Branches of Geography Class 11 Notes
Last Updated :
05 Apr, 2024
Geography is a vast field that encompasses the study of the physical and human aspects of our planet. It is a multidisciplinary subject that bridges the gap between the natural sciences and social sciences, providing a comprehensive understanding of the world we live in.
Let us study the various branches of geography and also their importance!
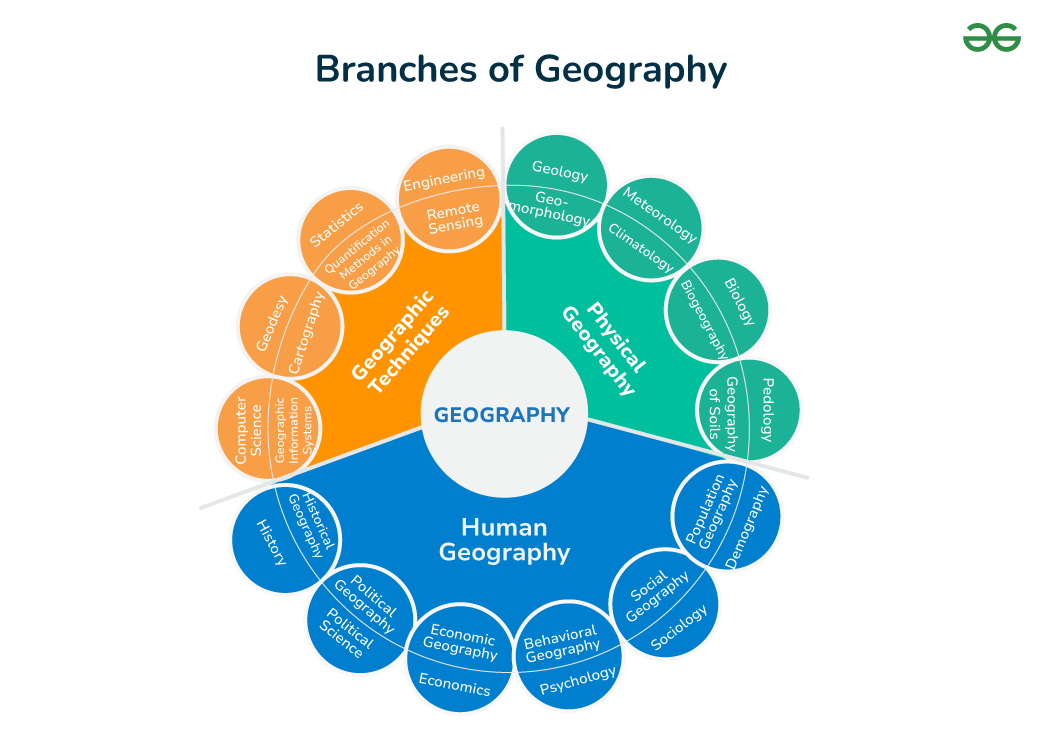
Branches of Geography
Branches of Geography
Geography is interdisciplinary, with two major approaches: systematic and regional. Systematic geography, introduced by Alexander Von Humboldt, involves studying phenomena worldwide to identify typologies or spatial patterns. For example, studying natural vegetation globally would identify and discuss forest types like equatorial rainforests or monsoon forests. In contrast, regional geography, developed by Karl Ritter, divides the world into regions at different hierarchical levels and studies all geographical phenomena within a specific region holistically.
Dualism is a key characteristic of geography, reflecting the emphasis on either physical or human geography. Earlier scholars focused on physical geography, but humans are integral to Earth’s surface and have shaped it through cultural development. Thus, human geography emerged, emphasizing human activities alongside natural phenomena.
Branches of Geography (Based on Systematic Approach)
- Physical Geography:
- Geomorphology focuses on studying landforms, their evolution, and related processes.
- Climatology involves the study of the atmosphere’s structure, weather elements, climatic types, and regions.
- Hydrology examines water bodies’ realm over the Earth’s surface, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and their impact on various life forms.
- Soil Geography is dedicated to understanding soil formation processes, soil types, fertility status, distribution, and utilization.
- Human Geography:
- Social/Cultural Geography explores society’s spatial dynamics and cultural elements.
- Population and Settlement Geography (Rural and Urban) analyze population growth, distribution, density, migration, occupational structure, and characteristics of rural and urban settlements.
- Economic Geography studies economic activities such as agriculture, industry, tourism, trade, transport, infrastructure, and services.
- Historical Geography examines historical processes shaping different regions and how geographical features undergo temporal changes.
- Political Geography studies political events’ spatial aspects, including boundaries, space relations between neighboring political units, constituency delimitation, election scenarios, and theoretical frameworks for understanding population’s political behavior.
- Biogeography:
- Plant Geography investigates the spatial pattern of natural vegetation in various habitats.
- Zoo Geography studies animals’ spatial patterns and geographic characteristics in their habitats.
- Ecology/Ecosystem focuses on the scientific study of species’ habitat characteristics.
- Environmental Geography addresses global environmental issues like land degradation, pollution, conservation concerns, and their geographical implications.
Branches of Geography ( Based on Regional Approach)
- Regional Studies/Area Studies:
- Comprises Macro, Meso, and Micro Regional Studies focusing on various spatial scales and levels of detail.
- Regional Planning:
- Involves Country/Rural and Town/Urban Planning aimed at spatial organization and development at regional levels.
- Regional Development:
- Addresses strategies and policies for promoting economic, social, and environmental development within specific regions.
- Regional Analysis:
- Involves the examination and interpretation of geographical phenomena within specific regions, considering their spatial contexts and interrelationships.
Common Aspects in Every Discipline:
- Philosophy:
- Encompasses Geographical Thought and Land and Human Interaction/Human Ecology, exploring the theoretical foundations and conceptual frameworks of geography.
- Methods and Techniques:
- Includes Cartography (including Computer Cartography), Quantitative Techniques/Statistical Techniques, Field Survey Methods, and Geo-informatics (such as Remote Sensing, GIS, GPS, etc.), facilitating data collection, analysis, and interpretation in geographical research.
This classification provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the various branches of geography based on a regional approach. While this format is commonly used in geography curricula, it is not static and evolves with new ideas, challenges, and technological advancements. For example, manual cartography has transitioned to computer-based cartography, and advancements in technology have enhanced the capacity for data analysis, synthesis, and theoretical understanding in geography.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the branches of geography offer a diverse range of perspectives, enabling us to comprehend the intricate relationships between the physical environment, human societies, and the interconnected nature of our world. By integrating these various disciplines, geography equips us with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complexities of our ever-changing planet.
Branches of Geography: FAQs
What is the primary focus of Physical Geography?
Physical Geography primarily focuses on the study of natural phenomena such as landforms, climate, water bodies, and soil composition.
How does Human Geography differ from Physical Geography?
Human Geography concentrates on the study of human activities, settlements, cultures, economic systems, and their interactions with the physical environment.
What is the role of Cartography in Geography?
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. It plays a crucial role in Geography by visually representing spatial data, enabling better understanding and analysis of geographical information.
What is the significance of Biogeography?
Biogeography is essential for understanding the distribution and diversity of plant and animal life on Earth. It helps us comprehend the complex relationships between living organisms and their environments, and aids in conservation efforts.
How does Geography contribute to addressing environmental issues?
Geography, particularly through branches like Environmental Geography and Ecology, provides insights into the impact of human activities on the environment, enabling the development of sustainable solutions and conservation strategies.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...