with time accompanied by reduced mortality rate. Improvements in sanitation and health conditions lead to decline in mortality.
- Both fertility and mortality decline considerably. Population becomes urbanised, literate and has high high technical know how and deliberately controls the family size.
Population Control Measures
Some of the measures through which population can be controlled are:
- Family planning is the spacing or preventing the birth of children.
- Easy and cheap availability of contraceptives
- Tax disincentives for large families
Conclusion
It is the people in a region, that add to its value. The role that population plays in a country’s development. The demographic characteristics of any area are understood by the patterns of population distribution and density. There are several reasons due to which people move in and move out of a region. Demographic Transition is the theory used to describe and predict the future population of any area. In a growing economy, a small increase in population, is considered to be desirable. However, if the population growth is more than a particular level, then there might be problems. Thus, we see how population of the world plays a major role in determining various changes that happen around the world.
People Also Read:
FAQs on Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 2 The World Population
What is density of population?
A land has limited capacity to support people living on it. It is essential to understand the ratio between the numbers of people to the land’s size. This ratio is known as the density of population. It is measured in persons per sq. km.
Density of Population= Number of People/Land Area
Define migration.
When people move from one place to another, it is known as migration.
What are the pull and push factors of migration?
There are several factors which influence migration such as:
- Push factors are reasons due to which people move out of a region. Such reasons are: unemployment, poor living conditions, political turmoil, unpleasant climate, natural disasters, epidemics and socio-economic backwardness
- Pull factors are reasons due to which people want to move into a place. Such reasons are: better job opportunities and living conditions, peace and stability, security of life and property and pleasant climate.
Define birth rate.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR): Number of live births in a year per thousand of women
CBR 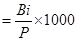
Bi= Live births
P= Mid-year population
Define death rate.
Crude Death Rate (CDR): No. of death in a particular year per 1000 of population.
CDR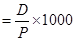
CDR= Crude Death Rate
D= No. of Deaths
P= Estimated Mid-Year Population
By and large mortality rates are affected by demographic structure, social advancement and economic development.
What are some population control measures?
Some of the measures through which population can be controlled are:
- Family planning is the spacing or preventing the birth of children.
- Easy and cheap availability of contraceptives
- Tax disincentives for large families
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...